What is ribbon
At present, the mainstream load schemes are divided into the following two types:
- Centralized load balancing uses independent agents between consumers and service providers, including hardware (e.g. F5) and software (e.g. nginx)
- The client does load balancing according to its own request, and the Ribbon belongs to the client to do load balancing
SpringCloud Ribbon is a set of client-side load balancing tools based on Netflix Ribbon. The Ribbon client component provides a series of perfect configurations, such as timeout, Retry, etc. Get all machine instances provided by the service through the Load Balancer, and the Ribbon will automatically call these services based on certain rules (polling, random, etc.), and the Ribbon can also implement our own load balancing algorithm.
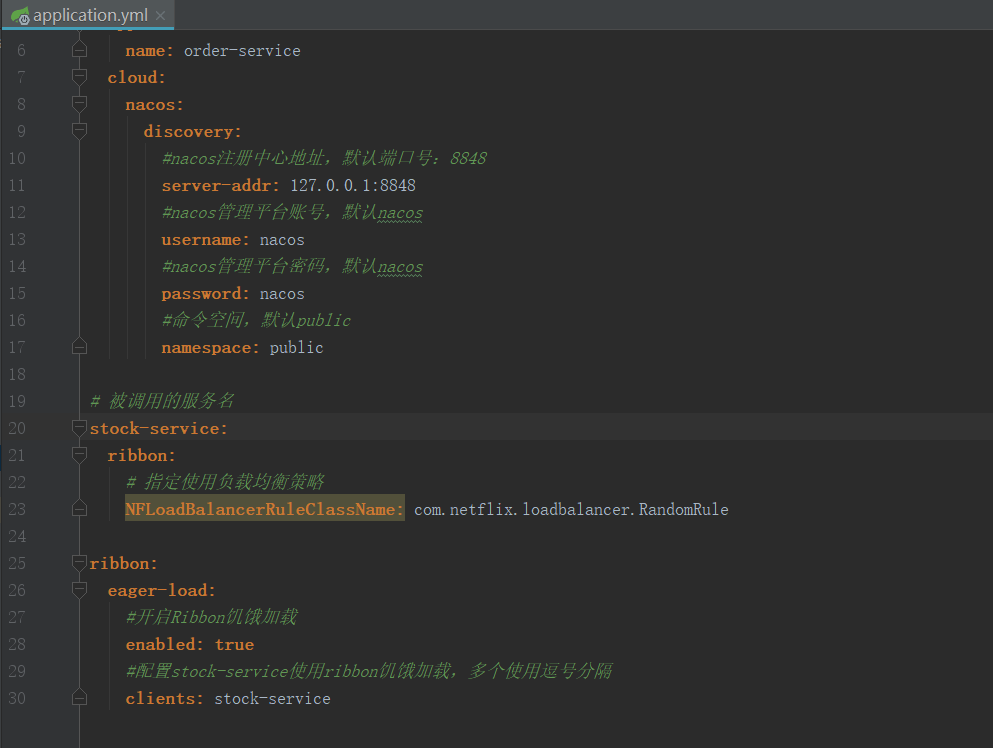
1.1 load balancing of client
For example, in the Ribbon in spring cloud, the client will have a server address list. Before sending a request, select a server through the load balancing algorithm, and then access it. This is client load balancing, that is, load balancing algorithm allocation is performed on the client.
