Spring Cloud Alibaba Seata handles distributed transactions
Distributed transaction management
preface
I don't want to post this blog, because the transaction rollback function is not perfectly implemented. If you see this blog, just understand it. If there is a solution in the future, I'll update it.
Distributed transaction
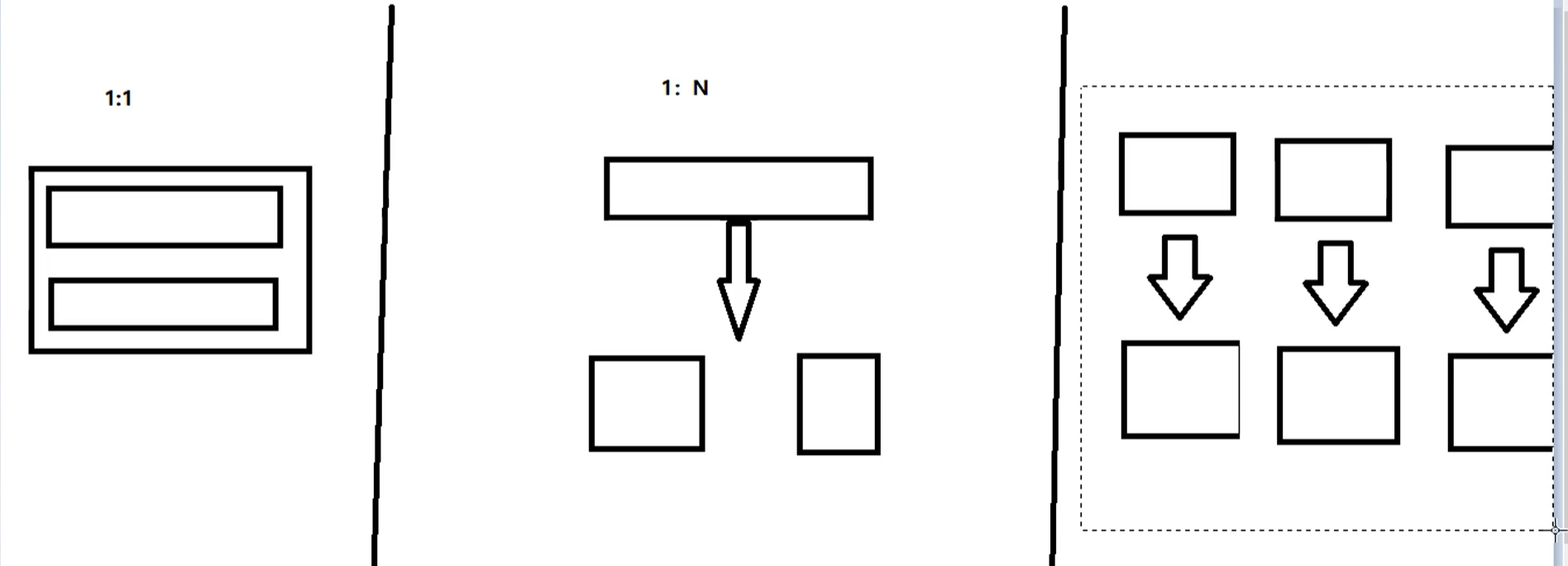
Before distribution, there is no such problem for single machine and single database, from 1:1 - > 1: n - > n: n
The unified scheduling of cross database and multi data sources will encounter the problem of distributed transactions
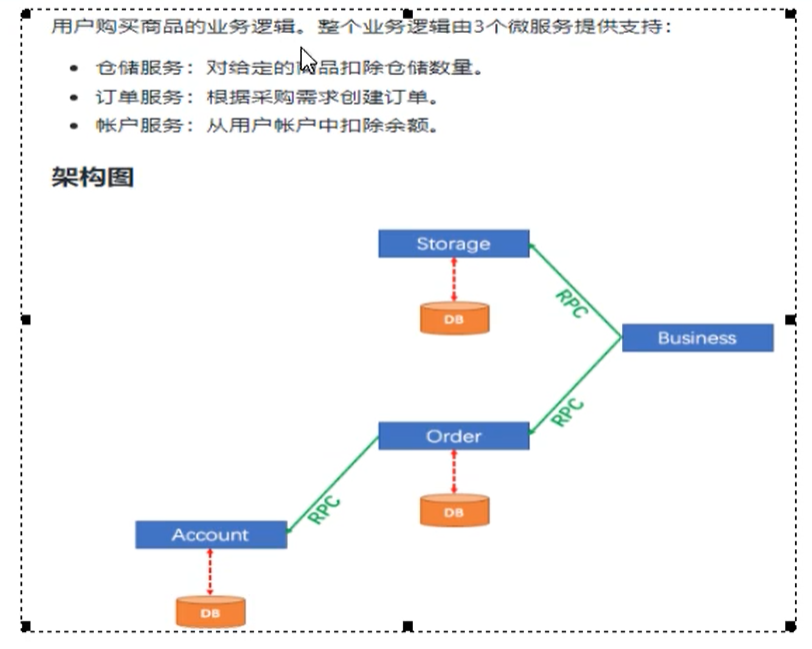
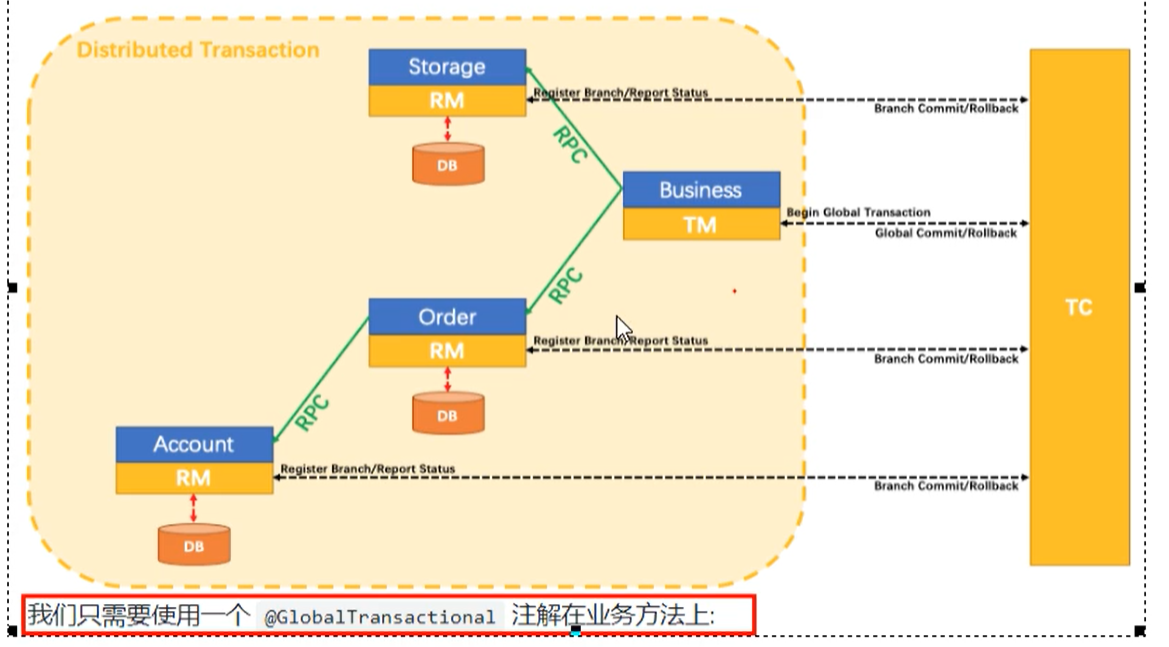
As shown in the figure below, the single application is split into micro service applications. The original three templates are split into three independent applications, using three independent data sources respectively. Business operations need to call three services to complete. At this time, the data consistency within each service is guaranteed by local transactions, but the global data consistency cannot be guaranteed.
