Notes from Dark horse Java video
Basic use of JdbcTemplate
01 basic use of jdbctemplate - Overview (understand)
JdbcTemplate is an object provided in the spring framework. It is a simple encapsulation of the original cumbersome Jdbc API object. The spring framework provides us with many operation template classes. For example: JdbcTemplate and HibernateTemplate for operating relational data, RedisTemplate for operating nosql database, JmsTemplate for operating message queue, etc.
02 basic use of jdbctemplate - development steps (understanding)
① Import spring JDBC and spring TX coordinates
② Create database tables and entities
③ Create a JdbcTemplate object
④ Perform database operations
03 basic use of jdbctemplate - quick start code implementation (application)
Import spring JDBC and spring TX coordinates
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>itheima_spring_jdbc</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>itheima_spring_jdbc Maven Webapp</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.32</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Create database tables and entities
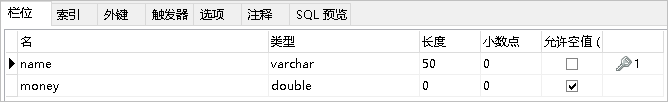
package com.itheima.domain;
public class Account {
private String name;
private double money;
public String getNa me() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
Create a JdbcTemplate object
Perform database operations
@Test
//Test the development steps of JdbcTemplate
public void test1() throws PropertyVetoException {
//Create data source object
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setUser("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//Set the data source object to know where the database is
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
//Perform operations
int row = jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values(?,?)", "tom", 5000);
System.out.println(row);
}
04-JdbcTemplate basic use - spring to generate template object analysis (understanding)
We can hand over the creation right of the JdbcTemplate to Spring and the creation right of the data source DataSource to Spring, inject the data source DataSource into the JdbcTemplate template object inside the Spring container, and then obtain the JdbcTemplate object through the Spring container to perform the operation.
05 jdbctemplate basically uses spring to generate template object code (application)
The configuration is as follows:
<!--Data source object-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--jdbc Template object-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
Test code
@Test
//Test the JDBC template object generated by Spring
public void test2() throws PropertyVetoException {
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = app.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
int row = jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values(?,?)", "lisi", 5000);
System.out.println(row);
}
06 jdbctemplate basically uses spring to generate template object code implementation (extract jdbc.properties) (application)
The connection information of the database is extracted into the external configuration file and separated from the spring configuration file, which is conducive to later maintenance
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
The configuration file is modified to:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<!--load jdbc.properties-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--Data source object-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--jdbc Template object-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
Configuration class mode
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource getDateSource() throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass(driver);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);
dataSource.setUser(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) throws PropertyVetoException {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
07 jdbctemplate basic use common operation update operation (application)
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JdbcTemplateCRUDTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//Modify update
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=? where name=?",10000,"tom");
}
//delete
@Test
public void testDelete(){
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from account where name=?","tom");
}
}
08 jdbctemplate basic usage - common operations - query operations (application)
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JdbcTemplateCRUDTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//Aggregate query
@Test
public void testQueryCount(){
Long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from account", Long.class);
System.out.println(count);
}
//Query one
@Test
public void testQueryOne(){
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from account where name=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), "tom");
System.out.println(account);
}
//Query all
@Test
public void testQueryAll(){
List<Account> accountList = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class));
System.out.println(accountList);
}
}
09 basic use of jdbctemplate - key points of knowledge (understanding, memory)
① Import spring JDBC and spring TX coordinates
② Create database tables and entities
③ Create a JdbcTemplate object
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = newJdbcTemplate(); jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
④ Perform database operations
Update operation:
jdbcTemplate.update (sql,params)
Query operation:
jdbcTemplate.query (sql,Mapper,params)
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,Mapper,params)
Declarative transaction control
1. Programming transaction control related objects
1.1 PlatformTransactionManager
The PlatformTransactionManager interface is the transaction manager of spring, which provides our common methods of operating transactions.
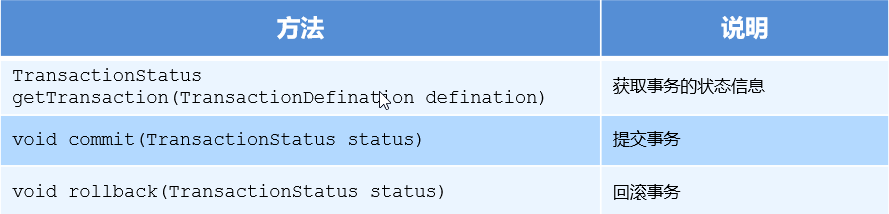
be careful:
PlatformTransactionManager is an interface type, and different Dao layer technologies have different implementation classes. For example, when Dao layer technology is JDBC or mybatis: org springframework. jdbc. datasource. DataSourceTransactionManager
When Dao layer technology is Hibernate: org springframework. orm. hibernate5. HibernateTransactionManager
1.2 TransactionDefinition
TransactionDefinition is the transaction definition information object, which contains the following methods:
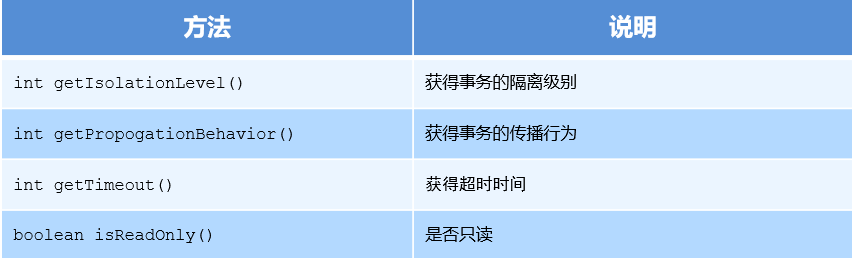
1. Transaction isolation level
Setting the isolation level can solve the problems caused by transaction concurrency, such as dirty reading, non repeatable reading and virtual reading.
