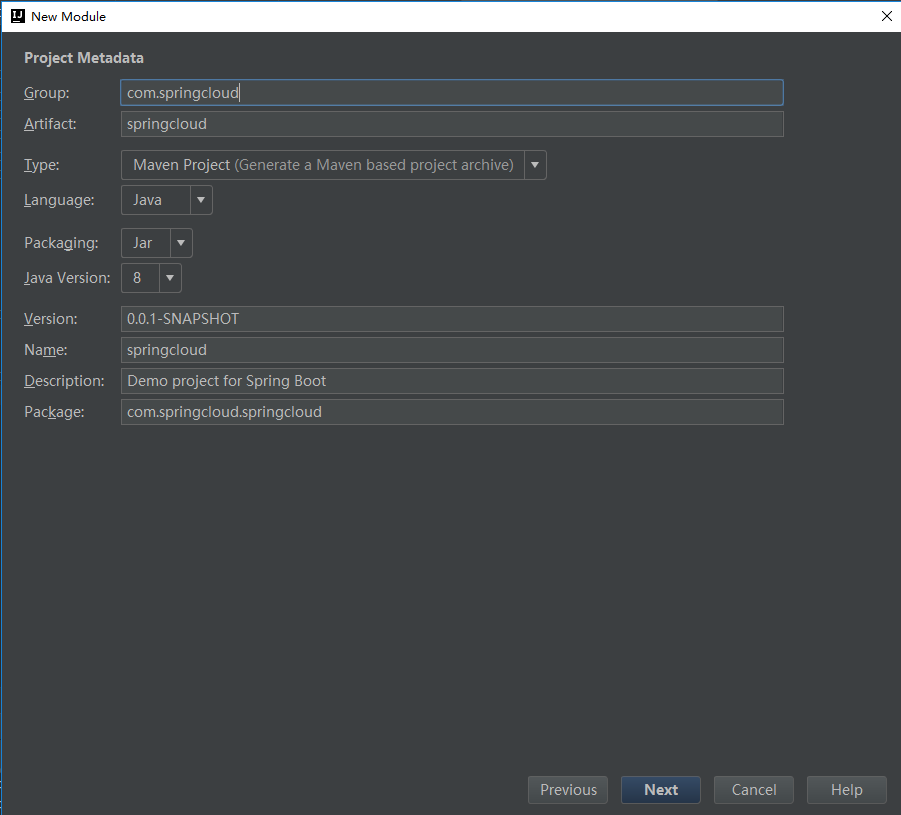
Firstly, the registration center should be established.
file-new-module
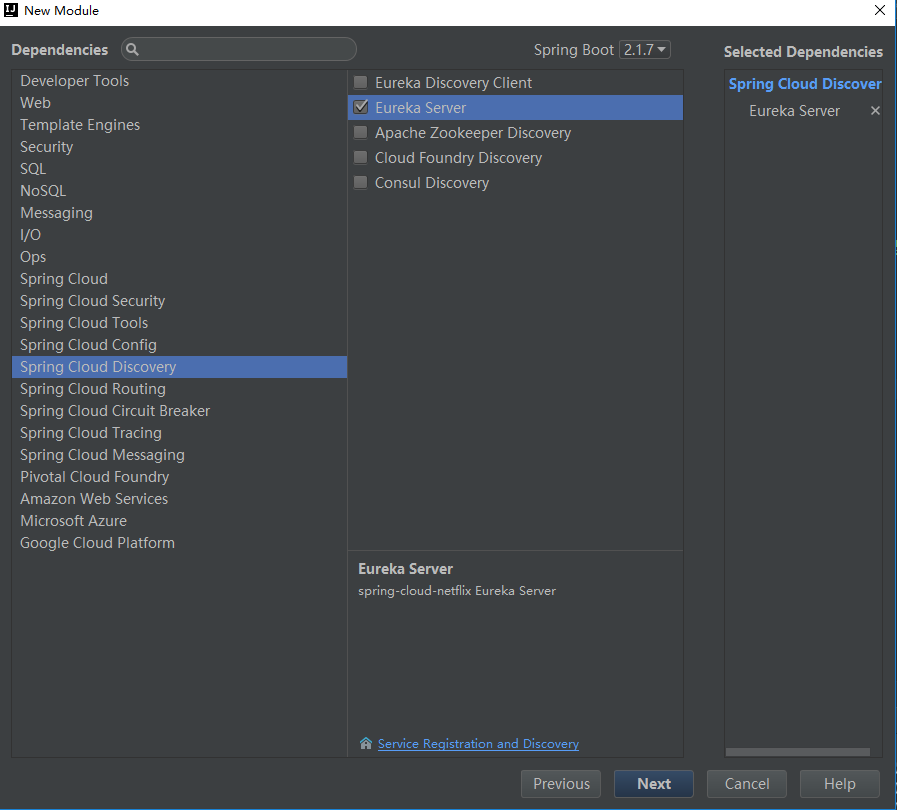
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.7.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.hand</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springcloud</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Greenwich.SR2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Rename application.properties to application.yml
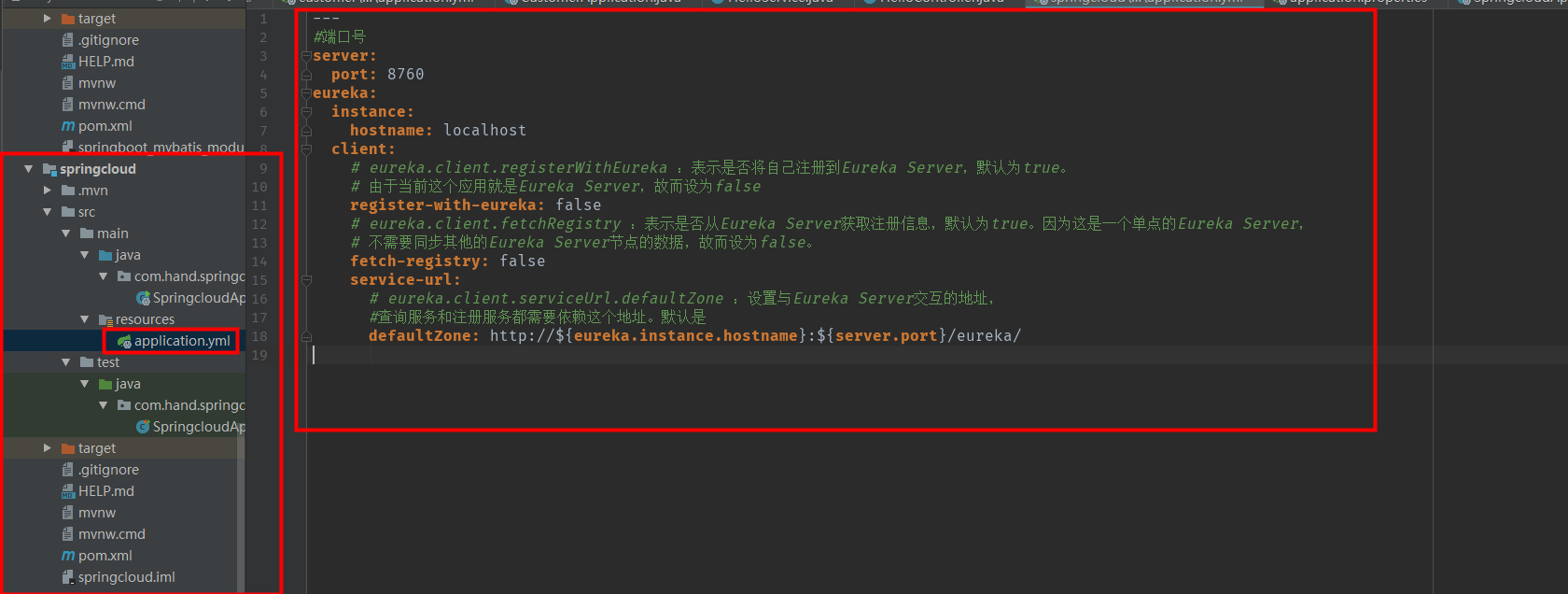
application.yml
---
#Port number
server:
