- summary
================================================================
Through the previous ten blogs, we have summarized and completed various login methods, such as form login, SMS verification code login and social account login. However, when the front and back ends are separated, the token based authentication method will be adopted. At this time, the content of spring security oauth is needed. spring security oauth is a sub module of the spring security framework.
Authentication method based on token
==========================================================================
In view of the separation of front-end and back-end and the open platform, it is difficult to meet the existing login mode. In fact, some existing front-end frameworks have their own independent web servers, such as node js. When the requests of these front-end applications are launched to the back-end, they first go to the Web Server to obtain the relevant static resources, and then go to the back-end server to obtain the relevant data. In fact, a request is not in a session, and if an applet is used, the cookie mechanism is not supported, and the session mechanism based on sessionid cannot meet the relevant interaction requirements. At this time, there is a new way of cognition - token based authentication.
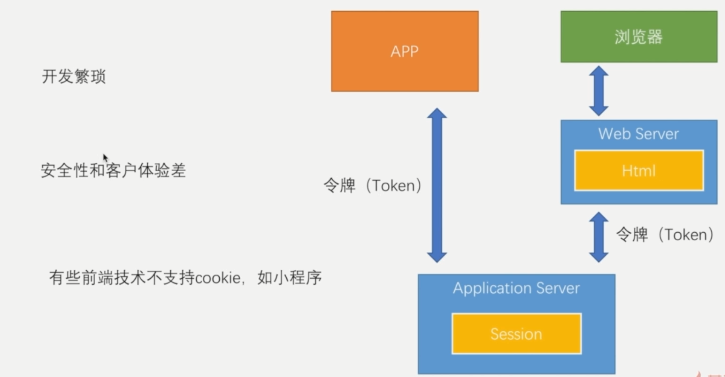
Let's go back to a picture of the previous blog
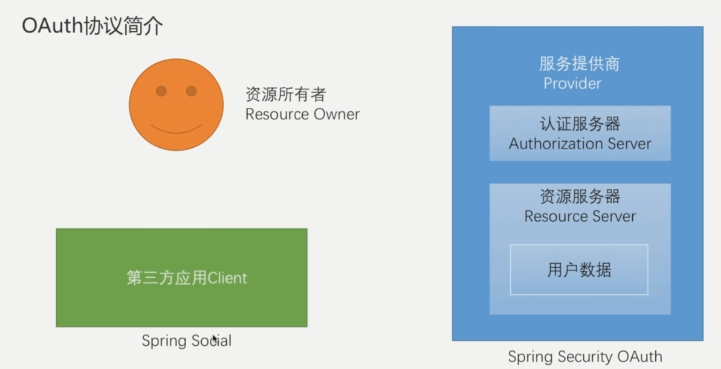
Spring social introduced in previous blogs encapsulates third-party applications, goes to service providers and obtains user information through OAuth protocol. Here we need to complete the logic development of the service provider, so we need to use spring security OAuth
Using spring security OAuth, we can quickly build the logic of the service provider, provide token s and verify them.
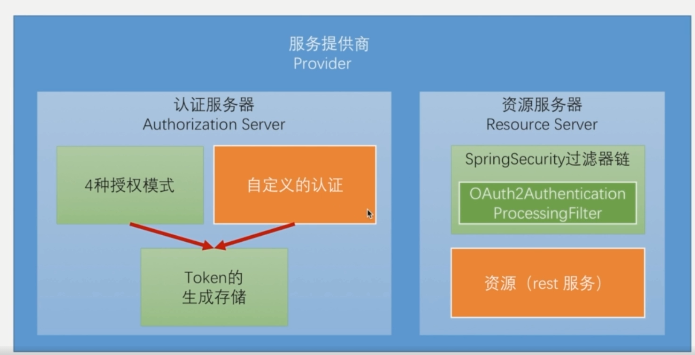
As a service provider, you need two pieces of content, one is the authentication server and the other is the resource server. In fact, the so-called authentication server can be simply understood as the logic of generating token. The so-called resource server is our business code. These two are just a logical concept, not two physically independent servers.
==================================================================
We still implement the relevant examples in the original project. For the code organization structure of the examples, please refer to our previous blog—— Introduction to spring -security.