Introduction to Seata
Official documents: Click me to transmit
Seata is an open source distributed transaction solution, which is committed to providing high-performance and easy-to-use distributed transaction services under the microservice architecture. Seata provides users with AT, TCC, SAGA and XA transaction modes to create a one-stop distributed solution for users.
Tell me about your understanding of Seata
Seata consists of a 1 + 3 suite
- Transaction ID XID: globally unique transaction ID. as long as there are several libraries under the same ID, three are three and 10 are 10, indicating that they are a whole.
- Of three components:
- Transaction Coordinator (TC): Transaction Coordinator, which maintains global transactions and drives global transaction commit or rollback
- Transaction Manager (TM): Transaction Manager, which defines the scope of global transactions, starts global transactions, commits or rolls back global transactions
- Resource Manager (RM): resource manager, which manages the resources of branch transaction processing, talks with TC to register branch transactions and report the status of branch transactions, and drives branch transaction submission or rollback.
Processing process
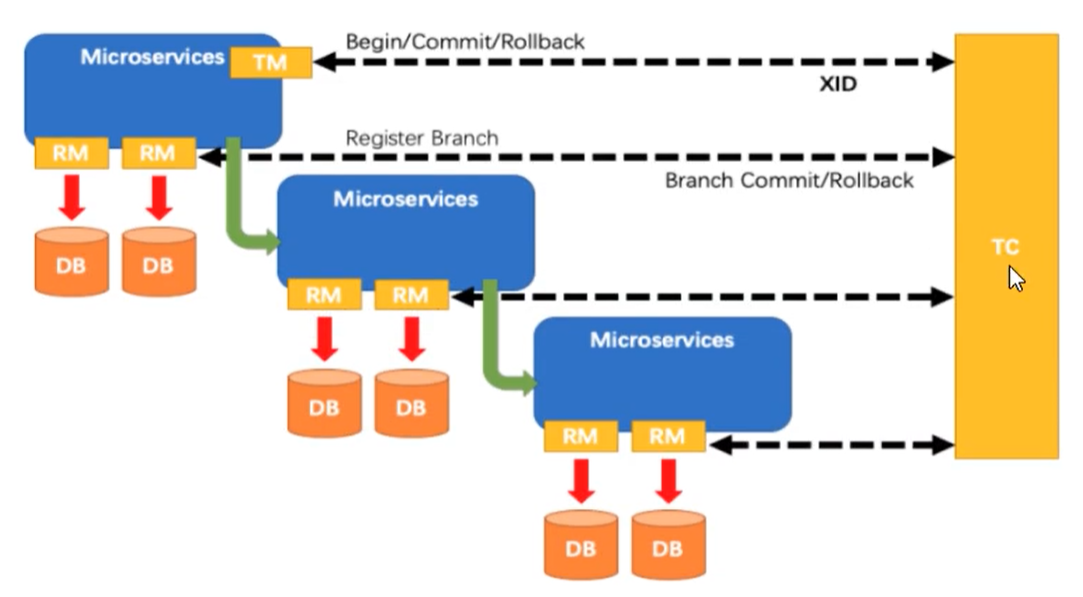
- TM (transaction manager) applies to TC (Transaction Coordinator) to start a global transaction. The global transaction is created successfully and generates a XID (globally unique transaction ID)
- XID (globally unique transaction ID) is propagated in the context of the microservice invocation link
- RM (Resource Manager) registers branch transactions with TC (Transaction Coordinator) and brings them into the jurisdiction of global transactions corresponding to XID (globally unique transaction ID)
- TM (transaction manager) initiates a global commit or rollback resolution for XID (globally unique transaction ID) to TC (Transaction Coordinator)
- TM (transaction manager) schedules all branch transactions under XID (globally unique transaction ID) to complete the commit or rollback request
use
Spring comes with @ Transaction to control local transactions
The @ GlobalTransaction controls the global transaction
- Local: @ Transaction
- Global: @ GlobalTransaction
We only need to use this annotation on business classes that need to support distributed transactions
Microservices: it represents a group in a class. There are 20 people in a group
TC: Instructor
TM: head teacher
1. The head teacher initiates an application to the teaching teacher, whether the class can be started or not, and a class number will be created after the class is successfully started.
2. The head teacher informs each student of the class number in the group
3. All students report to the teacher through this class number, and the teacher adds them to the class
4. The head teacher asked the teacher to call the roll
5. After the roll call, the head teacher told the teacher that he could teach the students
Seata installation configuration
1. Download
Address: https://github.com/seata/seata/releases
After downloading version 0.9, modify the file in the conf directory Conf configuration file
2. Decompression
3. Modify file conf
First, we need to back up the original file Conf file, in the conf directory
It is mainly modified. The user-defined transaction group name + transaction log storage mode is db + database connection information, that is, modify the stored database
Modify the service module
Modify grouping in service module
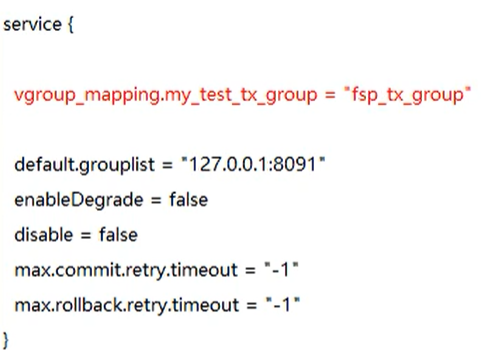
Modify the store module

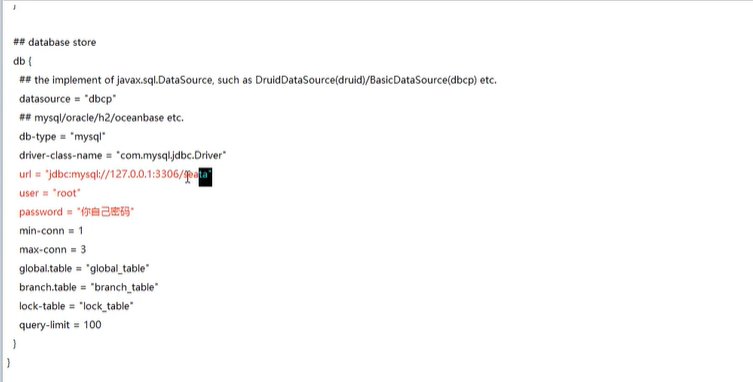
4. Create seata database
CREATE DATABASE `seata` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
Create a table in the seata database. The table creation statement is in DB under the seata/conf directory_ store. sql
5. Modify registry conf
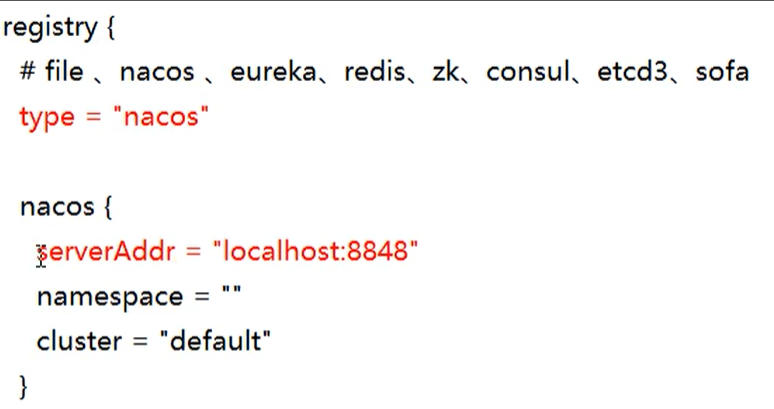
The purpose is to specify the registration center as nacos and modify the nacos connection information
Then start the server and the NAS
6. Start
Start nacos first, then start seata: seata \ bin \ seata server bat
Order / inventory / Account Business micro service preparation
The following demonstrations need to start Nacos first, and then start Seata to ensure that both are OK
Business description of distributed transaction
Here we will create three micro services, one order service, one inventory service and one account service.
