Sort summary:
The following figure shows the temporal and spatial complexity of each sorting: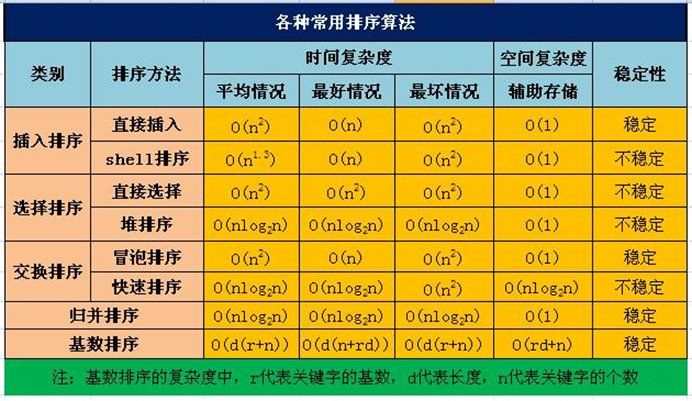
- Bubble sort:
//Bubble sort void bubble_sort(vector<int> &v){ for(int i = 0;i < v.size()-1;i++){//n-1 trip for(int j = 0;j< v.size()-i-1;j++){//n- trips -1 if(v[j] > v[j+1]){ int temp = v[j]; v[j] = v[j+1]; v[j+1] = temp; } } } }
2. Direct insertion sorting:
//Direct insert sort void insert_sort(vector<int> &v){ for(int i = 1;i < v.size();i++){ for(int j = i;j > 0;j--){ if(v[j] < v[j-1]){ int temp = v[j]; v[j] = v[j-1]; v[j-1] = temp; } } } }
- Hill sort (improved insert sort):
//Shell Sort void shell_sort(vector<int> &v){ //Find gap first int h = 1; while(h < v.size()/3){ h = h*3 + 1;//Knuth sequence } for(int gap = h;gap > 0;gap = (gap-1)/3){ //The insertion sort is as follows for(int i = gap;i < v.size();i++){ for(int j = i;j > gap-1;j-=gap){ if(v[j] < v[j-gap]){ int temp = v[j]; v[j] = v[j-gap]; v[j-gap] = temp; } } } } }
- Select sort:
//Selection sort void select_sort(vector<int> &v){ for(int i = 0;i < v.size()-1;i++){ int min = i; for(int j = i+1;j < v.size();j++){ if(v[j] < v[min]){ min = j; } } if(min != i){ int temp = v[min]; v[min] = v[i]; v[i] = temp; } } }
- Quick sort:
//Partitioning method int partition(vector<int> &v,int low,int high){ int mid = low + (high-low)/2;//Pivot on middle element int temp = v[mid]; v[mid] = v[low]; v[low] = temp; int pivot = v[low]; while(low < high){ while(low < high && pivot <= v[high]){ high--; } v[low] = v[high]; while(low < high && v[low] <= pivot){ low++; } v[high] = v[low]; } v[low] = pivot; return low; } //Quick sort void quick_sort(vector<int> &v,int low,int high){ if(low < high){ int mid = partition(v,low,high); quick_sort(v,low,mid-1); quick_sort(v,mid+1,high); } }
- Merge and sort:
//Merge void merge(vector<int> &v,int low,int mid,int high){ int i = low; int j = mid+1; int k = 0; vector<int> temp; temp.resize(high-low+1); while(i <= mid && j <= high){ if(v[i] <= v[j]){ temp[k++] = v[i++]; }else{ temp[k++] = v[j++]; } } while(i <= mid){ temp[k++] = v[i++]; } while(j <= high){ temp[k++] = v[j++]; } for(int m = 0;m < temp.size();m++){ v[low+m] = temp[m]; } } //Merge sort void merge_sort(vector<int> &v,int low,int high){ if(low < high){ int mid = low + (high - low) / 2; merge_sort(v,low,mid); merge_sort(v,mid+1,high); merge(v,low,mid,high); } }
- Count sort (one of bucket sort):
//Counting sort void count_sort(vector<int> &v){ int max = 0; //Find the maximum value in the array for(int i = 0; i < v.size();i++){ if(max < v[i]){ max = v[i]; } } //Create auxiliary array vector<int> result;//Array of last sort results result.resize(v.size()); vector<int> count; //Counting array count.resize(max+1); //Start counting for(int i = 0;i < v.size();i++){ count[v[i]]++; } //In order to maintain the stability of counting and sorting, it is necessary to calculate the accumulation array //The advantage of an additive array is that it can record the last position of the same element in the original array for(int