8. SpringBoot: MVC auto configuration principle
12.1. Official website reading
Before writing the project, we also need to know what configuration SpringBoot has made for our spring MVC, including how to extend and customize.
Only by making these clear can we use them more easily in the future. Way 1: source code analysis, way 2: official documents!
Address: https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-spring-mvc-auto-configuration
Copy code 12345678910112131415161718192021222324252627282930331323343536373839 JAVASpring MVC Auto-configuration // Spring Boot provides automatic configuration for Spring MVC, which works well with most applications. Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications. // Auto configuration adds the following functions based on Spring default settings: The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring's defaults: // Include view parser Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans. // Support the path of static resource folder and webjars Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars // Automatically registered Converter: // Converter, which is what we automatically encapsulate the data submitted by the web page into objects in the background, such as automatically converting the "1" string to int type // Formatter: [formatter, for example, the page gives us a 2019-8-10, which will automatically format it as a Date object] Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans. // HttpMessageConverters // Spring MVC is used to convert Http requests and responses. For example, if we want to convert a User object into a JSON string, you can see the official website document explanation; Support for HttpMessageConverters (covered later in this document). // To define error code generation rules Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (covered later in this document). // Home page customization Static index.html support. // icons customizing Custom Favicon support (covered later in this document). // Initialize the data binder: help us bind the request data to the JavaBean! Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (covered later in this document). /* If you want to keep the Spring Boot MVC functionality and want to add other MVC configurations (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own The @ configuration class of is webmvcconfigurer, but @ EnableWebMvc is not added. If you want to provide RequestMappingHandlerMapping,RequestMappingHandlerAdapter Or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver Instance, you can declare a webmvcreationadapter instance to provide such components. */ If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components. // If you want to fully control Spring MVC, you can add your own @ Configuration and annotate it with @ EnableWebMvc. If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
Let's compare it carefully and see how it is implemented. It tells us that SpringBoot has automatically configured SpringMVC for us, and then what has been automatically configured?
12.2. Content negotiation view resolver
The ViewResolver is automatically configured, which is the view parser of spring MVC we learned earlier;
That is, the View object is obtained according to the return value of the method, and then the View object determines how to render (forward, redirect).
Let's take a look at the source code here: we find webmvca autoconfiguration and search for content negotiatingviewresolver. Find the following method!
Copy code 12345678910 JAVA@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(ViewResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "viewResolver", value = ContentNegotiatingViewResolver.class)
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver();
resolver.setContentNegotiationManager(beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class));
// Content negotiatingviewresolver uses all other view parsers to locate views, so it should have higher priority
resolver.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return resolver;
}
We can click into this class to see! Find the code of the corresponding parsing view;
Copy code 1234567891011213141516 JAVA@Nullable // Note: @ Nullable means that the parameter can be null
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
RequestAttributes attrs = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
Assert.state(attrs instanceof ServletRequestAttributes, "No current ServletRequestAttributes");
List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes = this.getMediaTypes(((ServletRequestAttributes)attrs).getRequest());
if (requestedMediaTypes != null) {
// Get candidate view objects
List<View> candidateViews = this.getCandidateViews(viewName, locale, requestedMediaTypes);
// Select the most appropriate view object, and then return this object
View bestView = this.getBestView(candidateViews, requestedMediaTypes, attrs);
if (bestView != null) {
return bestView;
}
}
// .....
}
Let's continue to click in and see how he gets the candidate view?
In getCandidateViews, you can see that it brings all view parsers, performs a while loop, and parses them one by one!
Copy code 1 JAVAIterator var5 = this.viewResolvers.iterator();
Therefore, it is concluded that the view parser content negotiation view resolver is used to combine all view parsers
Let's study his combinatorial logic and see that there is an attribute viewResolvers to see where it is assigned!
Copy code 12345678910 JAVAprotected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// Here it is the parser that gets all the views in the container from the beanFactory tool
// ViewRescolver.class combines all the view parsers
Collection<ViewResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(this.obtainApplicationContext(), ViewResolver.class).values();
ViewResolver viewResolver;
if (this.viewResolvers == null) {
this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList(matchingBeans.size());
}
// ...............
}
Since it is looking for a view parser in the container, can we guess that we can implement a view parser?