- When the user places an order, an order will be created in the order service, and then the inventory of the ordered goods will be deducted by calling the inventory service remotely,
- Then deduct the amount in the user's account by calling the account service remotely,
- Finally, modify the order status to completed in the order service
This operation spans three databases and has two remote calls. It is obvious that there will be the problem of distributed transactions.
One sentence: place order - > deduct inventory - > deduct account (balance)
Create database
- seata_order: the database that stores the order
- seata_storage: a database that stores inventory
- seata_account: the database that stores account information
Database building SQL
create database seata_order DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; create database seata_storage DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; create database seata_account DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
Create business table
-- seata_order Create under database t_order surface use seata_order; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_order`; CREATE TABLE `t_order` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_id` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'user id', `product_id` bigint(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'product id', `count` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'quantity', `money` decimal(11, 0) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'amount of money', `status` int(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Order status: 0:Creating 1:Closed', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci COMMENT = 'Order form' ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; -- seata_storage Construction under reservoir t_storage surface use seata_storage; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_storage`; CREATE TABLE `t_storage` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `product_id` bigint(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'product id', `total` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Total inventory', `used` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Used inventory', `residue` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Remaining inventory', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci COMMENT = 'stock' ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; INSERT INTO `t_storage` VALUES (1, 1, 100, 0, 100); -- seata_account Construction under reservoir t_account surface use seata_account; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_account`; CREATE TABLE `t_account` ( `id` bigint(11) NOT NULL COMMENT 'id', `user_id` bigint(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'user id', `total` decimal(10, 0) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Total amount', `used` decimal(10, 0) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Balance used', `residue` decimal(10, 0) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Remaining available limit', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci COMMENT = 'Account table' ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; INSERT INTO `t_account` VALUES (1, 1, 1000, 0, 1000);
Create rollback log table
Each of the three databases of order inventory account needs to build its own rollback log table. The location of SQL file is seata\conf\db_undo_log.sql
-- the table to store seata xid data -- 0.7.0+ add context -- you must to init this sql for you business databese. the seata server not need it. -- This script must be initialized in your current business database for AT pattern XID record. And server End independent (Note: business database) -- Note here 0.3.0+ Add unique index ux_undo_log -- Open the following use Note, you can quickly create a table --use seata_order; --use seata_storage; --use seata_account; drop table if exists `undo_log`; CREATE TABLE `undo_log` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL, `xid` varchar(100) NOT NULL, `context` varchar(128) NOT NULL, `rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL, `log_status` int(11) NOT NULL, `log_created` datetime NOT NULL, `log_modified` datetime NOT NULL, `ext` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`,`branch_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Order / inventory / Account Business micro service preparation
Business requirements
Place order - > reduce inventory - > deduct balance - > Change (order) status
Create Seata service module 2001
appointment
Entity, domain: equivalent to entity class layer
vo: view object,value object
dto: data transmission class from foreground to background
Introducing POM
<!--seata--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>seata-all</artifactId> <groupId>io.seata</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.seata</groupId> <artifactId>seata-all</artifactId> <version>0.9.0</version> </dependency> <!--nacos--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId> </dependency> <!--openfeign--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency> <!--boot: web actuator--> <!--Common configuration without introducing hot deployment--> <!--Database configuration-->
Modify yml
server:
port: 2001
spring:
application:
name: seata-order-service
cloud:
alibaba:
seata:
#The user-defined transaction group name needs to correspond to that in Seata server
tx-service-group: fsp_tx_group
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata_order
username: root
password: 123456
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: false
logging:
level:
io:
seata: info
mybatis:
mapperLocations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
Add file conf
In the resources directory, create file Conf file
transport {
# tcp udt unix-domain-socket
type = "TCP"
#NIO NATIVE
server = "NIO"
#enable heartbeat
heartbeat = true
#thread factory for netty
thread-factory {
boss-thread-prefix = "NettyBoss"
worker-thread-prefix = "NettyServerNIOWorker"
server-executor-thread-prefix = "NettyServerBizHandler"
share-boss-worker = false
client-selector-thread-prefix = "NettyClientSelector"
client-selector-thread-size = 1
client-worker-thread-prefix = "NettyClientWorkerThread"
# netty boss thread size,will not be used for UDT
boss-thread-size = 1
#auto default pin or 8
worker-thread-size = 8
}
shutdown {
# when destroy server, wait seconds
wait = 3
}
serialization = "seata"
compressor = "none"
}
service {
vgroup_mapping.fsp_tx_group = "default" #Modify custom transaction group name
default.grouplist = "127.0.0.1:8091"
enableDegrade = false
disable = false
max.commit.retry.timeout = "-1"
max.rollback.retry.timeout = "-1"
disableGlobalTransaction = false
}
client {
async.commit.buffer.limit = 10000
lock {
retry.internal = 10
retry.times = 30
}
report.retry.count = 5
tm.commit.retry.count = 1
tm.rollback.retry.count = 1
}
## transaction log store
store {
## store mode: file,db
mode = "db"
## file store
file {
dir = "sessionStore"
# branch session size , if exceeded first try compress lockkey, still exceeded throws exceptions
max-branch-session-size = 16384
# globe session size , if exceeded throws exceptions
max-global-session-size = 512
# file buffer size , if exceeded allocate new buffer
file-write-buffer-cache-size = 16384
# when recover batch read size
session.reload.read_size = 100
# async, sync
flush-disk-mode = async
}
## database store
db {
## the implement of javax.sql.DataSource, such as DruidDataSource(druid)/BasicDataSource(dbcp) etc.
datasource = "dbcp"