port: 8760
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
# eureka.client.registerWithEureka: Indicates whether to register oneself to Eureka Server by default to true.
# Since the current application is Eureka Server, it is set to false.
register-with-eureka: false
# eureka.client.fetchRegistry: Represents whether registration information is obtained from Eureka Server by default to true. Because this is a single point Eureka Server,
# Instead of synchronizing data from other Eureka Server nodes, it is set to false.
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
# eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone: Set the address to interact with Eureka Server.
#Both query and registration services depend on this address. The default is
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
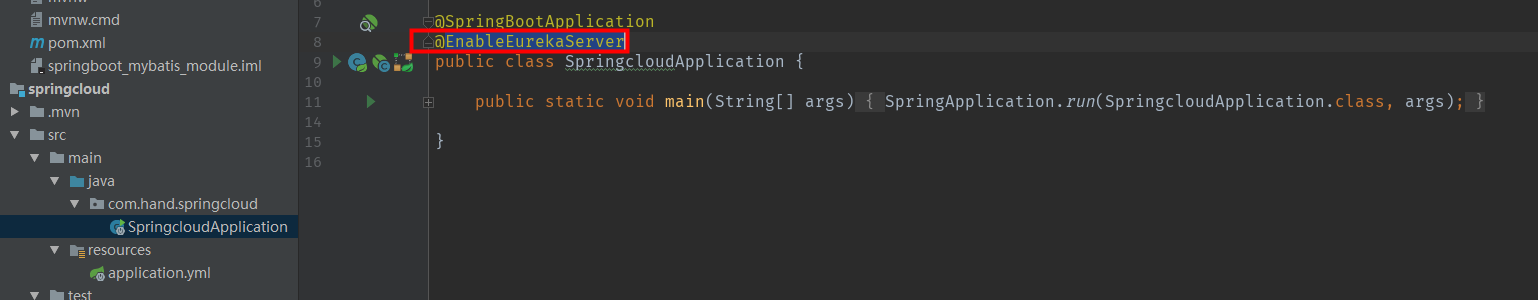
Browsers access localhost:8760 after startup
Next, build a new one on our github
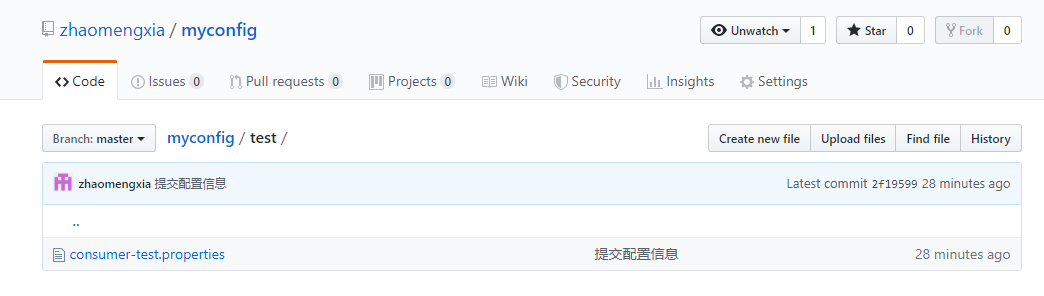
And then there it is.
Newly build
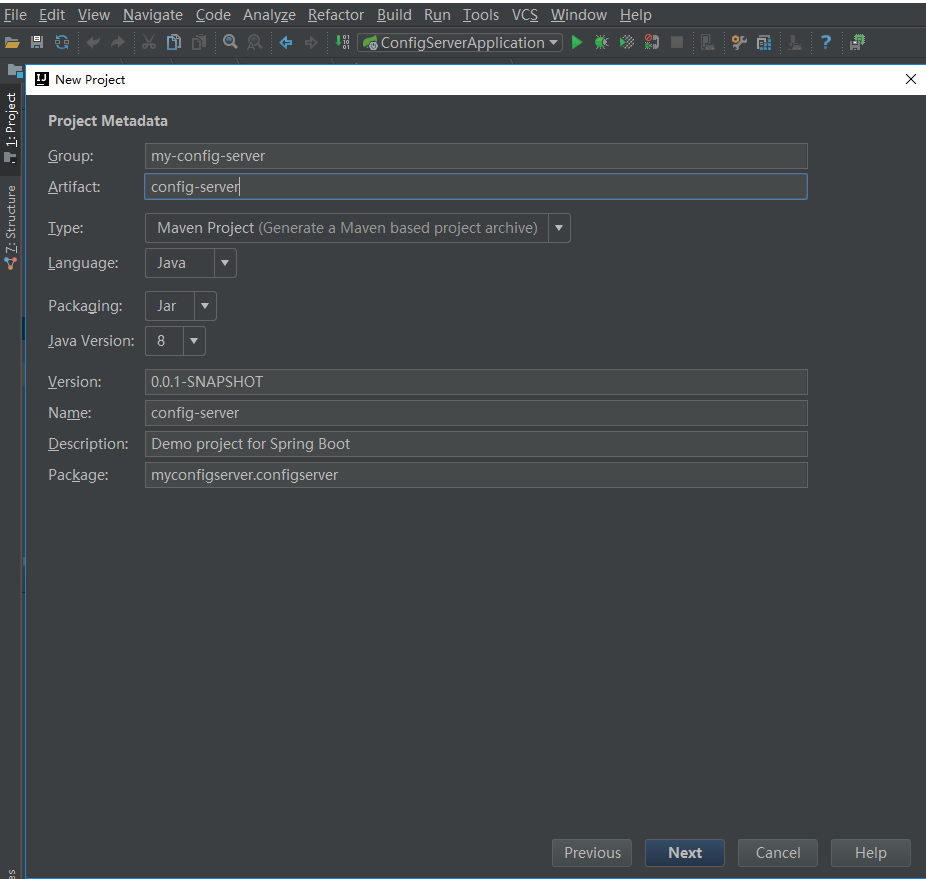
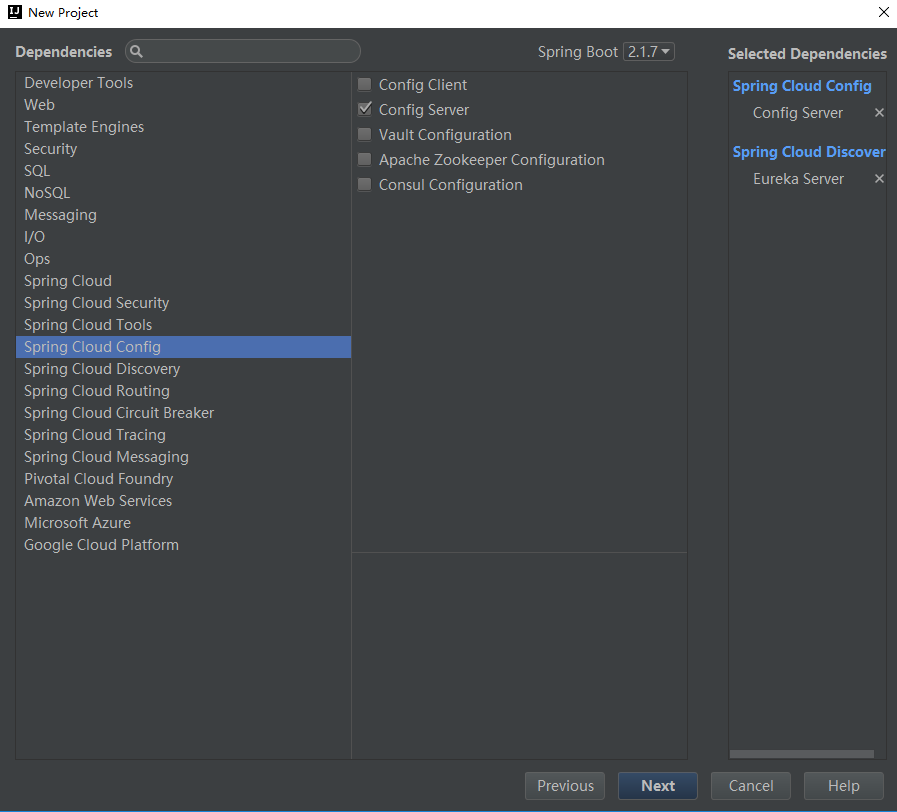
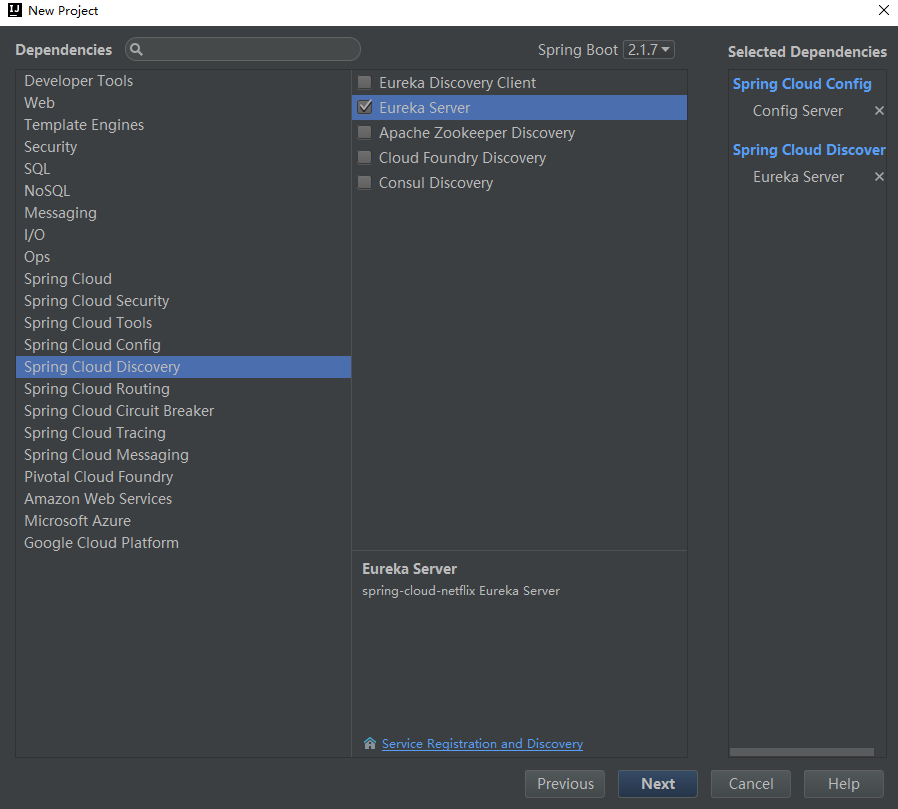
