In the last section, we introduced
SpringBoot
How to start a built-in
tomcat
of We know we're here
SpringBoot
Projects can be used directly, such as
@RequestMapping
This kind of
SpringMVC
Will the students be surprised
Strange, why? I have no configuration
SpringMVC
Why can it be used?
In fact, it only introduces
starter
Is not enough, recall, in an ordinary
WEB
How to use it in the project
SpringMVC
, I
The first thing we should do is
web.xml
The following configuration is configured in
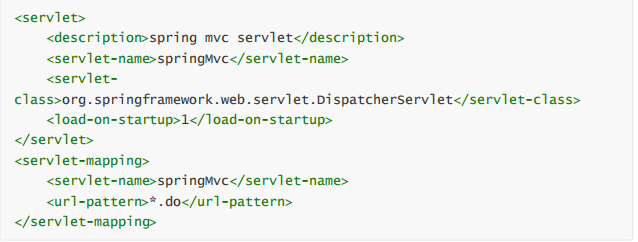
But in
SpringBoot
We don't have it
web.xml
File, how do we configure one
Dispatcherservlet
And?
actually
Servlet3.0
The specification specifies that one should be added
Servlet
, in addition to using
xml
There is also a way of configuration through code
The pseudo code is as follows:
servletContext
.
addServlet
(
name
,
this
.
servlet
);
So that is, if we can go dynamically
web
Add a container that we have constructed
DispatcherServlet
Object,
Does it realize automatic assembly
SpringMVC
Yes
I Automatically configure DispatcherServlet and DispatcherServletRegistry
springboot
Automatic configuration based on
SPI
Mechanism, the core point of realizing automatic configuration is to add an automatically configured class,
SpringBoot MVC
The automatic configuration of is naturally the same principle.
So, find it first
springmvc
Corresponding auto configuration class.
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConf
iguration
(1) Dispatcher servlet autoconfiguration autoconfiguration class
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {
1
First of all,
@Configuration
Table name this is a configuration class and will be
spring
Give me analysis.
2
,
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
It means that one
web
Project, and
Servlet
Will be solved when the project is completed
Analysis.
3
,
@ConditionalOnClass
to specify
DispatcherServlet
This core class must exist to resolve it.
4
,
@AutoConfigureAfter
Indicate in
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
This class will be solved later
Analysis, set a sequence.
In general, these annotations indicate that the parsed preconditions of the automatic configuration class need to be met.
secondly,
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
Class mainly contains two inner classes, namely
1
,
DispatcherServletConfiguration
2
,
DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration
As the name suggests, the former is configuration
DispatcherServlet
, the latter is configuration
DispatcherServlet
Registration class for. What is registration
Class? We know
Servlet
Instance is to be added (registered) to
tomcat
In this way
ServletContext
In order to
Enough to provide the requested service. So,
DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration
A will be generated
Bean
, responsible for
DispatcherServlet
Register to
ServletContext
Yes.
(2) Configure DispatcherServletConfiguration
Let's see first
DispatcherServletConfiguration
This configuration class
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ HttpProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class })
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
@Conditional
Indicates a precondition judgment, which is determined by
DefaultDispatcherServletCondition
realization. Mainly sentenced
Does the break already exist
DispatcherServlet
, if not, the resolution will be triggered.
@ConditionalOnClass
Indicates when
ServletRegistration
When this class exists, it will trigger parsing and generation
DispatcherServlet
To register with
ServletContext
Yes.
last,
@EnableConfigrationProperties
Will from
application.properties
Read from such a configuration file
spring.http
and
spring.mvc
Prefix properties generate configuration objects
HttpProperties
and
WebMvcProperties
.