## mysql/oracle/h2/oceanbase etc.
db-type = "mysql"
driver-class-name = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata"
user = "root"
password = "123456"
min-conn = 1
max-conn = 3
global.table = "global_table"
branch.table = "branch_table"
lock-table = "lock_table"
query-limit = 100
}
}
lock {
## the lock store mode: local,remote
mode = "remote"
local {
## store locks in user's database
}
remote {
## store locks in the seata's server
}
}
recovery {
#schedule committing retry period in milliseconds
committing-retry-period = 1000
#schedule asyn committing retry period in milliseconds
asyn-committing-retry-period = 1000
#schedule rollbacking retry period in milliseconds
rollbacking-retry-period = 1000
#schedule timeout retry period in milliseconds
timeout-retry-period = 1000
}
transaction {
undo.data.validation = true
undo.log.serialization = "jackson"
undo.log.save.days = 7
#schedule delete expired undo_log in milliseconds
undo.log.delete.period = 86400000
undo.log.table = "undo_log"
}
## metrics settings
metrics {
enabled = false
registry-type = "compact"
# multi exporters use comma divided
exporter-list = "prometheus"
exporter-prometheus-port = 9898
}
support {
## spring
spring {
# auto proxy the DataSource bean
datasource.autoproxy = false
}
}
registry.conf
registry {
# file ,nacos ,eureka,redis,zk,consul,etcd3,sofa
type = "nacos"
nacos {
serverAddr = "localhost:8848"
namespace = ""
cluster = "default"
}
eureka {
serviceUrl = "http://localhost:8761/eureka"
application = "default"
weight = "1"
}
redis {
serverAddr = "localhost:6379"
db = "0"
}
zk {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:2181"
session.timeout = 6000
connect.timeout = 2000
}
consul {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8500"
}
etcd3 {
cluster = "default"
serverAddr = "http://localhost:2379"
}
sofa {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:9603"
application = "default"
region = "DEFAULT_ZONE"
datacenter = "DefaultDataCenter"
cluster = "default"
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
addressWaitTime = "3000"
}
file {
name = "file.conf"
}
}
config {
# file,nacos ,apollo,zk,consul,etcd3
type = "file"
nacos {
serverAddr = "localhost"
namespace = ""
}
consul {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8500"
}
apollo {
app.id = "seata-server"
apollo.meta = "http://192.168.1.204:8801"
}
zk {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:2181"
session.timeout = 6000
connect.timeout = 2000
}
etcd3 {
serverAddr = "http://localhost:2379"
}
file {
name = "file.conf"
}
}
domain
Order.java
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Order {
private Long id;
private Long userId;
private Long productId;
private Integer count;
private BigDecimal money;
private Integer status; // Order status: 0: being created, 1: closed
}
CommonResult.java
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CommonResult<T> {
private Integer code;
private String message;
private T data;
public CommonResult(Integer code, String message) {
this(code,message,null);
}
}
Dao interface and its implementation
OrderDao.java
@Mapper
public interface OrderDao {
void create(Order order);
void update(@Param("userId") Long userId, @Param("status") Integer status);
}
OrderMapper.xml, create a mapper folder under the Resources folder and put it under the mapper folder
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.indi.springcloud.alibaba.dao.OrderDao">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.indi.springcloud.alibaba.domain.Order">
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="user_id" property="userId" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="product_id" property="productId" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="count" property="count" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="money" property="money" jdbcType="DECIMAL"/>
<result column="status" property="status" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
</resultMap>
<insert id="create">
insert into t_order (id, user_id,product_id,count,money,status)
values(null, #{userId},#{productId},#{count},#{money},0);
</insert>
<update id="update">
update t_order set status = 1
where user_id = #{userId} and status = #{status}
</update>
</mapper>
Service implementation class
OrderService.java, the orderservice here is an empty shell, and the specific operation is implemented by its implementation class.
public interface OrderService {
void create(Order order);
}
StorageService.java
@FeignClient(value = "seata-storage-service")
public interface StorageService {
@PostMapping("/storage/decrease")