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.7.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>my-config-server</groupId>
<artifactId>config-server</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>config-server</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Greenwich.SR2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
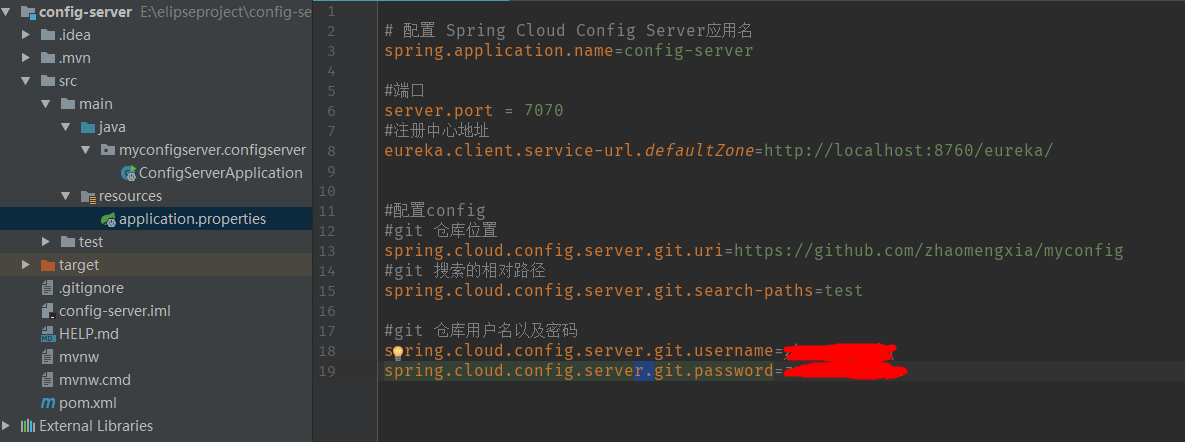
application.properties
# Configure Spring Cloud Config Server application name spring.application.name=config-server #port server.port = 7070 #Registry Address eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:8760/eureka/ #Configure config #git warehouse location spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri=https://github.com/zhaomengxia/myconfig #Relative Path of git Search spring.cloud.config.server.git.search-paths=test #git warehouse username and password spring.cloud.config.server.git.username=Your github Account number spring.cloud.config.server.git.password=Your github Password
- spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri: Configure the location of the Git repository and copy it directly from the browser address bar.