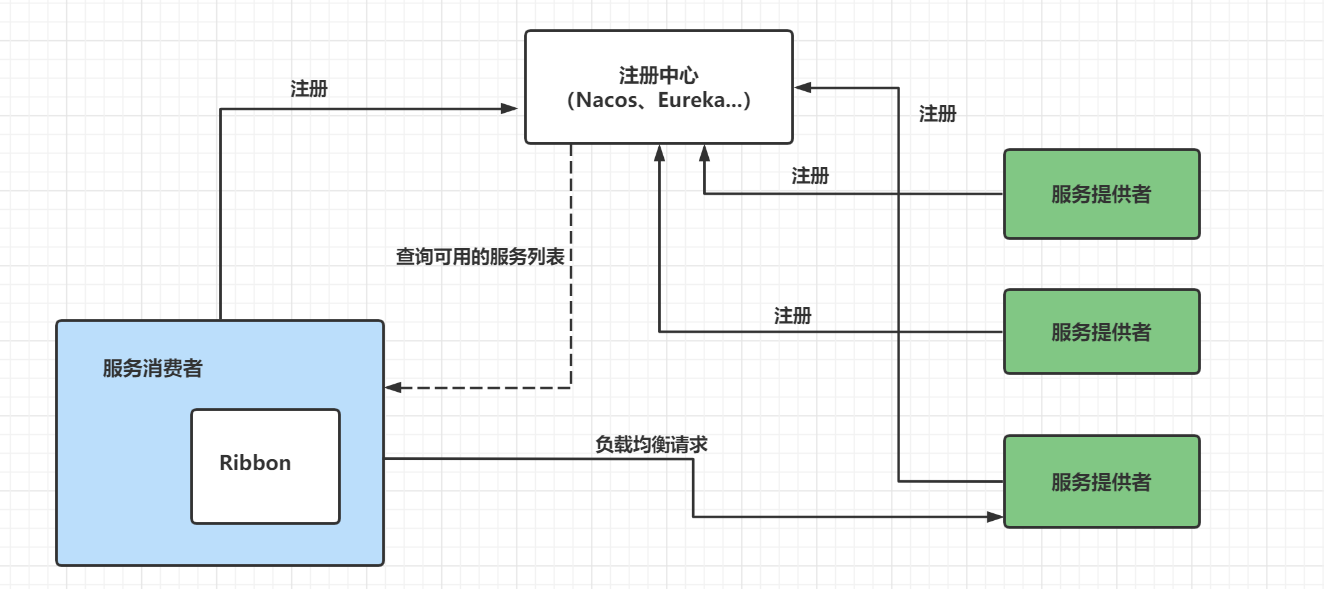
1.2 load balancing at the server
For example, nginx performs load balancing through nginx, first sends a request, then selects one of multiple servers for access through the load balancing algorithm; That is, the load balancing algorithm is allocated at the server.
1.3 common load balancing algorithms
- Random. It is generally used less by randomly selecting services for execution
- Polling. The default implementation method of load balancing is to queue up for processing after the request comes
- Weighted polling. Through the classification of server performance, the servers with high configuration and low load are assigned higher weights to balance the pressure of each server
- Address hash. Server scheduling is carried out through modular mapping of hash value of client request address. ip hash
- The minimum number of connections. Even if the request is balanced, the pressure may not be balanced. The minimum number of connections method is to allocate the request to the server with the lowest current pressure according to the server's conditions, such as request backlog and other parameters. Minimum active number
Nacos uses Ribbon
1. Nacos discovery relies on the ribbon, so you can no longer refer to the ribbon dependency
2. Add @ LoadBalanced annotation
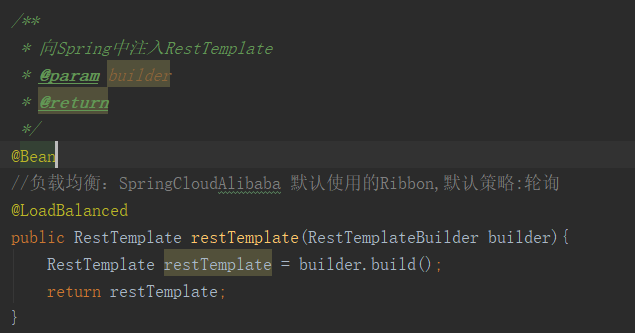
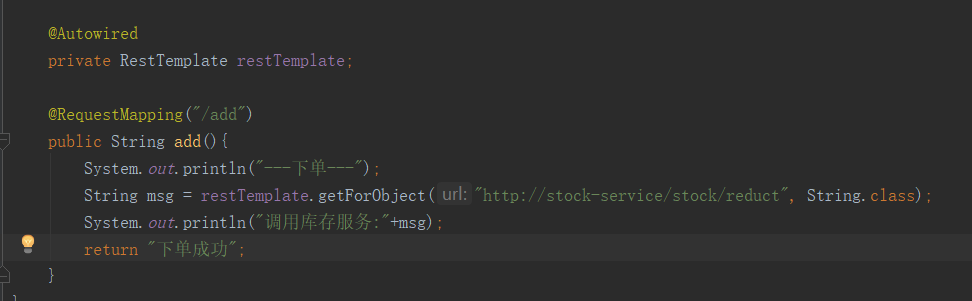
3. Modify Controller
Ribbon load balancing strategy
IRule
This is the parent interface of all load balancing policies. The core method inside is the choose method, which is used to select a service instance.