CommonResult decrease(@RequestParam("productId") Long productId, @RequestParam("count") Integer count);
}
AccountService.java
@FeignClient(value = "seata-account-service")
public interface AccountService {
@PostMapping("/account/decrease")
CommonResult decrease(@RequestParam("userId") Long userId, @RequestParam("money") BigDecimal money);
}
OrderServiceImpl.java implementation class
/**
* Place order - > reduce inventory - > reduce balance - > change status
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Resource
private OrderDao orderDao;
@Resource
private StorageService storageService;
@Resource
private AccountService accountService;
@Override
public void create(Order order) {
log.info("----->Start new order");
orderDao.create(order);
log.info("----->The order micro service starts to call inventory and deduct Count");
storageService.decrease(order.getProductId(), order.getCount());
log.info("----->End of inventory deduction");
log.info("----->The order micro service starts to call the account and deduct Money");
accountService.decrease(order.getUserId(), order.getMoney());
log.info("----->End of account deduction");
// Modify the order status from 0 to 1, and 1 means it has been completed
log.info("Start modifying order status");
orderDao.update(order.getUserId(), 0);
log.info("End of modifying order status");
log.info("Order placement completed");
}
}
controller
@RestController
public class OrderController {
@Resource
private OrderService orderService;
@GetMapping("/order/create")
public CommonResult create(Order order){
orderService.create(order);
return new CommonResult(200, "Order created successfully");
}
}
Config configuration
MyBatisConfig.java
@Configuration
@MapperScan({"com.indi.springcloud.alibaba.dao"})
public class MyBatisConfig {
}
DataSourceProxyConfig.java here is to use Seata to proxy the data source
package com.indi.springcloud.alibaba.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import io.seata.rm.datasource.DataSourceProxy;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.transaction.SpringManagedTransactionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* Proxy data sources using Seata
*/
@Configuration
public class DataSourceProxyConfig {
@Value("${mybatis.mapperLocations}")
private String mapperLocations;
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public DataSource druidDataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@Bean
public DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSourceProxy);
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mapperLocations));
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setTransactionFactory(new SpringManagedTransactionFactory());
return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
}
Startup class
SeataOrderMainApp2001.java
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class) // Cancel automatic creation of data source
public class SeataOrderMainApp2001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SeataOrderMainApp2001.class,args);
}
}
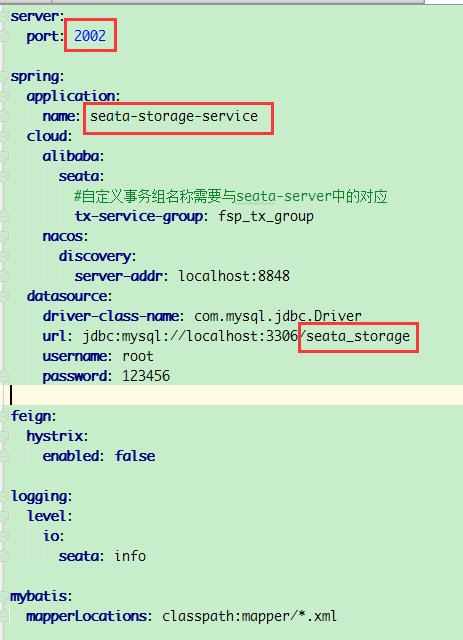
New Seata storage service2002
yml
domain
Storage.java
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Storage {
private Long id;
private Long productId;
private Integer total;
private Integer used;
private Integer residue;
}
CommonResult.java
Same as 2001
Dao interface and its implementation
StorageDao.java
@Mapper
public interface StorageDao {
void decrease(@Param("productId") Long productId, @Param("count") Integer count);
}
StorageMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.indi.springcloud.alibaba.dao.StorageDao">
<resultMap id="BaseResultmap" type="com.indi.springcloud.alibaba.domain.Storage">
<id property="id" column="id" jdbcType="BIGINT"></id>
<result property="productId" column="product_id" jdbcType="BIGINT"></result>
<result property="total" column="total" jdbcType="INTEGER"></result>
<result property="used" column="used" jdbcType="INTEGER"></result>
<result property="residue" column="residue" jdbcType="INTEGER"></result>
</resultMap>
<update id="decrease">
update
t_storage
set
used = used + #{count}, residue = residue - #{count}
where
product_id = #{productId}
</update>
</mapper>
Service implementation class
StorageService.java
public interface StorageService {
void decrease(@RequestParam("productId") Long productId, @RequestParam("count") Integer count);
}
StorageServiceImpl.java implementation class
@Service
public class StorageServiceImpl implements StorageService {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StorageServiceImpl.class);
@Resource
private StorageDao storageDao;
@Override