Pictured
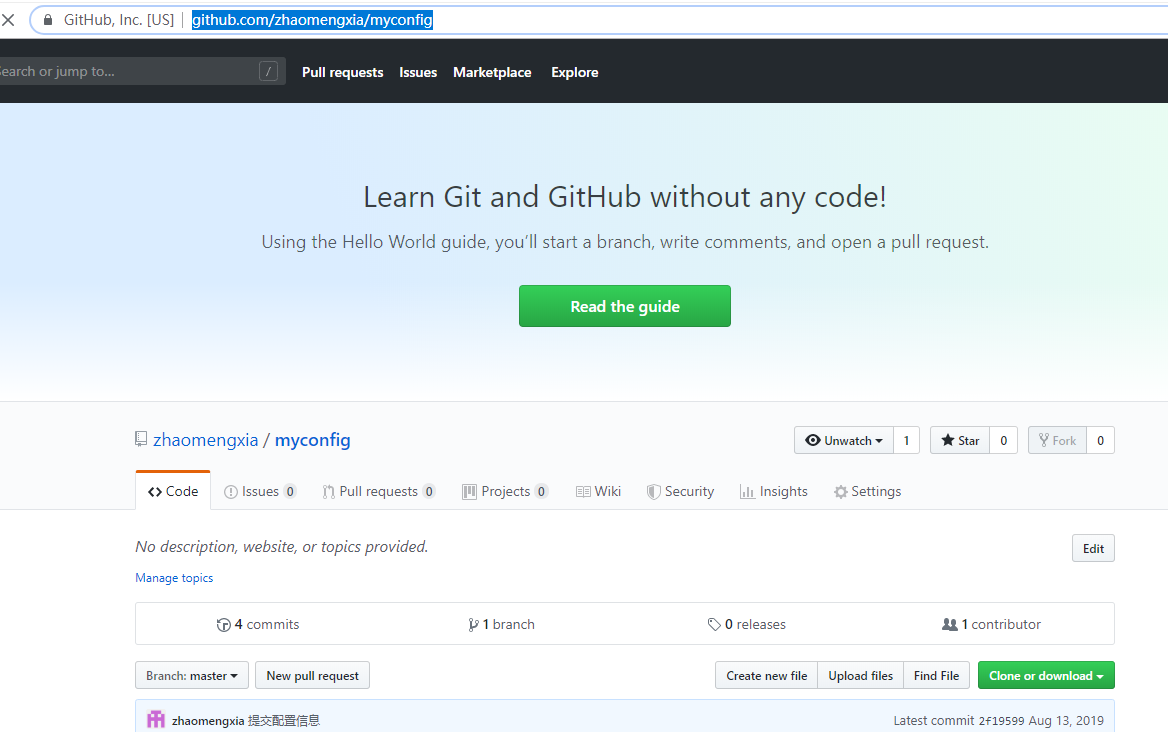
- spring.cloud.config.server.git.search-paths: Search the relative path of the configuration file. Here is the test folder in the figure above.
- spring.cloud.config.server.git.username/password:Git warehouse account password, which can be matched here or not.
Start ConfigServerApplication.java
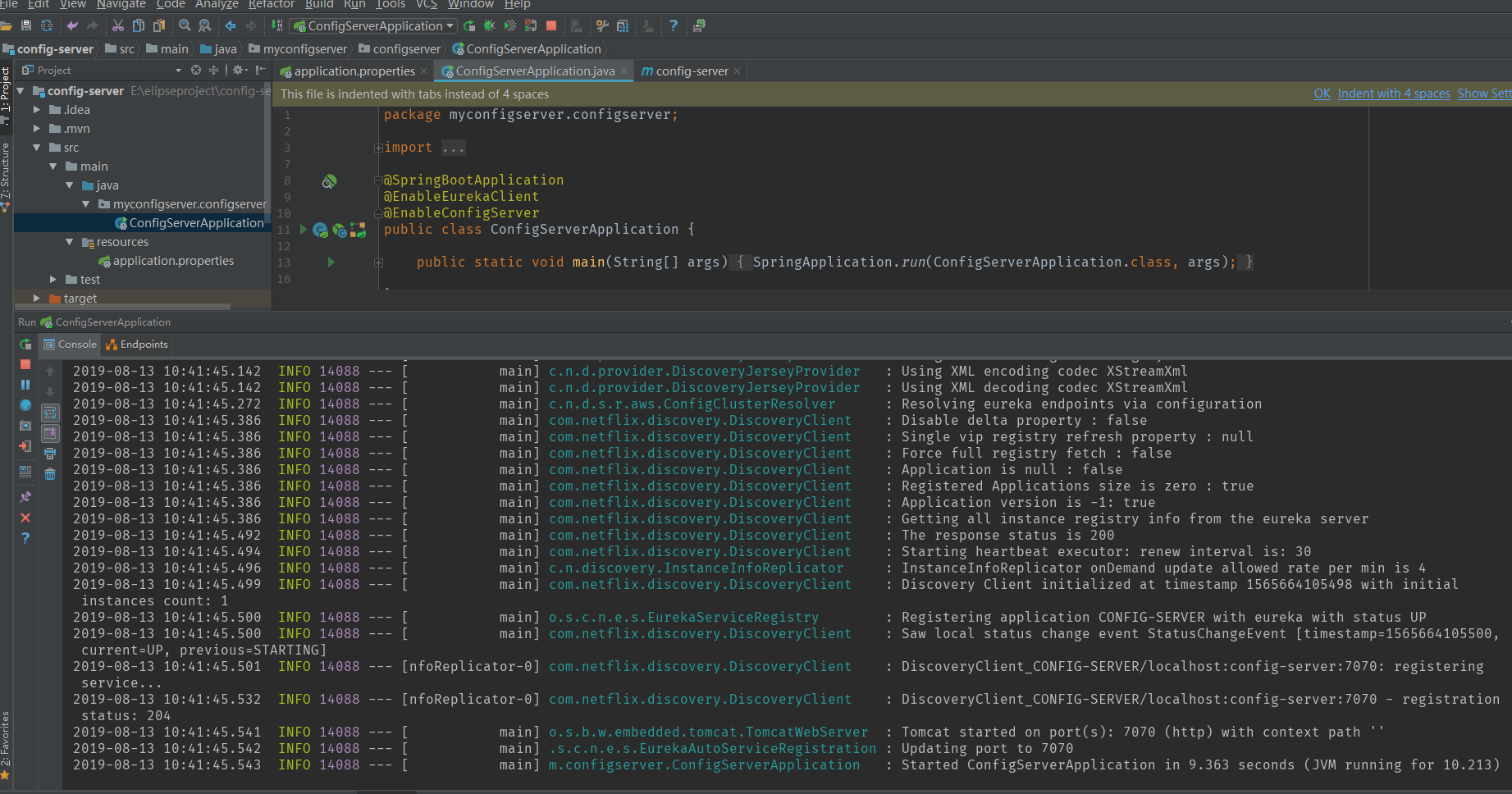
Re-visit localhost:8760
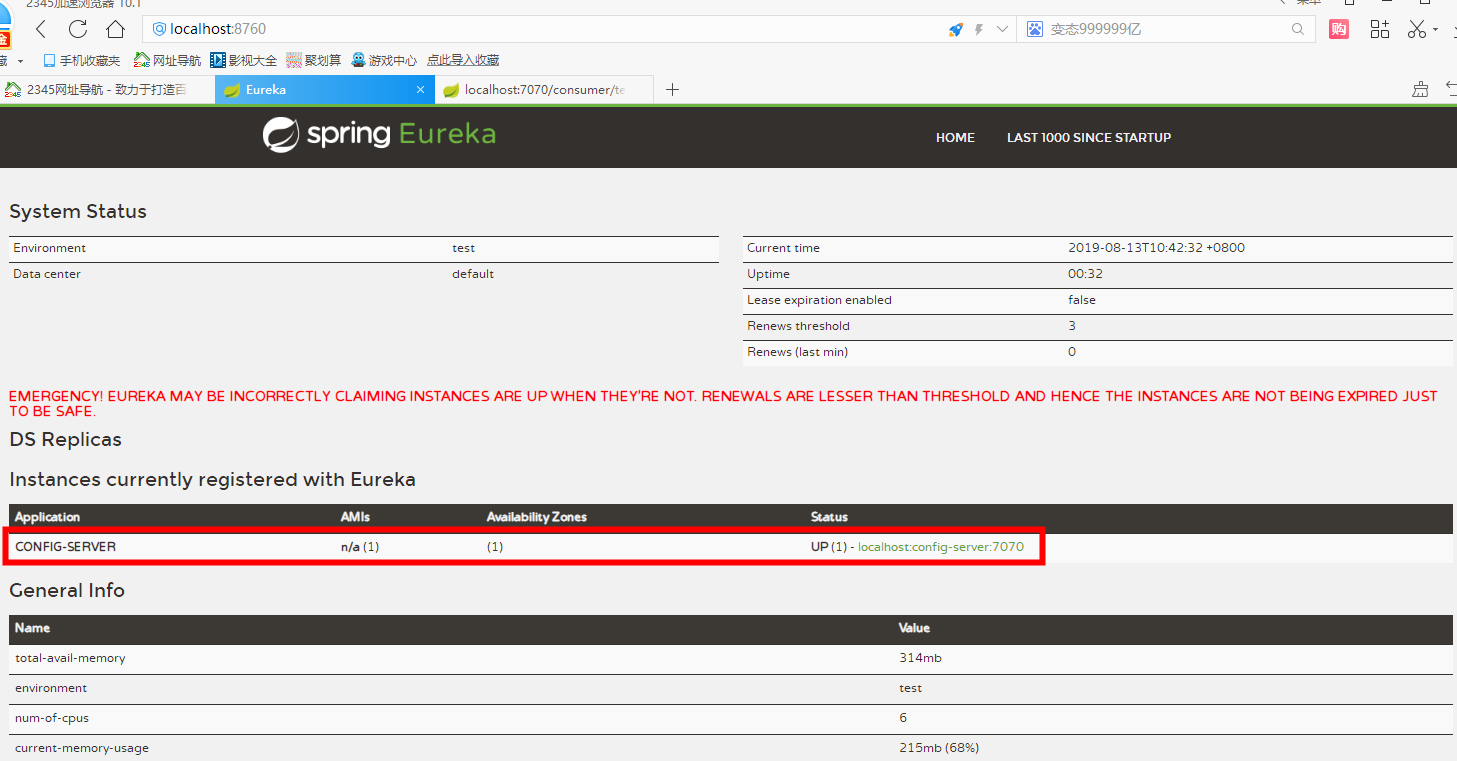