The example of this blog will be completed in the App module. Meanwhile, the reference of demo needs to be modified to apply App, as shown below:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.coderman.learn</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-core</artifactId>
<version>${self.app.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
At the same time, prepare a business interface to obtain user information
@GetMapping("/me")
public Object getCurrentUser(@AuthenticationPrincipal UserDetails userDetails){
log.info("user me test");
return userDetails;
}
The previously customized UserDetailsService also needs to exist
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/7/8
* comment:
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyUserDetailService implements UserDetailsService{
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
/**
* Find user information by user name
* @param username
* @return
* @throws UsernameNotFoundException
*/
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
log.info("Find user information by user name:{}",username);
return new User(username,passwordEncoder.encode("123456"),
true,true,true,true,
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"));
}
}
In order to avoid the tedious task of inputting the clientid every time you restart, configure the clientid and clientsecret in the configuration file
security.oauth2.client.clientId=selfclientid security.oauth2.client.clientSecret=selfclientsecret
Implement authentication server
Recall the function of the authentication server in social login (taking the authorization code login as an example), you need to generate the authorization code based on the OAuth2 protocol and attach the authorization code to the callback address configured by the third-party application. Then the third-party application exchanges the token according to the obtained authorization code, and finally obtains the corresponding user information according to the token.
Based on spring security oauth, this is not difficult, and several configurations are completed.
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/7/22
* comment: app Authentication server configuration class
*
*/
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AppAuthorizationServerConfig {
}
Obtain authorization code
At this time, our application has the function of authentication server. When the project starts, we will find that spring security oauth adds several request paths starting with oauth for us, as shown below:
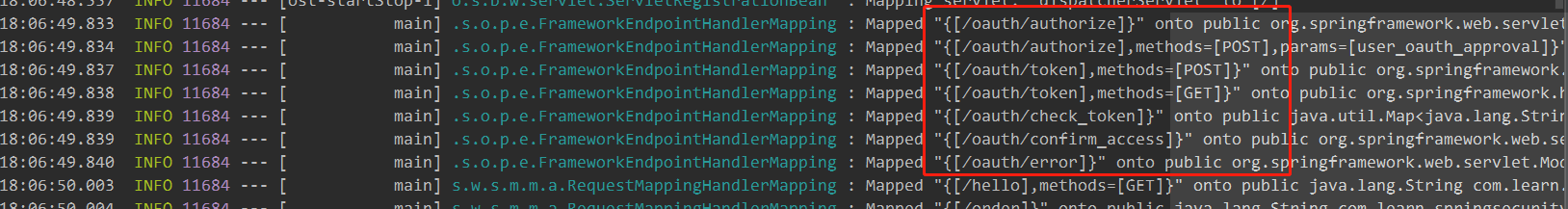
These request paths are the corresponding OAuth access paths. We can access oauth/authorize according to the relevant protocol parameters of OAuth2. For the protocol request parameters of OAuth2, please refer to Chapter 4 of the OAuth2 official website—— OAuth2 protocol official website.
Enter the following path in the browser
http://localhost:8090/oauth/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=selfclientid&redirect_uri=http://example.com&scope=all # At the end of the paper, java interview questions, advanced technology outline, architecture and data sharing I sorted out all the topics of the three Ali interviews, attached with detailed answer analysis, and generated a copy**PDF file**,Interested friends[You can click here to get it for free](https://gitee.com/vip204888/java-p7) * **The first thing to share with you is algorithms and data structures**  * **The second is the high-frequency knowledge points and performance optimization of the database**  * **The third is concurrent programming (72 knowledge points learning)**  * **The last one is the major JAVA Interview points for architecture topics+analysis+Some of my learning books**  In storage...(img-znBkEUie-1628589490316)] * **The second is the high-frequency knowledge points and performance optimization of the database** [External chain picture transfer...(img-GkPhfhk9-1628589490318)] * **The third is concurrent programming (72 knowledge points learning)** [External chain picture transfer...(img-U3rQfKCe-1628589490320)] * **The last one is the major JAVA Interview points for architecture topics+analysis+Some of my learning books** [External chain picture transfer...(img-zxqkyeK4-1628589490322)] There are more Redis,MySQL,JVM,Kafka,Microservices Spring The family bucket and other study notes are not listed here one by one