public void decrease(Long productId, Integer count) {
LOGGER.info("------storage-service Start deducting inventory");
storageDao.decrease(productId,count);
LOGGER.info("------storage-service End of inventory deduction");
}
}
controller
@RestController
public class StorageController {
@Resource
private StorageService storageService;
@RequestMapping("/storage/decrease")
public CommonResult decrease(@RequestParam("productId") Long productId,@RequestParam("count") Integer count){
storageService.decrease(productId,count);
return new CommonResult(200, "Inventory deduction succeeded");
}
}
Startup class
Same as 2001
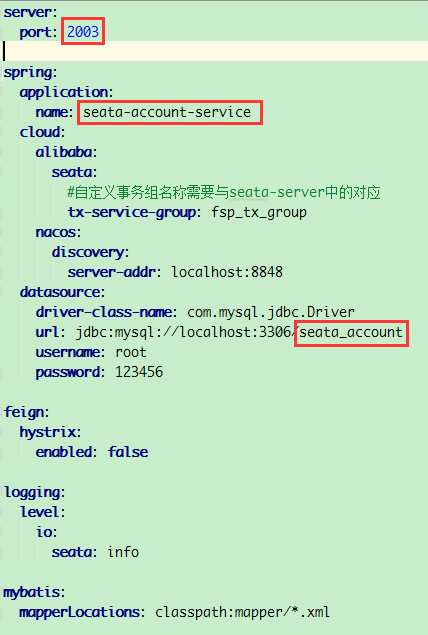
New Seata account service2003
yml
domain
Account.java
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Account {
private Long id;
private Long userId;
private BigDecimal total;
private BigDecimal used;
private BigDecimal residue;
}
CommonResult.java
Same as 2001
Dao
AccountDao.java
@Mapper
public interface AccountDao {
void decrease(@Param("userId") Long userId, @Param("money") BigDecimal money);
}
AccountMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.indi.springcloud.alibaba.dao.AccountDao">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.indi.springcloud.alibaba.domain.Account">
<id property="id" column="id" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result property="userId" column="user_id" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result property="total" column="total" jdbcType="DECIMAL"/>
<result property="used" column="used" jdbcType="DECIMAL"/>
<result property="residue" column="residue" jdbcType="DECIMAL"/>
</resultMap>
<update id="decrease">
update
t_account
set
used = used + #{money} , residue = residue + #{money}
where
user_id = #{userId}
</update>
</mapper>
Service
AccountService.java
public interface AccountService {
void decrease(@RequestParam("userId") Long userId, @RequestParam("money") BigDecimal money);
}
AccountServiceImpl.java
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AccountServiceImpl.class);
@Resource
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void decrease(Long userId, BigDecimal money) {
LOGGER.info("------account-service Start deducting balance");
accountDao.decrease(userId, money);
LOGGER.info("------account-service End of deduction balance");
}
}`
Controller
AccountController.java
@RestController
public class AccountController {
@Resource
private AccountService accountService;
@RequestMapping("/account/decrease")
public CommonResult decrease(@RequestParam("userId") Long userId, @RequestParam("money") BigDecimal money){
accountService.decrease(userId,money);
return new CommonResult(200,"Balance deducted successfully");
}
}
Startup class
Same as 2001
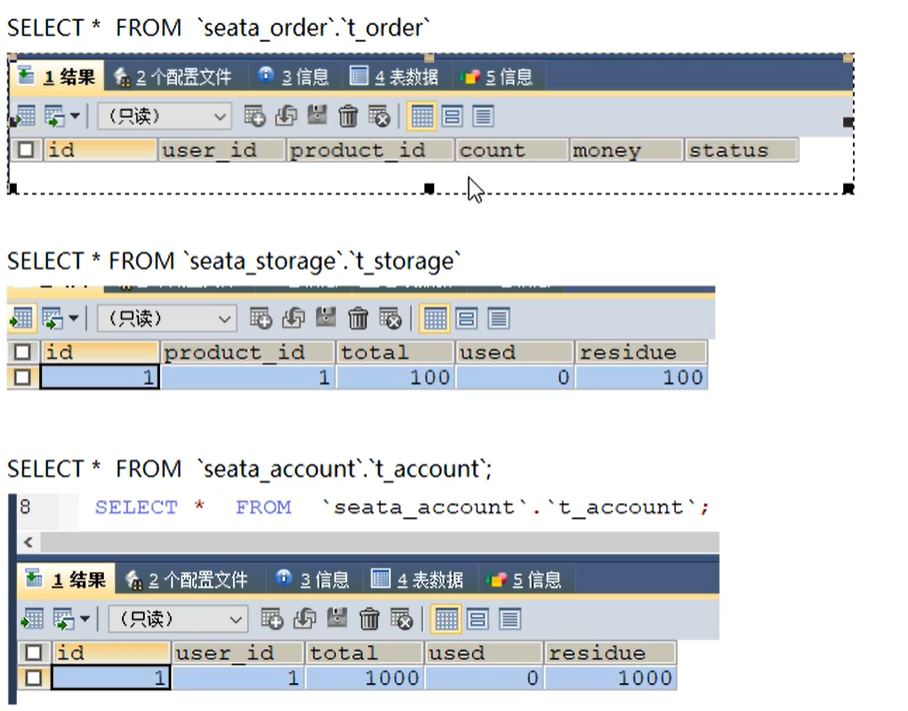
test
Initial condition of database
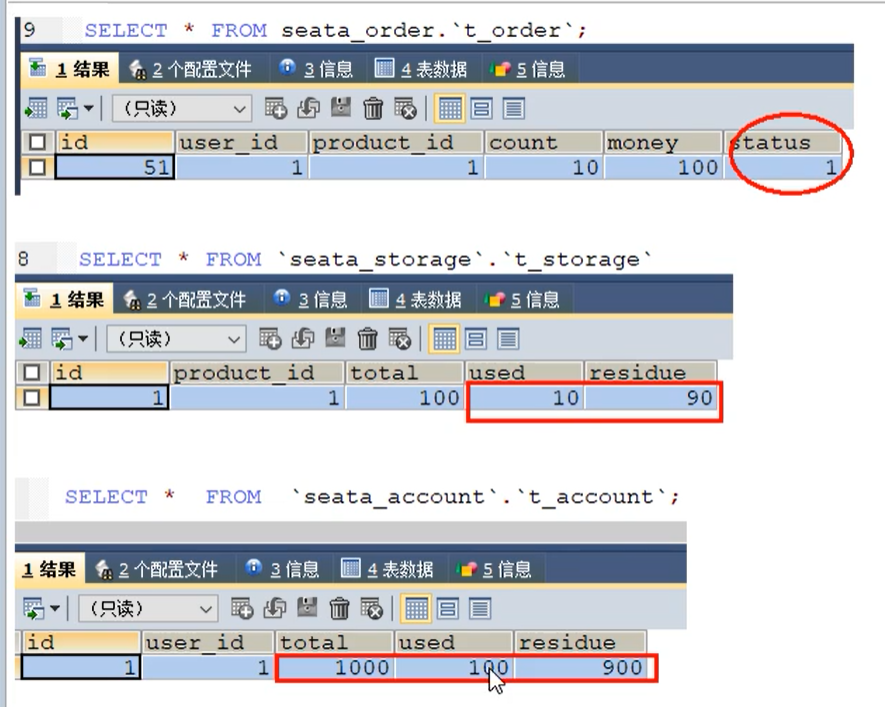
Normal order
visit
http://localhost:2001/order/create?userId=1&productId=1&count=10&money=100
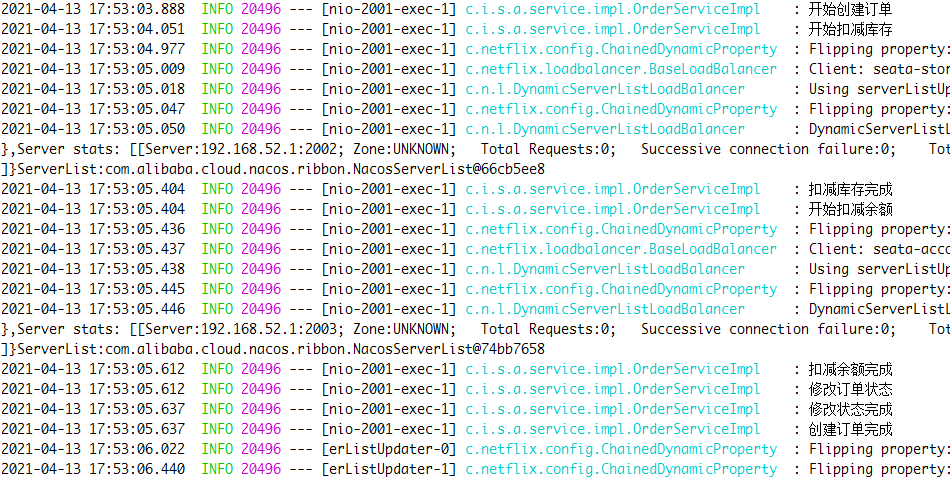
Timeout exception, no @ GlobalTransaction added
In the 2003 module, we added a sleep time of 20 seconds. The default time of openFeign is 1 second, so we will report timeout exception
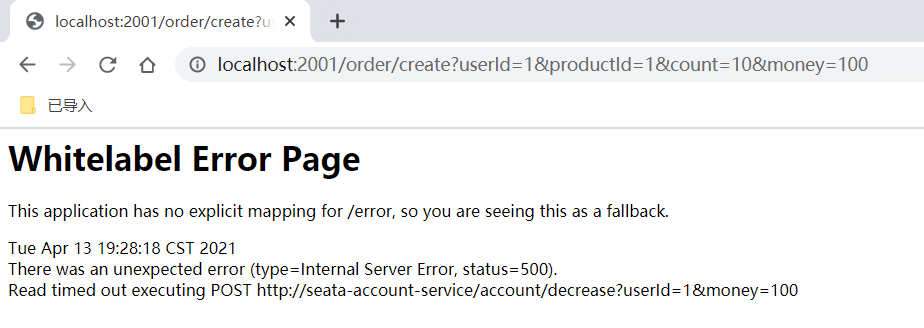
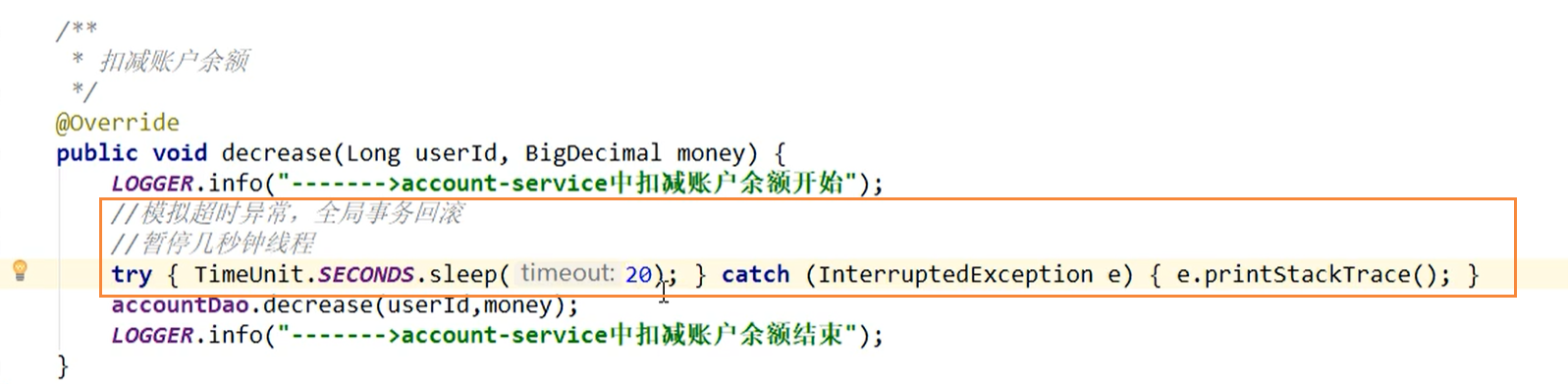
Fault condition
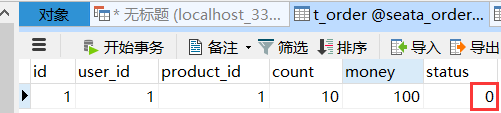
After the order is created, the inventory is deducted and the balance is deducted. When the inventory and account amount are deducted, the order status is not changed from 0 to 1 and set to completed
Moreover, due to Feign's retry mechanism, the account balance may be deducted many times
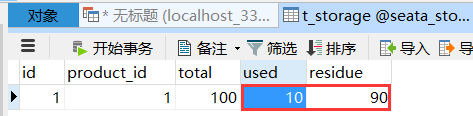
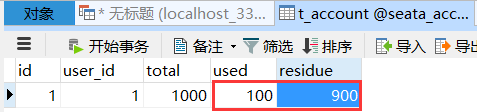
Timeout exception, add @ GlobalTransaction
Modify orderserviceimpl. Of 2001 module java
@GlobalTransactional(name = "fsp-create-order",rollbackFor = Exception.class)
name can start at will, as long as it does not conflict with other configurations
Rollback for indicates that any error will be rolled back
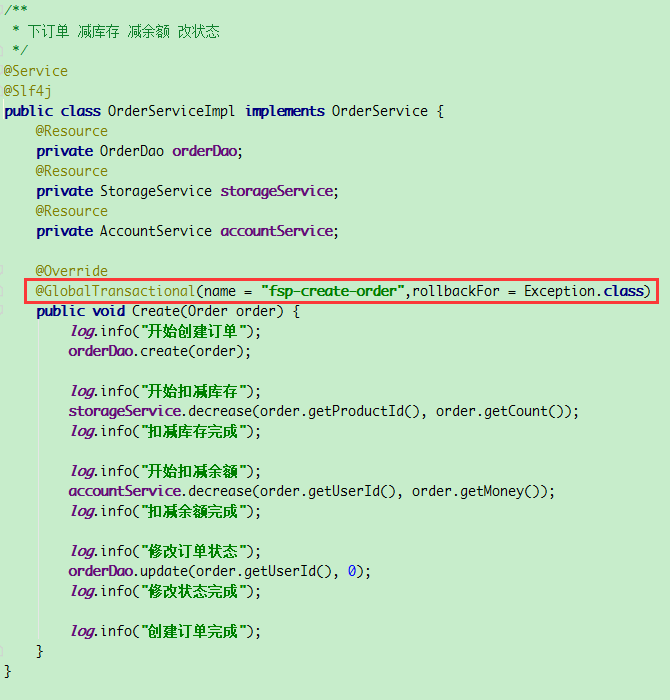
After adding this, the error is still reported, but the database after placing the order has not changed. That is the ideal state. In fact, only the order database has not changed, and both storage and account have changed. This problem has not been solved. If you have a way, please comment below. Thank you very much!

Part supplement
Seata
In January 2019, ant financial services and Alibaba jointly launched an open source distributed transaction solution
Seata: Simple Extensible Autonomous Transaction Architecture
Starting from 2020, the version after 1.0 will be used after working.