We can see that we have registered, so let's see if our externalization configuration has been read. Here we have a rule, which is excerpted from Zhai Yongchao's Spring Cloud Microservice Actual Warfare.
/{application}/{profile}/[{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
Here label refers to the different branches corresponding to Git. The default is master. The rest can be shown in the figure.
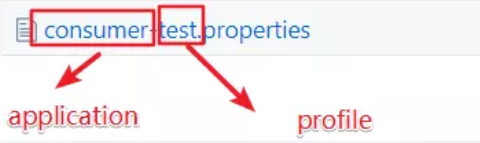
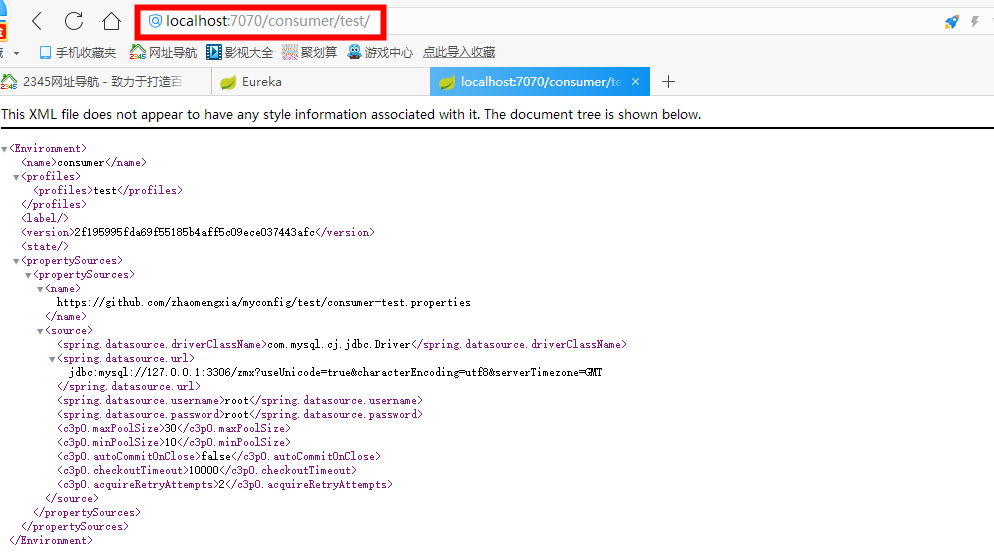
Our configuration center has been set up here. Next let's do the client.
Client Configuration (ribbon-consumer)
The client here, I use the client I created before. Simple, how to build, you can go back and have a look.
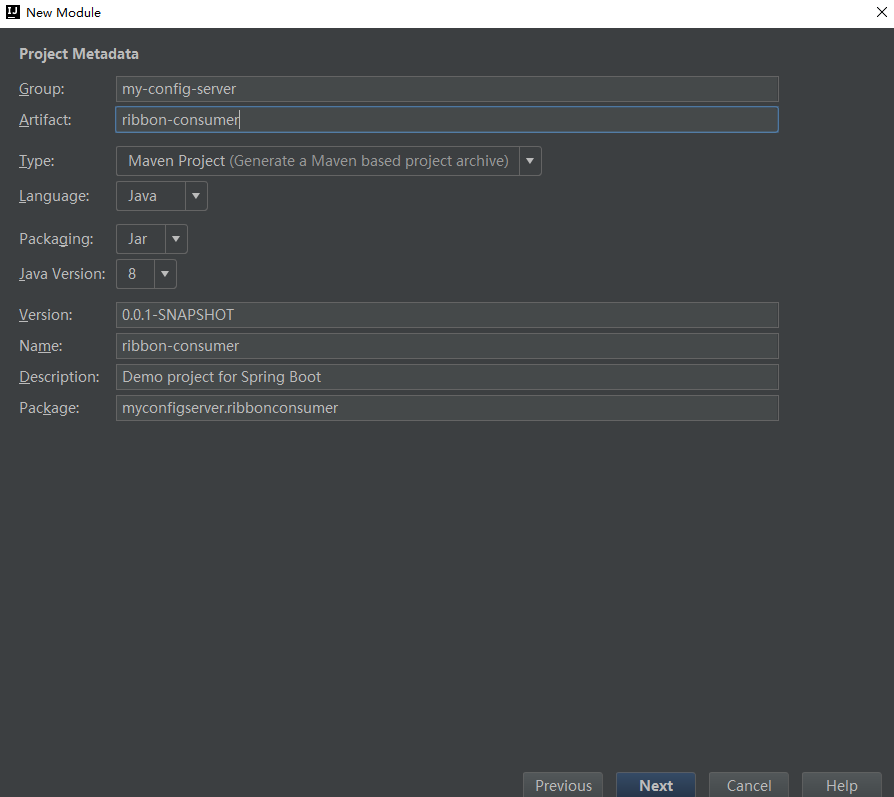
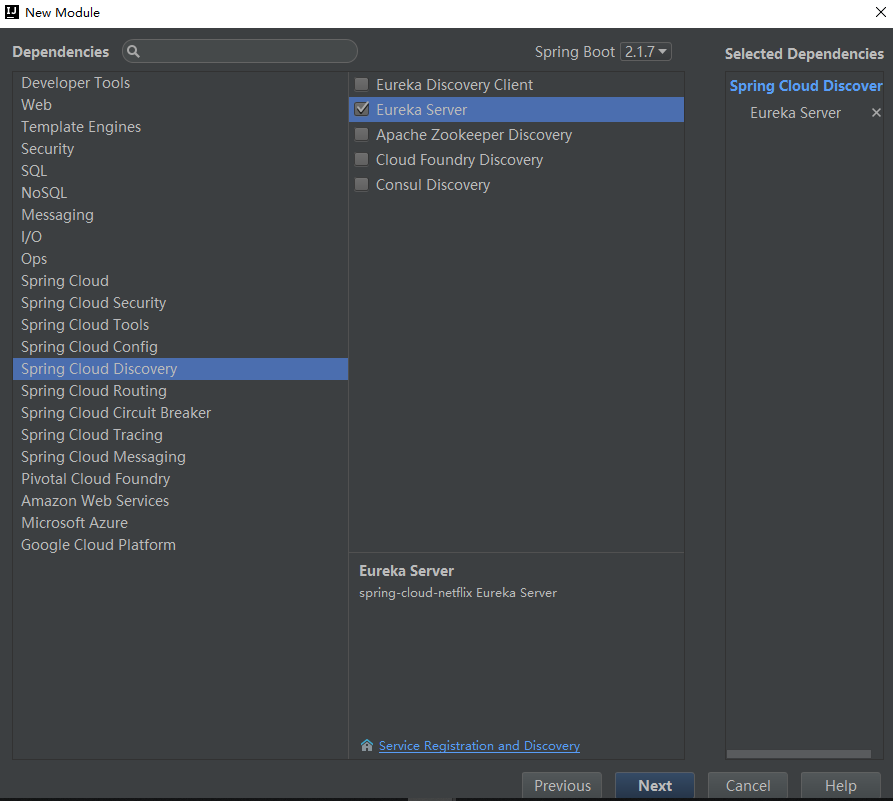
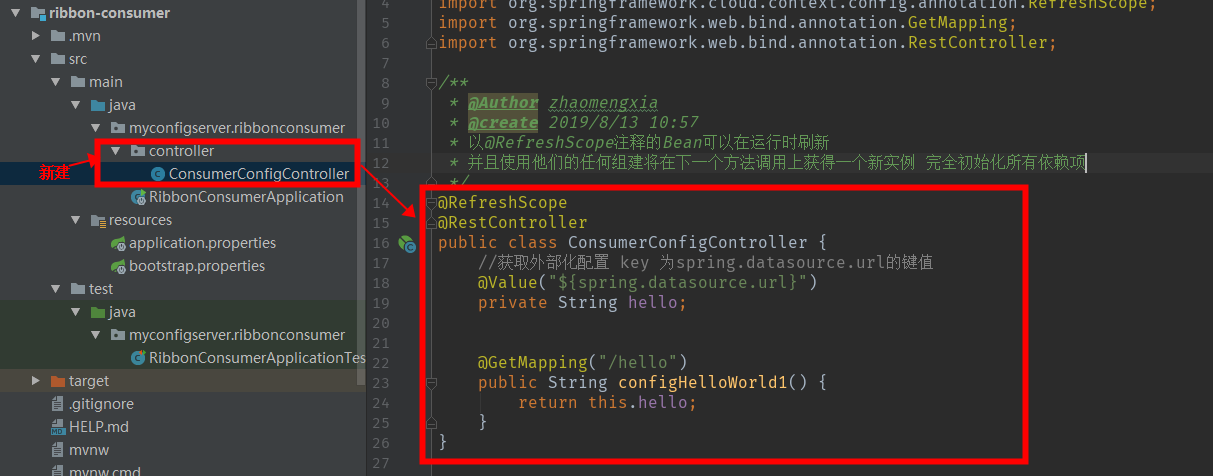