-
ISOLATION_DEFAULT
-
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED
-
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED
-
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ
-
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE
2. Business communication behavior
-
REQUIRED: if there is no transaction at present, create a new transaction. If there is already a transaction, join it. General selection (default)
-
SUPPORTS: SUPPORTS the current transaction. If there is no transaction, it will be executed in a non transactional manner (no transaction)
-
If there is no current transaction, the number of exceptions will be thrown
-
REQUERS_NEW: create a new transaction. If it is currently in a transaction, suspend the current transaction.
-
NOT_SUPPORTED: perform operations in a non transactional manner. If there is a transaction, suspend the current transaction
-
NEVER: run in non transaction mode. If there is a transaction currently, throw an exception
-
NESTED: if a transaction currently exists, it is executed within a NESTED transaction. If there is no current transaction, perform an operation similar to REQUIRED
-
Timeout: the default value is - 1. There is no timeout limit. If yes, set in seconds
-
Read only: it is recommended to set it as read-only when querying
1.3 TransactionStatus
The TransactionStatus interface provides the specific running status of transactions. The methods are described below.
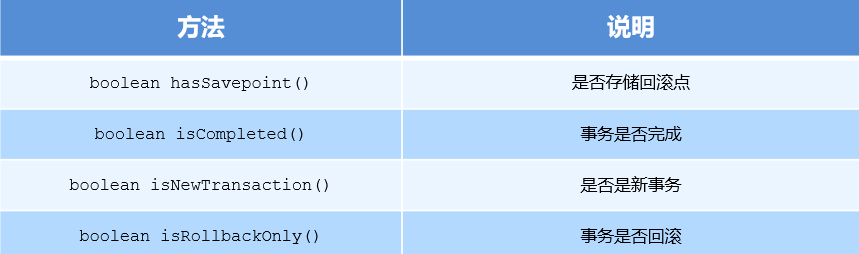
1.4 key points of knowledge
Three objects of programming transaction control
-
PlatformTransactionManager
-
TransactionDefinition
-
TransactionStatus
2 declarative transaction control based on XML
2.1 what is declarative transaction control
Spring's declarative transaction, as its name suggests, is to handle transactions in a declarative way. The declaration mentioned here refers to the declaration in the configuration file, and the declarative transaction in the spring configuration file is used to replace the code transaction.
The role of declarative transaction processing
-
Transaction management does not invade developed components. Specifically, the business logic object will not realize that it is in the process of transaction management. In fact, it should be the same, because transaction management is a service at the system level, not a part of business logic. If you want to change the transaction management plan, you only need to reconfigure it in the definition file
-
When transaction management is not needed, the transaction management service can be removed by modifying the setting file without changing the code and recompiling, which is very convenient for maintenance
Note: the underlying layer of Spring declarative transaction control is AOP.
2.2 implementation of declarative transaction control
Explicit matters of declarative transaction control:
-
Who is the cut point?
-
Who is the notice?
-
Configuration section?
① Introduce tx namespace
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
② Configure transaction enhancements
<!--Platform transaction manager-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--Transaction enhanced configuration-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
③ Configure transaction AOP weaving
<!--Transactional aop enhance-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
④ Test transaction control transfer business code
@Override
public void transfer(String outMan, String inMan, double money) {
accountDao.out(outMan,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.in(inMan,money);
}
2.3 configuration of transaction parameters of pointcut method
<!--Transaction enhanced configuration-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
Where tx:method represents the configuration of transaction parameters of pointcut method, for example:
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" timeout="-1" read-only="false"/>
-
Name: tangent point method name
-
Isolation: isolation level of transaction
-
Propagation: propagation behavior of transactions
-
Timeout: timeout
-
Read only: read only
2.4 key points of knowledge
Configuration points of declarative transaction control
-
Platform transaction manager configuration
-
Configuration of transaction notifications
-
Configuration of transaction aop weaving
3 annotation based declarative transaction control
3.1 configuring declarative transaction control using annotations
- Write AccoutDao
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void out(String outMan, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money-? where name=?",money,outMan);
}
public void in(String inMan, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money+? where name=?",money,inMan);
}
}
- Write AccoutService
@Service("accountService")
@Transactional
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void transfer(String outMan, String inMan, double money) {
accountDao.out(outMan,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.in(inMan,money);
}
}
- Write ApplicationContext XML configuration file
<!—Omitted before datsSource,jdbcTemplate,Configuration of platform transaction manager-->
<!--Component scan-->
#The main configuration class uses @ ComponentScan("com.itheima") instead
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/>
<!--Annotation driven transactions-->
<tx:annotation-driven/>
You can use a configuration class instead of an xml file configuration
//Use @ EnableTransactionManagemen instead of < TX: annotation driven / > in the configuration class and the main configuration class
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
3.2 annotation configuration declarative transaction control resolution
① Use @ Transactional to modify classes or methods that need transaction control. The attributes available for annotation are the same as xml configuration methods, such as isolation level, propagation behavior, etc.
② If annotations are used on a class, all methods under the class use the same set of annotation parameter configuration.
③ In terms of methods, different methods can adopt different transaction parameter configurations.
④ Annotation driven to enable transaction in Xml configuration file < TX: annotation driven / >
3.3 key points of knowledge
Annotated control points of transaction configuration
-
Platform transaction manager configuration (xml mode)
-
Configuration of transaction notification (@ Transactional annotation configuration)
-
Transaction annotation driven configuration < TX: annotation driven / >