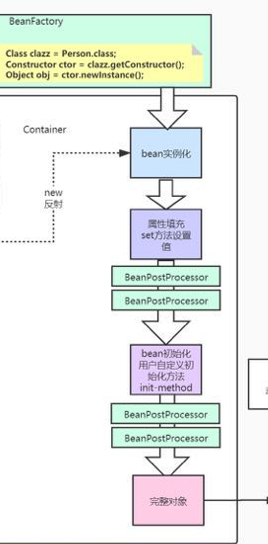
Let's start with a flow chart:

The detailed process in the right part
Then I will not cut off my own source code for the refresh method:

prepareRefresh

meaning:
Do some foreplay preparation for refresh preparation
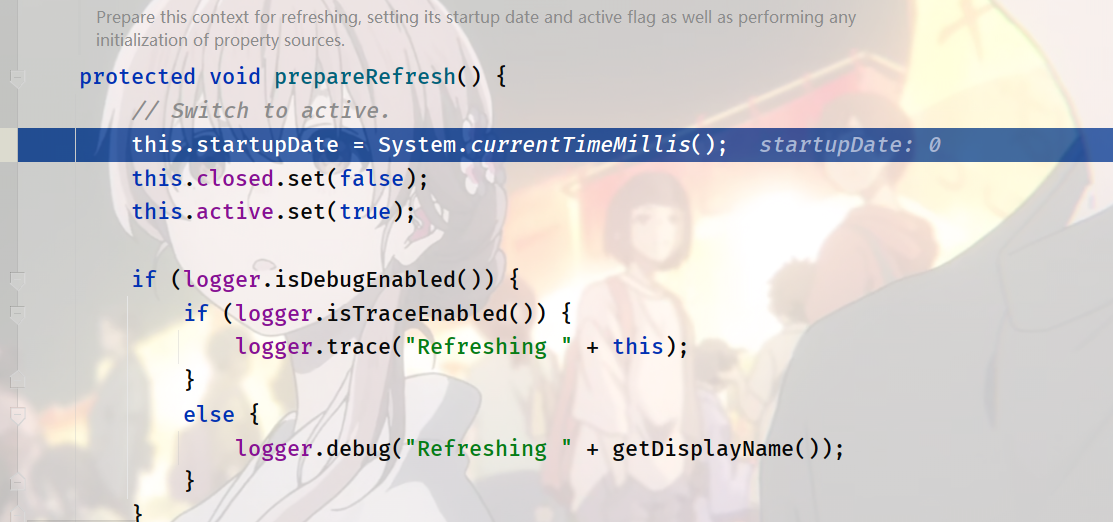
Part 1:
Set start time
Close flag
Active flag

Part 2:
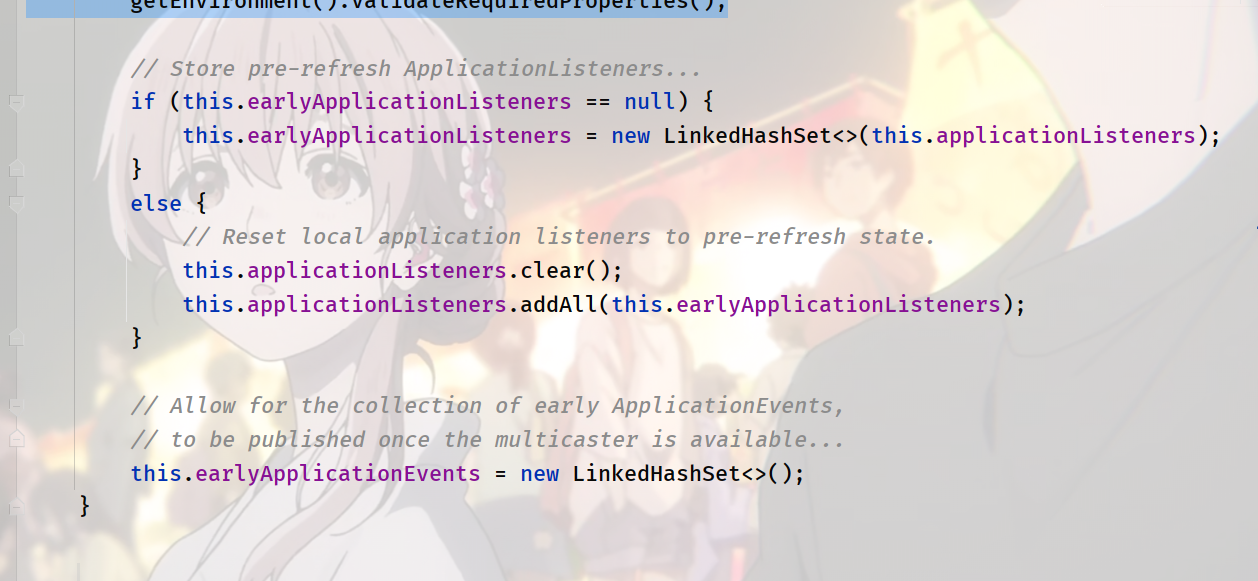
It is empty and left to subclasses to implement
Initialize some resources, such as placeholder property
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment. initPropertySources(); // Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable: // see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
Part 3:
Create a series of collections:
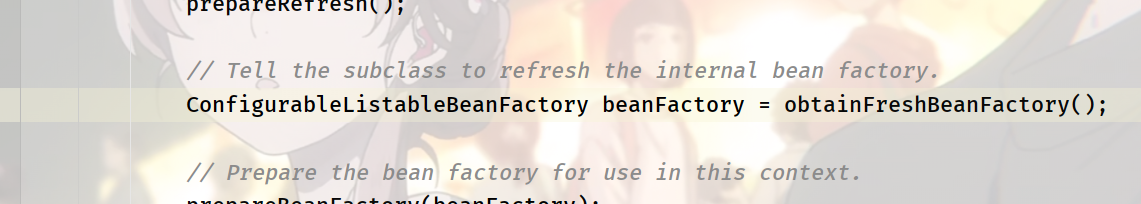
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory()
Overall operation:
Just to see if you have created a beanfactory and deleted it for you
Let's have a Freshbenfactory
The main code inside
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//This step is what I just said to see if it is a new factory. If not, I'll give you a new factory
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//This step is to new a factory. I don't have to say
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
//This step sets a serialization id for the factory (see the picture below)
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//Customize a beanfactory (figure below)
//Whether to allow overwriting of different defined objects with the same name and whether to allow circular dependencies between bean s.
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//The key step is to load the beandefinition information into the factory (see the figure)
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
Picture supplement
Serialization id:

customizeBeanFactory supplement:
To set two properties:
allowBeanDefinitionOverriding: Whether to allow overwriting of different defined objects with the same name. allowCircularReferences: Allow bean Cyclic dependency between.

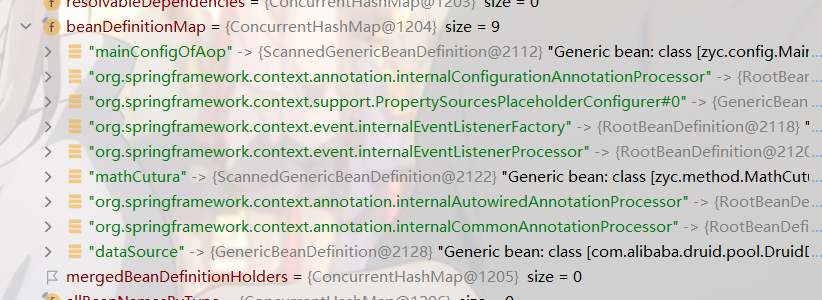
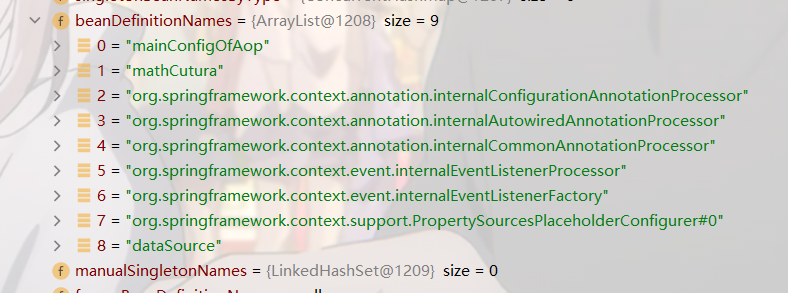
loadBeanDefinitions
Note this attribute:

After executing this method:
He passed in our beandefinition information and completed one step of our flowchart.
prepareBeanFactory
Meaning: set some properties for beanfactory:
To be added
postProcessBeanFactory
Meaning: it is the method of BeanFactorypostProcess interface class
It's empty. It's left for subclasses to supplement springboot. There are a lot of things in it
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
Meaning: materialize and call the registered beanfactoryprocessors
As shown in the flow chart, you can customize the information used to modify the beandification
registerBeanPostProcessors
Meaning: register BeanPostProcessors. Note that it is not the same class as the one above!
Instead of just registering, you can see the flow chart
initMessageSource
Meaning: Initialize message source for this context
Initialize information source
Explanation: it's the process of internationalization (switching languages on websites)
initApplicationEventMulticaster
Meaning: initialize event multicast for this context
Initialize event broadcaster
Explanation: it is convenient to publish listening events later
onRefresh
Meaning: Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses
Initialize other special beans according to the specific context subclass
Explanation: empty is left for subclass implementation
registerListeners
Meaning Check for listener beans and register them
Check the listener bean s and register them
Explanation: None
finishBeanFactoryInitialization
Key points: explain in a separate article Point me
Meaning: instance all remaining (non lazy init) singletons
Instantiate all remaining (non deferred initialization) singletons.
Explanation: previously, the beandefinition information was stored in the beanfactory map. This step is to create and inject.
This is the right part of the flowchart, the life cycle part of bena