In the following figure, all the contents in application.properties are commented out and replaced by bootstrap.properties, which is based on spring boot's external configuration loading order.
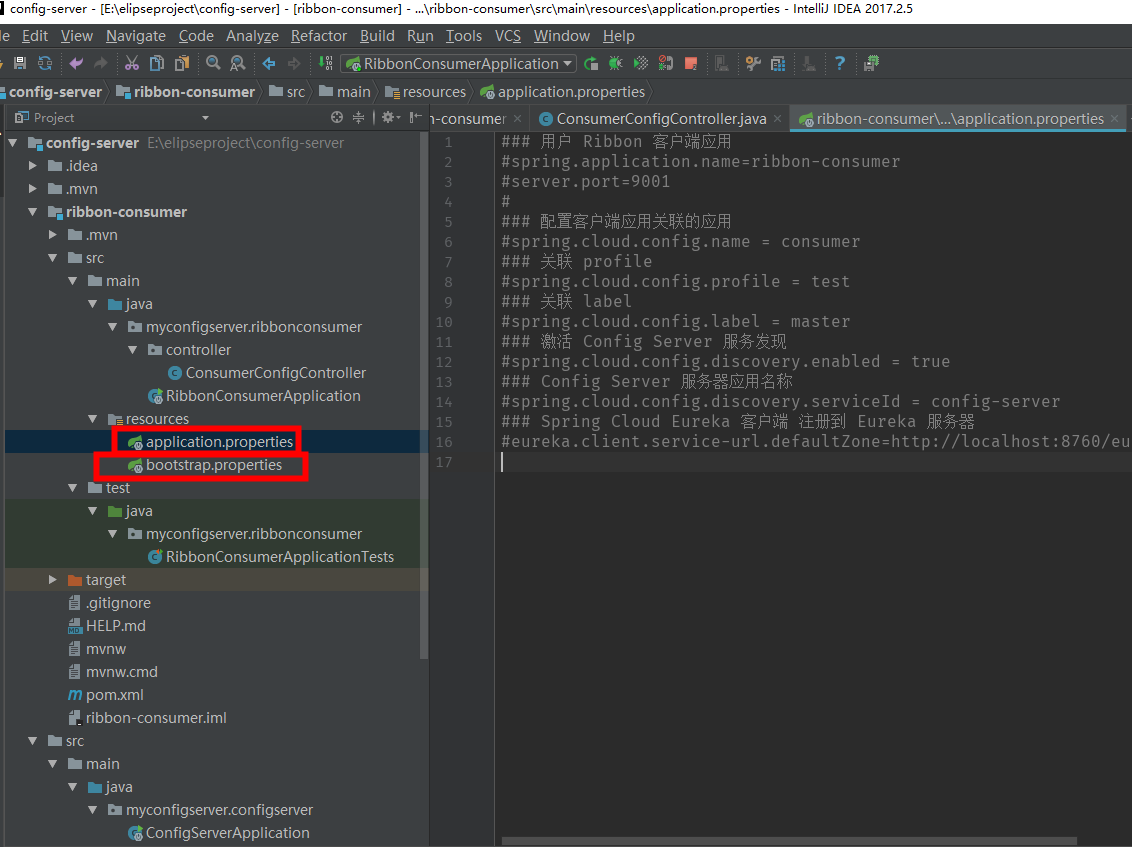
If you use application.properties, the startup will appear as follows
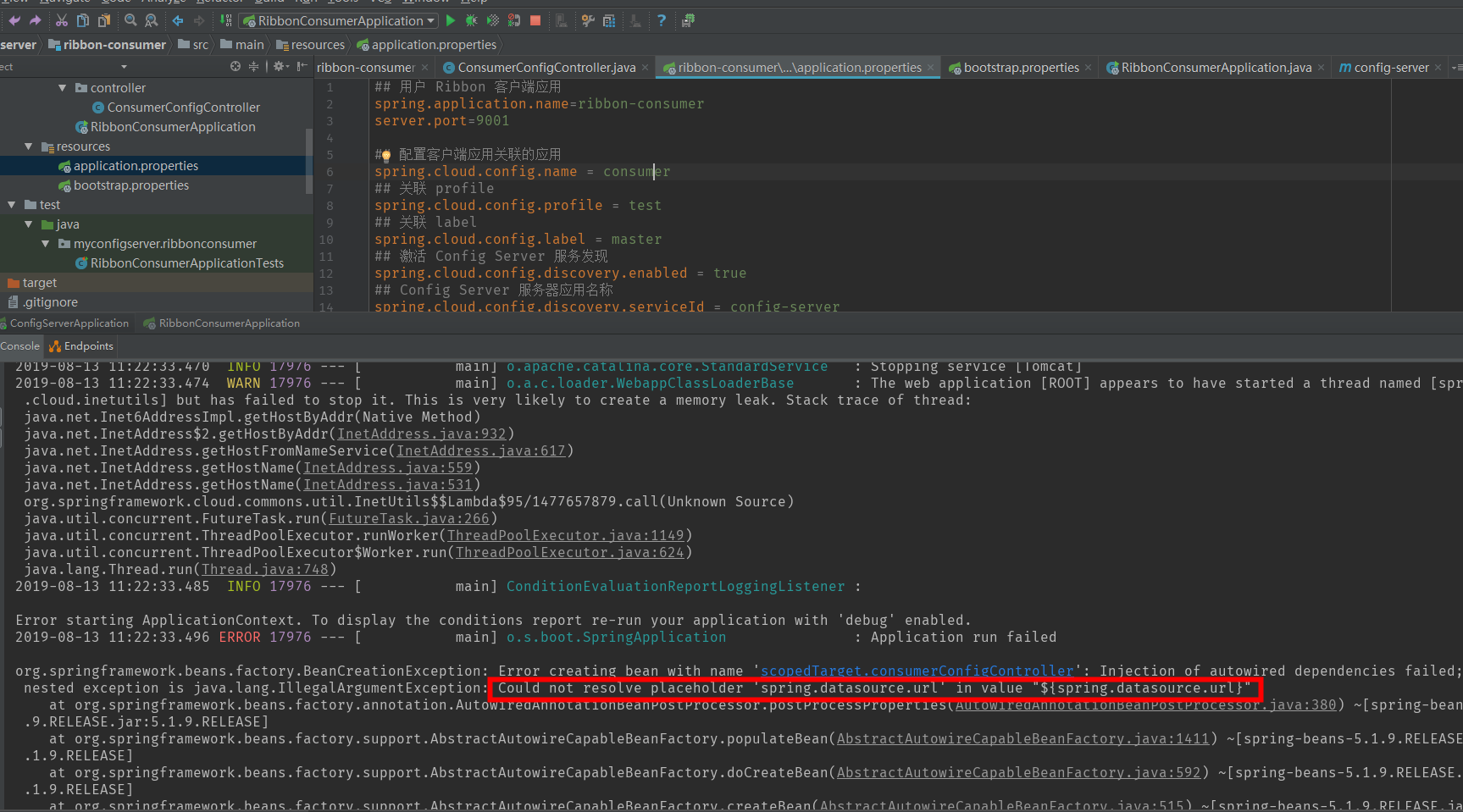
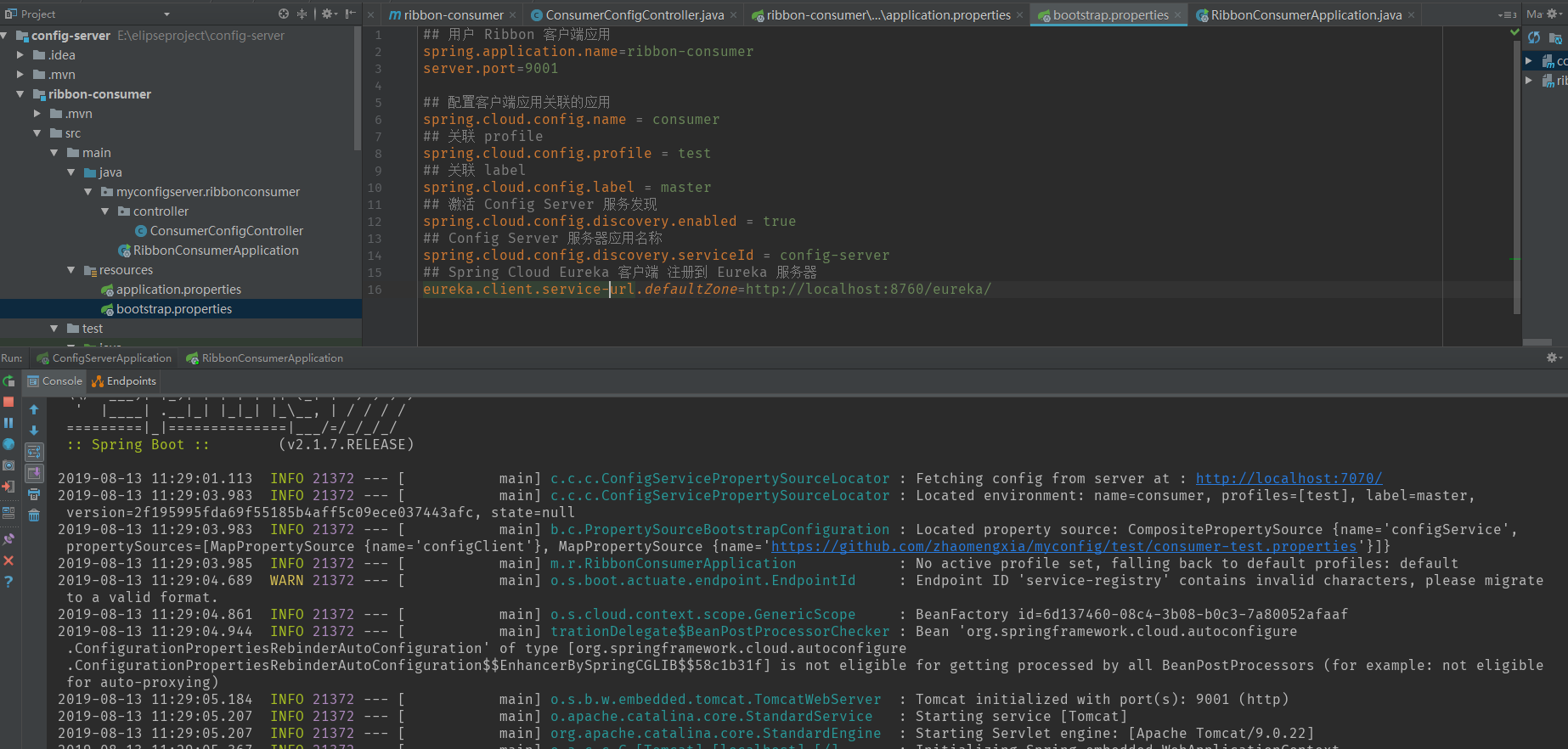
Conversely, if we use bootstrap.properties
The results are as follows.