i = 1;i < count.size();i++){ count[i] = count[i] + count[i-1]; } //Traverse the original array in reverse order, and assign to the result array for(int i = v.size()-1;i >=0;i--){ int index = count[v[i]]-1;//The relative position of the number of the original array, corresponding to the relative position of the result array result[index] = v[i]; count[v[i]]--;//Because there are repeating elements, you need to subtract one. } //Copy result array to element group for(int i = 0;i < result.size();i++){ v[i] = result[i]; } }
- Cardinality sort (one of bucket sort):
//Radix sorting void radix_sort(vector<int> &v){ int max = 0; //Find the maximum value in the array for(int i = 0;i < v.size();i++){ if(max < v[i]){ max = v[i]; } } int k = 0;//The number of digits of the largest number, i.e. k cardinal numbers are required while(max!=0){ k++; int num = max % 10;//Calculate each bit max = max/10; } vector<int> result;//Result array result.resize(v.size()); vector<int> count;//Counting array count.resize(10);//Each number is from 0-9, so it needs 10 lengths for(int m = 0;m < k;m++){ //Here's the count sort int division = pow(10,m);//Calculate the value divided by each time, i.e. 1, 10100 //Find the count array for(int i = 0;i < v.size();i++){ int num = v[i]/division % 10;//Calculate each bit count[num]++; } //Find the accumulation array for(int i = 1;i < count.size();i++){ count[i] = count[i] + count[i-1]; } //Find the result array for(int i = v.size()-1;i >=0;i--){ int n = v[i]/division % 10;//Calculate the number of current bits for each value int index = count[n]-1; result[index] = v[i]; count[n]--;//Because there are duplicate numbers, you need to subtract one } for(int i = 0;i < result.size();i++){ v[i] = result[i]; } //count array empty for(int i = 0;i < count.size();i++){ count[i] = 0; } } }
- Heap sort:
//Adjusting reactor void heapify(vector<int> &v,int len,int pos){ if(len <= pos){ return; } int left = pos * 2 + 1;//Left node int right = pos * 2 +2;//Right node int max = pos;//The default current location is the maximum if(left < len && v[max] < v[left]){ max = left; } if(right < len && v[max] < v[right]){ max = right; } if(max != pos){ swap(v[max],v[pos]); heapify(v,len,max); } } //Build heap void build_heap(vector<int> &v){ int lastNode = v.size() - 1; int parent = (lastNode - 1) / 2; for(int i = parent;i >= 0;i--){ heapify(v,v.size(),i); } } //Heap sort void heap_sort(vector<int> &v){ //Build a given array as a heap build_heap(v); for(int i = v.size()-1;i >= 0;i--){ swap(v[i],v[0]);//Last node and root node exchange heapify(v,i,0); } }
Binary search:
//Binary search, return to find the subscript of the number, not found return - 1 int binary_search(vector<int> v,int key){//v is the ordered array if(v.size()==0){ return -1;//not found } int low = 0; int high = v.size()-1; int mid = 0; while(low <= high){ mid = (low+high)/2; if(v[mid]==key){ return mid; }else if(v[mid] > key){ high = mid-1;//Find from front half }else{ low = mid +1;//Find from the second half } } return -1; }