AbstractLoadBalancerRule
AbstractLoadBalancerRule is an abstract class. It mainly defines an ILoadBalancer, which is the load balancer mentioned above. The purpose of defining it here is to assist the load balancing strategy to select appropriate server instances.
- Random rule: this load balancing strategy is to randomly select a service instance
- Round robin rule: this load balancing strategy is a linear polling load balancing strategy
- RetryRule: retry based on polling
- WeightResponseTimeRule: weight. The shorter the average response time of a service, the greater the weight, and the greater the probability that the service instance is selected to perform tasks.
- Clientconfignenabledroundrobin rule: consistent with the selection policy of roundrobin rule.
- Best available rule: filter out the failed service instances, and then find the service instance with the smallest concurrent request to use
- ZoneAvoidanceRule: default rule
- AvailabilityFilteringRule:
Modify the default load balancing policy
There are two ways to modify the default load balancing policy
1. Implementation based on configuration class
1.1 add configuration class
package com.zjb.ribbon;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* Ribbon Load balancing policy configuration class
*/
@Configuration
public class RibbonRandomRuleConfig {
/**
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public IRule iRule(){
return new RandomRule();
}
}
Note that there are pits here. It cannot be written in the @ CompentScan scan of the @ SpringBootApplication annotation, otherwise the custom configuration class will be shared by all RibbonClients. This is not recommended. yml is recommended.
1.2 modify the startup class, add the @ RibbonClients annotation, and use @ RibbonClient to specify the service name and its load balancing policy
package com.zjb.order;
import com.zjb.ribbon.RibbonRandomRuleConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClients;
@SpringBootApplication
//Configuring multiple RibbonRandomRuleConfig cannot be scanned by @ CompentScan of @ SpringBootApplication, otherwise it is the global configuration effect
@RibbonClients({
@RibbonClient(name = "stock-service",configuration = RibbonRandomRuleConfig.class)
})
public class OrderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderApplication.class,args);
}
}
2. Implementation based on configuration file
2.1 modify application YML file
# Called service name
stock-service:
ribbon:
# Specifies to use a load balancing policy
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRuleCustom load balancing policy
Here we implement a simple random load balancing strategy, focusing on how to customize the load balancing strategy
Add diyribonrule and inherit AbstractLoadBalancerRule class
package com.zjb.ribbon;
import com.alibaba.nacos.shaded.io.grpc.netty.shaded.io.netty.util.internal.ThreadLocalRandom;
import com.netflix.client.config.IClientConfig;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.AbstractLoadBalancerRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.Server;
import java.util.List;
public class DIYRibbonRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
public Server choose(Object o) {
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = this.getLoadBalancer();
//Or get the currently requested service instance
List<Server> reachableServers = loadBalancer.getReachableServers();
int i = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(reachableServers.size());
Server server = reachableServers.get(i);
return server;
}
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig iClientConfig) {
}
}
When calling, we find that the first call will be very slow. This is because of lazy loading. We load only when calling. How should we solve this problem?
Enable hungry loading to solve the problem of slow calling for the first time
ribbon:
eager-load:
#Turn on Ribbon starvation loading
enabled: true
#Configure stock service to load using ribbon, and multiple are separated by commas
clients: stock-service