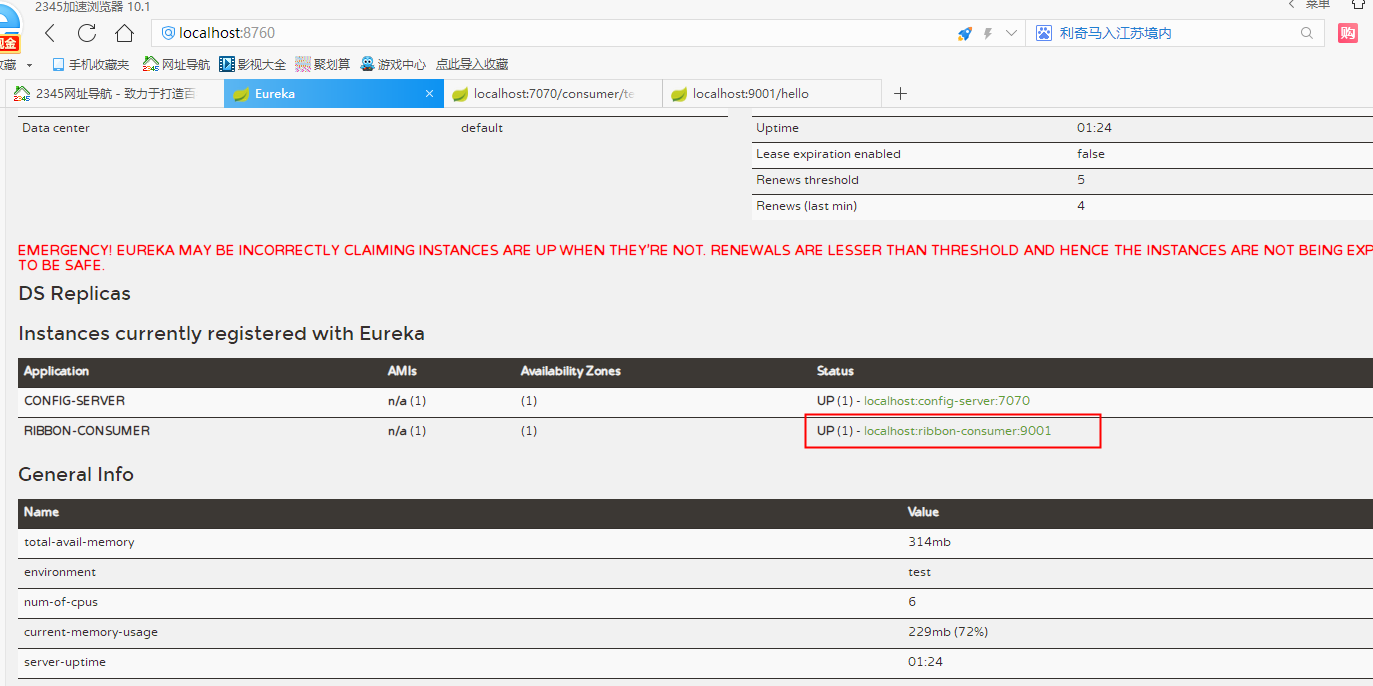
First go to the registry to check, the results are as follows, indicating that the registration has been successful
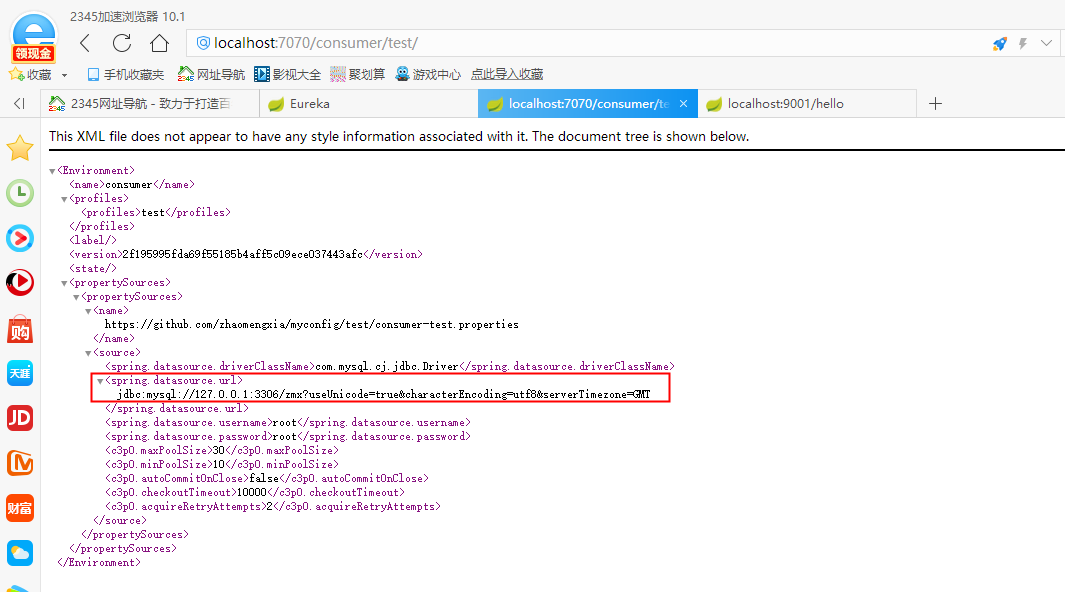
Next let's test whether we can read the configuration of the configuration center. From the first two pictures below, we can see that the result of the third one is exactly what we want, so we succeeded.
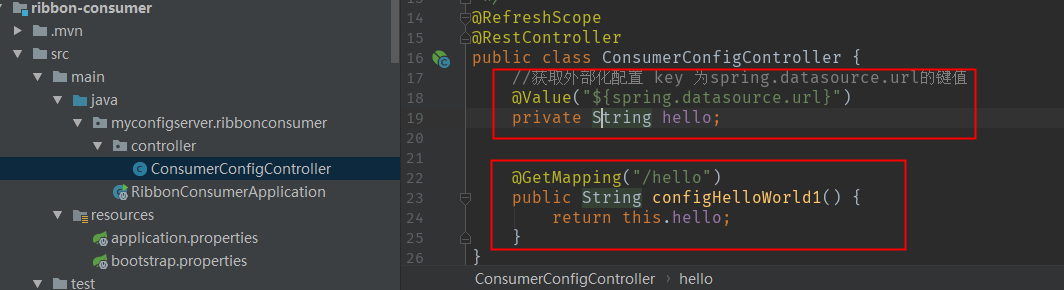
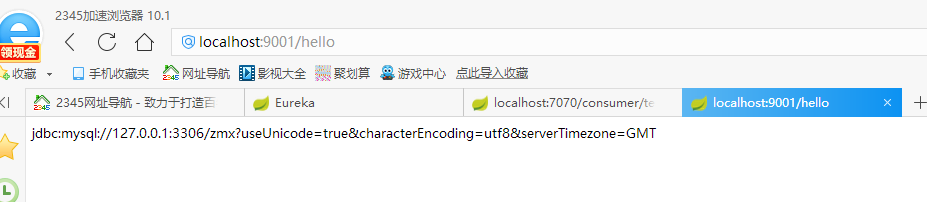
summary
Distributed configuration center facilitates the operation, maintenance and management of our overall project, and makes our project development, deployment and testing perfect.