1. First import the jar package using Maven
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.62</version> </dependency>
2. Configure information in application.properties
# Redis database index (0 by default)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis server address
spring.redis.host=localhost
# Redis server connection port
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis server connection password (empty by default)
spring.redis.password=123456
# Maximum number of connections in the connection pool (use a negative value to indicate no limit)
spring.redis.pool.max-active=200
# Connection pool maximum block wait time (use a negative value to indicate no limit)
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1
# Maximum free connections in connection pool
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=10
# Minimum free connections in connection pool
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
# Connection timeout (MS)
spring.redis.timeout=1000ms
3. Write Redis tool class
@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass(RedisOperations.class) //There are RedisOperations Class time @EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class) //start-up RedisProperties This class @EnableCaching public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport { @Autowired RedisTemplate redisTemplate; // Configure cache manager @Bean public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) { LettuceConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory = (LettuceConnectionFactory) redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory(); jedisConnectionFactory.setDatabase(2); //Appoint dbindex redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(jedisConnectionFactory); jedisConnectionFactory.resetConnection(); RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() .entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(60*20)) // 20 Minute cache failure // Set up key Serialization of // .entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(10)) .serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())) // Set up value Serialization of .serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new FastJsonRedisSerializer(Object.class))) // No caching null value .disableCachingNullValues(); RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(connectionFactory) .cacheDefaults(config) .transactionAware() .build(); return redisCacheManager; } }
package com.FireService.config; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.SerializationException; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig; import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature; public class FastJsonRedisSerializer<T> implements RedisSerializer<T> { public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); private Class<T> clazz; static { ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().addAccept("com.FireService"); } public FastJsonRedisSerializer(Class<T> clazz) { super(); this.clazz = clazz; } @Override public byte[] serialize(T t) throws SerializationException { if (null == t) { return new byte[0]; } return JSON.toJSONString(t, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName).getBytes(DEFAULT_CHARSET); } @Override public T deserialize(byte[] bytes) throws SerializationException { if (null == bytes || bytes.length <= 0) { return null; } String str = new String(bytes, DEFAULT_CHARSET); return (T) JSON.parseObject(str, clazz); } }
4. Some notes about caching in springboot
@Cacheable: query
Optional properties:
cacheNames/value: Specifies the name of the cache component;
Key: the key used to cache data, which can be specified. The value of the method parameter is used by default
keyGenerator: the generator of key. You can specify the component id of the generator of key.
//Custom configuration class configuration keyGenerator @Configuration public class MyCacheConfig { @Bean("myKeyGenerator") public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){ return new KeyGenerator() { @Override public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { return method.getName()+"["+ Arrays.asList(params).toString() +"]"; } }; } }
cacheManager: Specifies the cache manager; or cacheResolver gets the specified parser
Condition: specifies to cache only when the condition is met, such as condition = "ාid > 0"
Unless: negates the cache. When the condition specified by unless is true, the return value of the method will not be cached, and the result can be obtained for judgment. For example, unless="#result==null";
sync: whether to use asynchronous mode
For example:
@Cacheable(value = "RedisInfo", key = "#root.methodName+'['+#account+']'") @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/RedisTest") public Result findUserOrder(String account) throws Exception{ if(account!=null) { List<Map<String, Object>> list=orderFindGoods.findUserOrder(account); return Results.successWithData(list, BaseEnums.SUCCESS.code(), BaseEnums.SUCCESS.desc()); }else { return Results.failure(); } }
Run project view results
1. First visit

View Druid connection information

You can see that the current execution of sql statement is once
Refresh the page again
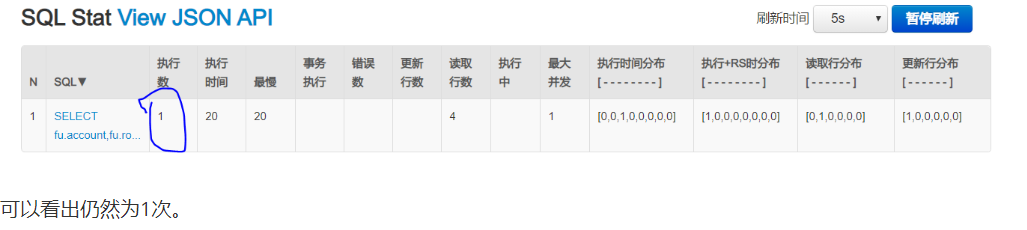
Use redisdestop manager to view data at this time

Success!!
@CachePut: update
The method can be called and the cache data can be updated simultaneously.
Modify a data in the database and update the cache at the same time
Operation time:
1. Call the running method first;
2. Cache the results of the target method
value: cache name key: the key of the cache, where ා result represents the result returned by the method (to ensure that the updated key is consistent with the query, you can update the database data and the data in the cache at the same time)
@CachePut(value="user",key = "#result.id") public User updateUser(User user){ System.out.println("updateUser:"+user); userMapper.updateUser(user); return user; }
@CacheEvict: delete
Cache clear: the purpose is to delete a data and delete the cache
Key: Specifies the data to be cleared (corresponding to the key, the purpose is to delete the data in the database and cache at the same time)
allEntries =true: specifies to clear all data in this cache
beforeInvocation = false: whether the cached clarity is executed before the method, and the default is executed after the method
@CacheEvict(value = "user",key = "#id") public void deleteUser(Integer id){ System.out.println("deleteUser:"+id); userMapper.deleteUserById(id); }
I will not write the specific code. You can try it yourself!