Spring Cloud Stream message driven integration RabbitMQ
1. What do you do?
At present, there are too many message oriented middleware MQ used (for example, java uses RabbitMQ, while the background big data uses Kafka). Is there a new technology to make us no longer pay attention to the details of specific MQ? We only need to use an adaptive binding method to automatically give us the technology to switch within various MQ? This is the birth of Spring Cloud Stream technology.
In a word: shield the differences between the underlying message middleware, reduce the switching cost, and unify the programming model of message.
Official website: https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-stream
2. What is spring cloudstream
It is a framework of component message driven microservices.
The application interacts with the binder object in Spring Cloud Stream through inputs and outputs.
We configure binding, and the binder object of Spring Cloud Stream interacts with the message middleware.
Therefore, we only need to know how to interact with Spring Cloud Stream to facilitate the use of message driven mode.
By using Spring Integration to connect the message broker middleware to realize message time driving.
Spring Cloud Stream provides personalized automatic configuration implementation for some vendors' message middleware products, citing the three core concepts of publish subscribe, consumption group and partition.
Note: currently only RabbitMQ and Kafka are supported
3. Implementation mode
By defining Binder as the middle layer, the isolation between application and message middleware details is realized.
The message communication mode in Stream follows the publish subscribe mode.
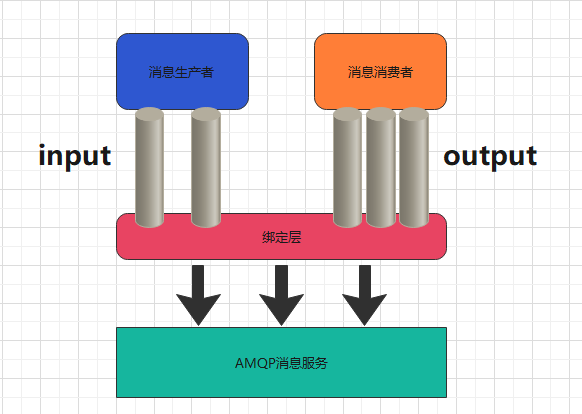
| form | explain |
|---|---|
| Middleware | Middleware, RabbitMQ/Kafka |
| Binder | Binder is applied to the encapsulation between message middleware. Binder can easily connect the middleware and dynamically change the message type (corresponding to Kafka topic and RabbitMQ exchange), which can be realized through the configuration file |
| @Input | The annotation identifies the input pipeline through which messages received enter the application |
| @Output | Annotations identify the output pipeline through which published messages leave the application |
| @StreamListener | Listening queue is used for receiving messages from the consumer's queue |
| @EnalbeBinding | Refers to the binding of channel and exchange |
4. Message driven producer (rabbitmq based)
Add dependency to pom file:
<!--introduce stream of RabbitMQ Message driven-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
yml profile:
server:
port: 8801
spring:
application:
name: cloud-stream-provider
cloud:
stream:
binders: #Configure the service information to bind rabbitmq here
defaultRabbit: #Represents the name of the definition, which is used in the binding collection
type: rabbit #Information component type
environment: #Set the related environment configuration of rabbitmq
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
bindings: #Integration of services
output: #This name is the name of a channel
destination: studyExchange #Indicates that you want to use the Exchange name definition (send messages to this Exchange)
content-type: application/json #Set the message type, json this time, and "text/plain" for text
binder: defaultRabbit #Set the specific settings of the message service to be bound
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
instance:
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 2 #Set the heartbeat interval (the default is 30 seconds)
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 5 #If no heartbeat is received within this time, it will be removed
instance-id: send-8801.com #Displays the host name in the information list
prefer-ip-address: true #The access path becomes an IP address
Interface:
public interface IMessageProvider {
public String send();
}
Implementation class:
import com.atguigu.springcloud.service.IMessageProvider;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.messaging.Source;
import org.springframework.messaging.MessageChannel;
import org.springframework.messaging.support.MessageBuilder;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.UUID;
@EnableBinding(Source.class) //Defines the push pipeline for messages
public class IMessageProviderImpl implements IMessageProvider {
@Resource
private MessageChannel output; //Message sending pipeline
@Override
public String send() {
String serial = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
output.send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(serial).build());
System.out.println("--------------serial:" + serial);
return null;
}
}
controller layer call:
import com.atguigu.springcloud.service.IMessageProvider;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
public class SendMessageController {
@Resource
private IMessageProvider messageProvider;
@GetMapping(value = "/sendMessage")
public String sendMessage() {
return messageProvider.send();
}
}
5. Message driven consumers
Add dependency to pom file:
<!--introduce stream of RabbitMQ Message driven-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
yml profile:
server:
port: 8802
spring:
application:
name: cloud-stream-consumer
cloud:
stream:
binders: #Configure the service information to bind rabbitmq here
defaultRabbit: #Represents the name of the definition, which is used in the binding collection
type: rabbit #Information component type
environment: #Set the related environment configuration of rabbitmq
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
bindings: #Integration of services
input: #This name is the name of a channel
destination: studyExchange #Indicates that the Exchange name definition is to be used (messages from this Exchange will be received)
content-type: application/json #Set the message type, json this time, and "text/plain" for text
binder: defaultRabbit #Set the specific settings of the message service to be bound (red does not affect startup!!!)