Look again
DispatcherServletConfiguration
The inner code of this inner class
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(HttpProperties httpProperties, WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
dispatcherServlet.setPublishEvents(webMvcProperties.isPublishRequestHandledEvents());
dispatcherServlet.setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(httpProperties.isLogRequestDetails());
return dispatcherServlet;
}@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
We are familiar with these two methods, that is, generation
Bean
.
dispatcherServlet
Method generates a
DispatcherServlet
of
Bean
Object. Relatively simple, is to get a real
Example, and then add some attribute settings.
multipartResolver
The main method is to configure your
MultipartResolver
of
Bean
Rename it to prevent you from using it
multipartResolver
The name as
Bean
Your name.
(3) Configure DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration
Look at the registration class
Bean
to configure
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
@Import(DispatcherServletConfiguration.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
alike,
@Conditional
There is a pre judgment,
DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition
Mainly judged the
Registered class
Bean
Whether it exists.
@ConditionOnClass
Also judged
ServletRegistration
Does it exist
@EnableConfigurationProperties
Generated
WebMvcProperties
Property object for
@Import
Imported
DispatcherServletConfiguration
, that is, the configuration object above.
Look again
DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration
Internal implementation of
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet,
WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig) {
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,
webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
}
There is only one method inside, generated
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean
. The core logic is to instantiate a
Bean
, some parameters are set, such as
dispatcherServlet
,
loadOnStartup
etc.
summary
springboot mvc
The autoconfiguration class is
DispatcherServletAutoConfigration
, mainly did two things:
1
)Disposition
DispatcherServlet
2
)Disposition
DispatcherServlet
Registration of
Bean(DispatcherServletRegistrationBean)
II Register DispatcherServlet to ServletContext
In the source code browsing in the previous section, we saw
DispatcherServlet
and
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean
these two items.
Bean
Automatic configuration of.
DispatcherServlet
We're familiar,
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean
negative
Responsible general
DispatcherServlet
Register to
ServletContext
among
(1) Class diagram of DispatcherServletRegistrationBean
Since the responsibility of this class is to register
DispatcherServlet
, then we need to know when to trigger the registration operation. To this end,
Let's see first
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean
Class diagram of this class
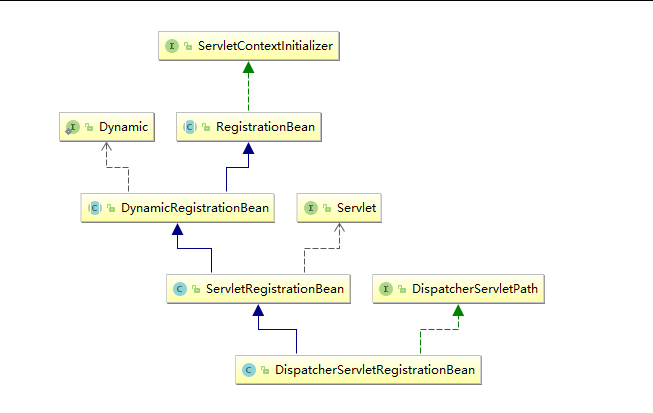
(II) process of registering dispatcher Servlet
1. ServletContextInitializer
We see, at the top is a
ServletContextInitializer
Interface. As we can see, implementing the interface means using
To initialize
ServletContext
of Let's look at the interface
public interface ServletContextInitializer {
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}2. RegistrationBean
See how RegistrationBean implements the onStartup method
@Override
public final void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
//Get whether it is a filter, a servlet or a listener
String description = getDescription();
if (!isEnabled()) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (disabled)");
return;
}
register(description, servletContext);
}
Internal call
register
Method, follow it up
3. DynamicRegistrationBean
Look again
DynamicRegistrationBean
How
register
Methodical
@Override
protected final void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
D registration = addRegistration(description, servletContext);
if (registration == null) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
configure(registration);
}
follow-up
addRegistration
method
protected abstract D addRegistration(String description, ServletContext servletContext);
4.ServletRegistrationBean
Look again
ServletRegistrationBean
How
addRegistration
Methodical
@Override
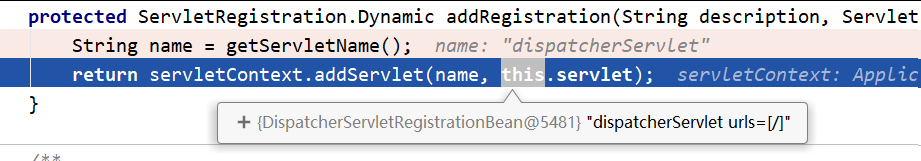
protected ServletRegistration.Dynamic addRegistration(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
String name = getServletName();
//Be responsible for registering DispatcherServlet in servletContext
return servletContext.addServlet(name, this.servlet);
}
We see that here will be directly
DispatcherServlet
to
add
here we are
servletContext
among.