Let's look at the three components of TC/TM/RM
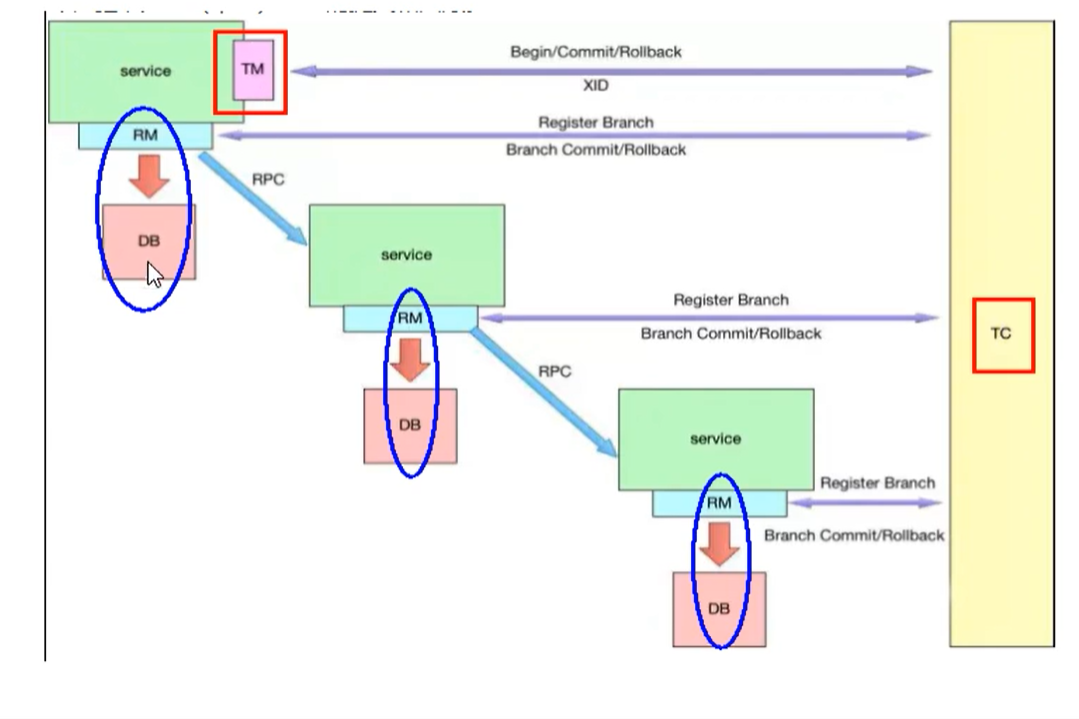
What is TC, TM, RM
TC: seata server
TM: method with @ GlobalTransaction annotation
RM: database, that is, transaction participants
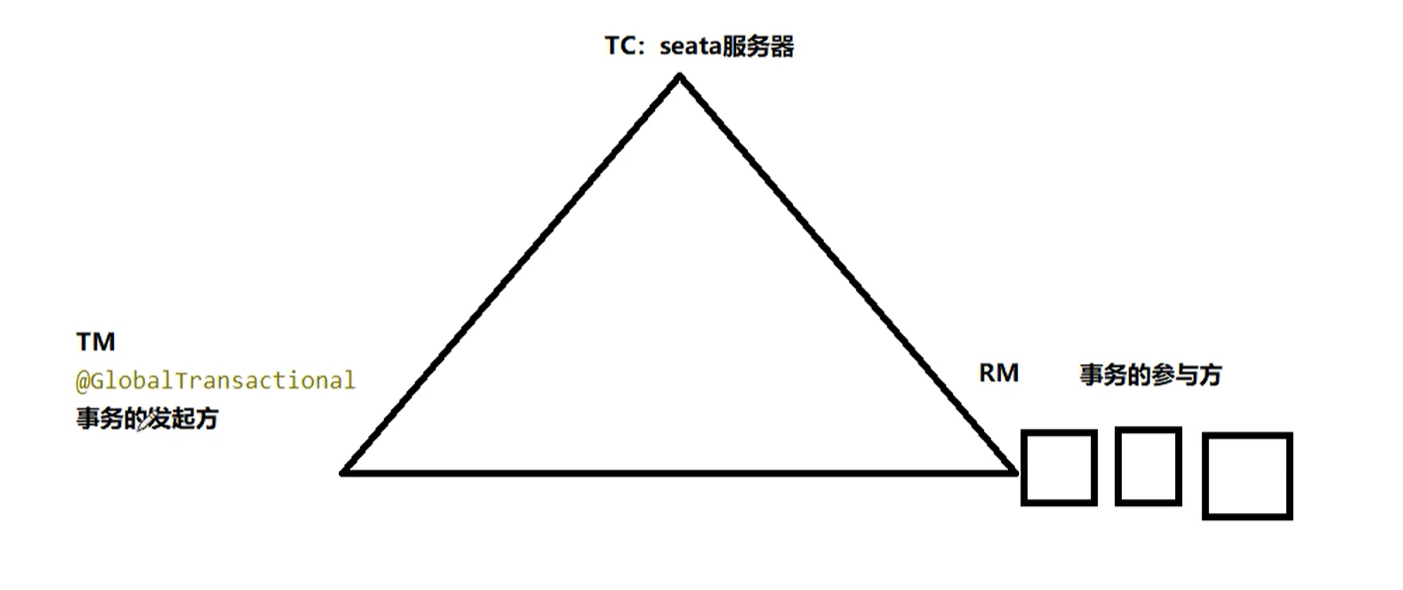
Execution flow of distributed transactions
- TM starts the distributed transaction (TM registers the global transaction record with TC), which is equivalent to the annotation @ globaltransaction annotation
- Arrange internal resources of database, service and other transactions according to business scenarios (RM reports resource preparation status to TC)
- TM ends the distributed transaction, and the first phase of the transaction ends (TM notifies TC to commit and roll back the distributed transaction)
- TC summarizes transaction information and determines whether distributed transactions are committed or rolled back
- TC notifies all RM S to commit and roll back resources, and the second phase of the transaction ends
How does AT mode achieve no intrusion into business
The default AT mode is Alibaba cloud GTS
AT mode
premise
- Based on relational database supporting local ACID transactions
- Java application, accessing database through JDBC
Overall mechanism
Evolution of two-stage submission agreement
- Phase I: the business data and rollback log records are committed in the same local transaction, and the local lock and connection resources are released
- Second stage
- Asynchronous submission, very fast completion
- Rollback makes reverse compensation through the rollback log of one stage