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
instance:
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 2 #Set the heartbeat interval (the default is 30 seconds)
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 5 #If no heartbeat is received within this time, it will be removed
instance-id: receive-8802.com #Displays the host name in the information list
prefer-ip-address: true #The access path becomes an IP address
controller layer receiving:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.StreamListener;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.messaging.Sink;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@EnableBinding(Sink.class) //Open message driven binding
public class ReceiveMessageListenerController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@StreamListener(Sink.INPUT)
public void input(Message<String> message) {
System.out.println("Consumer 1, the message received is:" + message.getPayload() + "\t" + "port:" + serverPort);
}
}
6. Consumer grouping
The following cases:
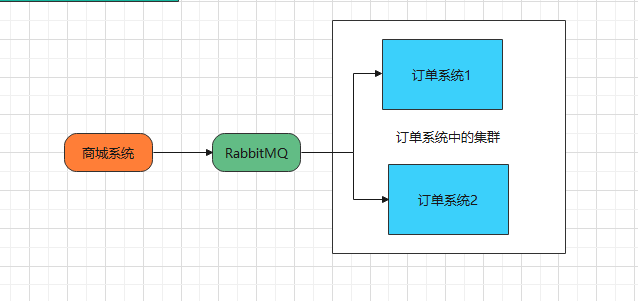
If an order is obtained by multiple services at the same time, it will cause data errors.
Stream uses message grouping to solve this problem.
Multiple consumers in the same group in the Stream are competitive, which can ensure that messages will only be consumed by one application, and different groups can consume comprehensively (repeated consumption).
We only need to add the configuration in the message consumer's yml configuration file:
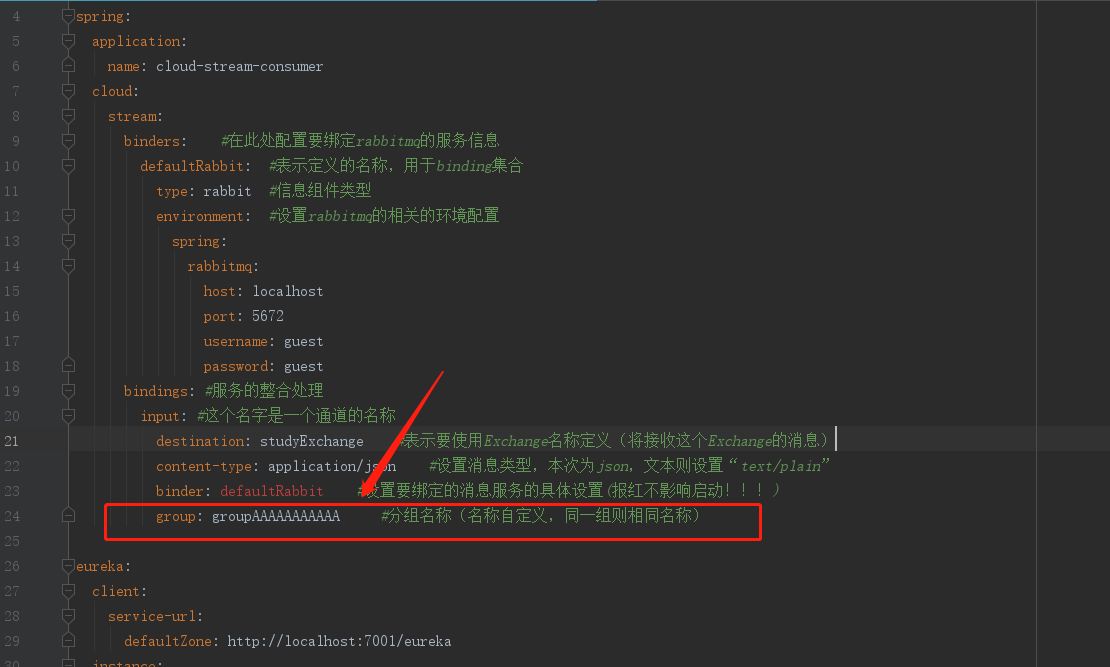
7. Persistent message
If there are multiple message consumers, when one of the consumer services crashes, the message producer is still pushing messages. If persistence is not configured, the crashed service will not receive messages after restart. The configured attribute is also group, which supports persistence.
That is, adding the group attribute supports message persistence