(3) It is embodied in the SpringBoot startup process
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
This code is actually to load
SpringMVC
So how did he do it?
getSelfInitializer()
Eventually
To call to
ServletWebServerApplicationContext
of
selfInitialize
Method, the method code is as follows
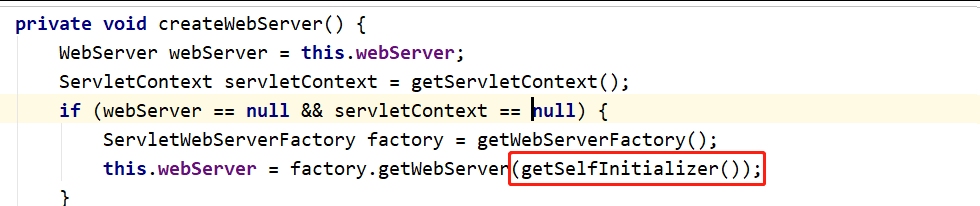
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
Through debugging, we know
getServletContextInitializerBeans()
Returns a
ServletContextInitializer
Collection, which contains the following objects
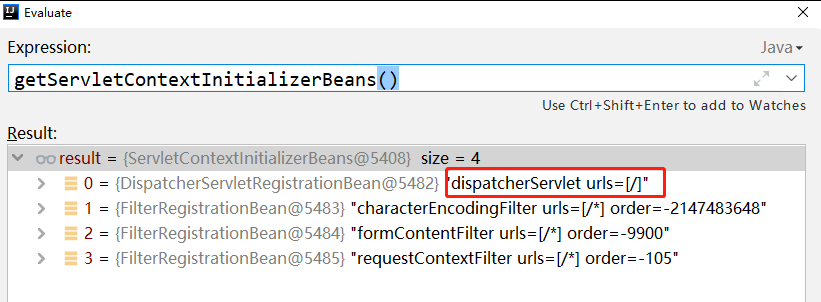
Then call the object in turn
onStartup
Method, then for the object with the red icon on it, it will call
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean
of
onStartup
Method, this class does not have this method, so in the end
Will be called to the parent class
RegistrationBean
of
onStartup
Method, the method code is as follows
@Override
public final void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
//Get whether it is a filter, a servlet or a listener
String description = getDescription();
if (!isEnabled()) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (disabled)");
return;
}
register(description, servletContext);
}
here
register(description, servletContext)
;
Will call
DynamicRegistrationBean
of
register
Method, the code is as follows:
@Override
protected final void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
D registration = addRegistration(description, servletContext);
if (registration == null) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
configure(registration);
}
addRegistration(description, servletContext)
Will call again
ServletRegistrationBean
Medium
addRegistration
Method, the code is as follows:
@Override
protected ServletRegistration.Dynamic addRegistration(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
String name = getServletName();
//Be responsible for registering DispatcherServlet in servletContext
return servletContext.addServlet(name, this.servlet);
}
See the key
servletContext.addServlet
Code, we can know through debugging
this.servlet
Just
yes
dispatcherServlet
summary
SpringBoot
automatic assembly
SpringMvc
It's actually going to
ServletContext
Added a
Dispatcherservlet
.
Servlet3.0
The specification has this description, except that it can be added dynamically
Servlet,
It can also be added dynamically
Listener
,
Filter
- addServlet
- addListener
- addFilter