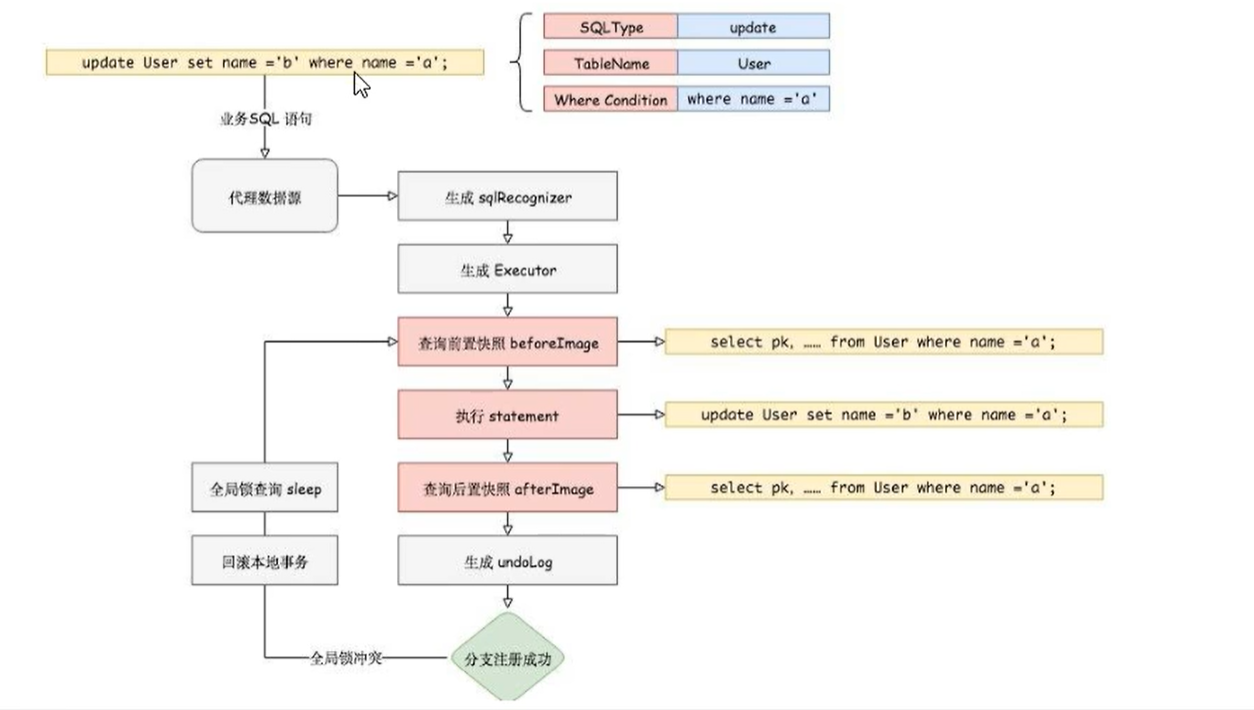
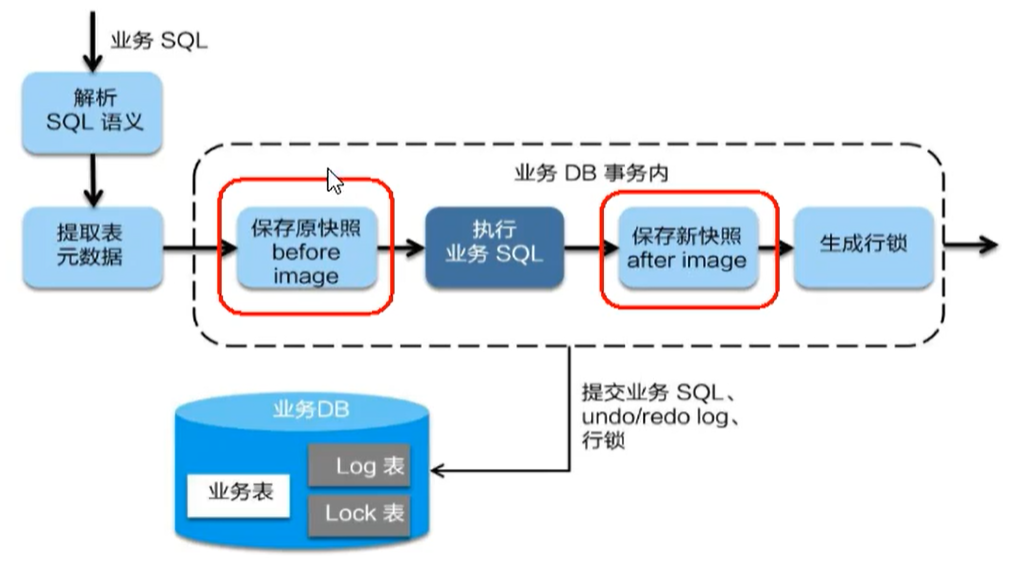
One stage loading
In the first phase, Seata intercepts business SQL
- Analyze the SQL semantics, find the business SQL, and save the business data to be updated as a before image (pre image) before the business data is updated
- Execute business SQL to update business data. After the business data is updated
- Save it as after image, and finally generate row lock
All the above operations are completed in one database transaction, which ensures the atomicity of one-stage operation
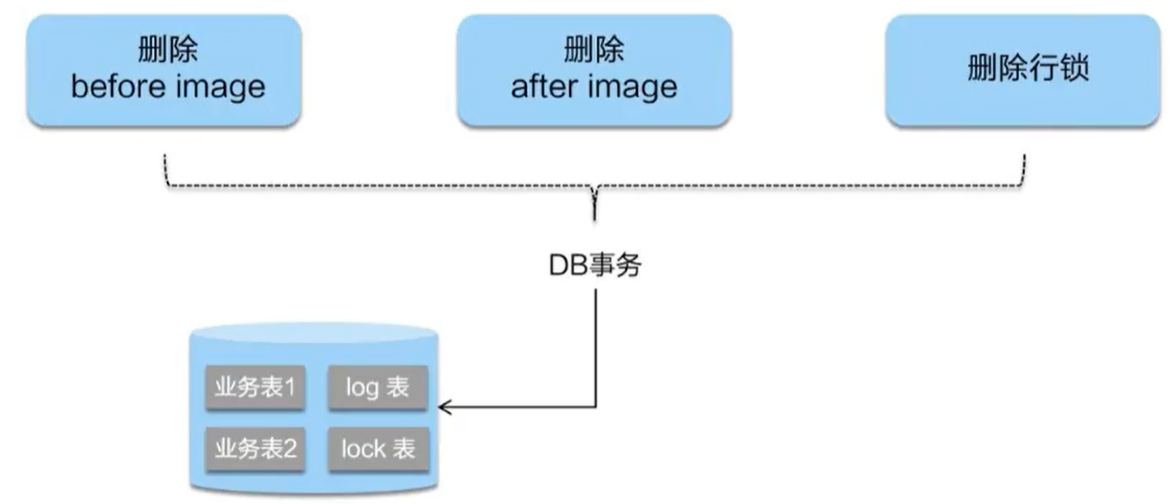
Phase II submission
If the second phase is successfully submitted, because the business SQL has been submitted to the database in the first phase, the Seata framework only needs to delete the snapshot and row lock saved in the first phase and complete the data cleaning
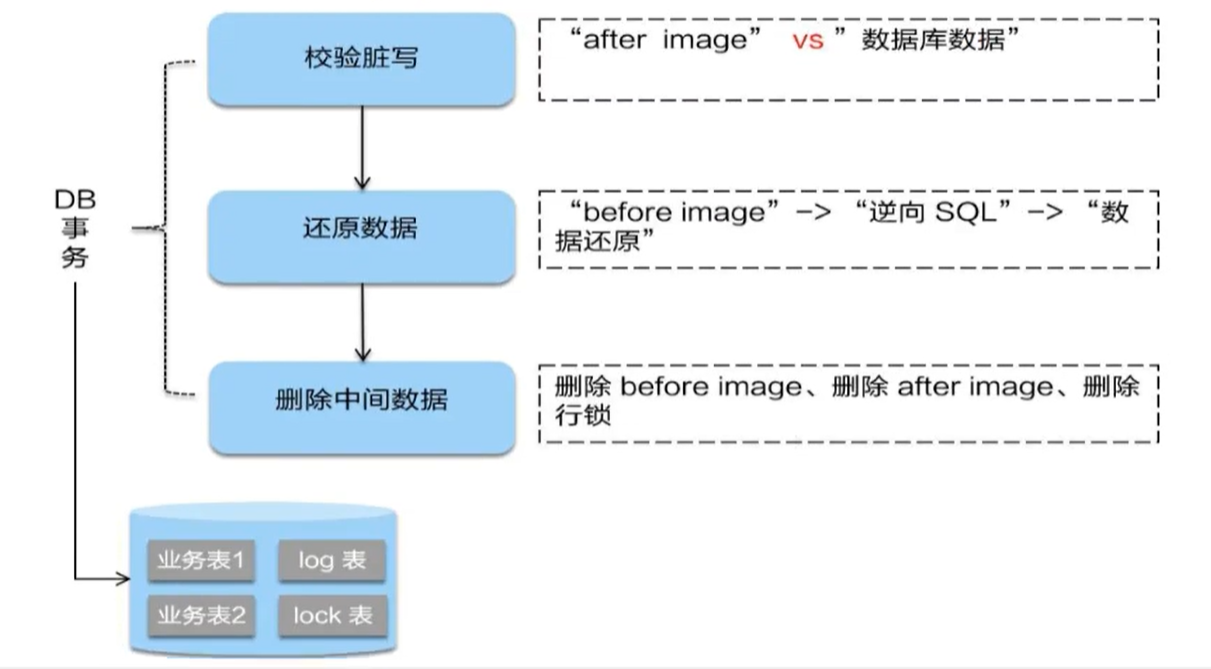
Two phase rollback
If the second phase is rolled back, Seata needs to roll back to the business SQL executed in the first phase to restore the business data
The rollback method is to restore the business data with before image. However, before restoring, the dirty write must be verified first. Compare the current business data of the database with the after image. If the two data are completely consistent and there is no dirty write, the business data can be restored. If the two data are inconsistent, it indicates that there is dirty read, and the dirty read needs to be transferred to manual processing
summary