We can add a view parser to the container by ourselves; This class will help us automatically combine it; Let's do it
1. Let's try to write a view parser in our main program;
Copy code 123456789101112 JAVA@Bean //Put in bean
public ViewResolver myViewResolver(){
return new MyViewResolver();
}
//When we write a static inner class, the view parser needs to implement the ViewResolver interface
private static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String s, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
2. What do you think about whether the view parser we wrote ourselves works?
We add a breakpoint to the doDispatch method in the dispatcher servlet for debugging, because all requests will go to this method

3. We start our project, then visit a random page to see the Debug information;
Find this
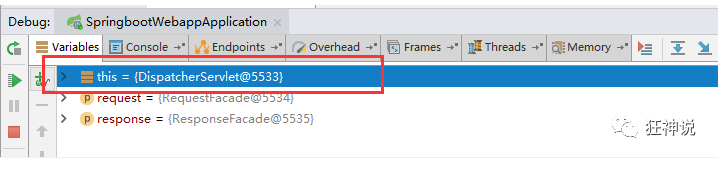
Find the view parser, and we see that our own definition is here;
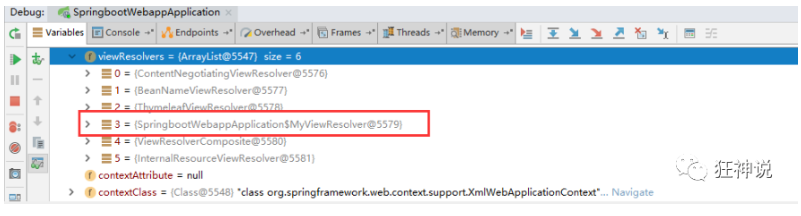
Therefore, if we want to use our own customized things, we just need to add this component to the container! SpringBoot will do the rest for us!
12.3 converter and formatter
Format converter found:
Copy code 123456789 JAVA@Bean
@Override
public FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() {
// Get the formatting rules in the configuration file
WebConversionService conversionService =
new WebConversionService(this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat());
addFormatters(conversionService);
return conversionService;
}
Click to:
Copy code 12345678 JAVApublic String getDateFormat() {
return this.dateFormat;
}
/**
* Date format to use. For instance, `dd/MM/yyyy`. default
*/
private String dateFormat;
You can see that in our Properties file, we can automatically configure it!
If you configure your own formatting method, it will be registered in the Bean and take effect. We can configure the date formatting rules in the configuration file:
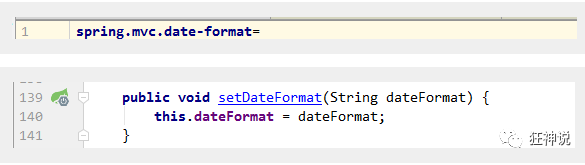
The rest will not give examples one by one. You can go on and study more!
12.4. Modify the default configuration of SpringBoot
The principle of so many automatic configurations is the same. Through the analysis of the automatic configuration principle of WebMVC, we should learn a learning method and draw a conclusion through source code exploration; This conclusion must belong to itself and be all-round.
The bottom layer of SpringBoot uses a lot of these design details, so you need to read the source code! come to conclusion;
When SpringBoot automatically configures many components, first check whether there are user configured components in the container (if the user configures @ bean s), if so, use user configured components, and if not, use automatically configured components;
If there are multiple components, such as our view parser, you can combine the user configured with your own default!
The official documents for extension using spring MVC are as follows:
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
All we need to do is write a @ Configuration annotation class, and the type should be WebMvcConfigurer, and the @ EnableWebMvc annotation cannot be marked; Let's write one by ourselves; We create a new package called config and write a class MyMvcConfig;
Copy code 1234567891011 JAVA//The expected type requires WebMvcConfigurer, so we implement its interface
//You can use custom classes to extend the functionality of MVC
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// When the browser sends / test, it will jump to the test page;
registry.addViewController("/test").setViewName("test");
}
}
Let's visit the browser:
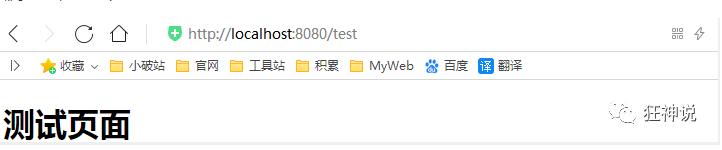
It did jump over! Therefore, we want to extend spring MVC. The official recommends that we use it in this way, so that we can not only keep all the automatic configurations of spring boot, but also use our extended configurations!
We can analyze the principle:
1. Webmvcoautoconfiguration is the automatic configuration class of spring MVC, which has a class webmvcoautoconfigurationadapter
2. There is an annotation on this class, which will be imported during other automatic configuration: @ Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
3. Let's click EnableWebMvcConfiguration to see that it inherits a parent class: delegatingwebmvccconfiguration
There is such a piece of code in this parent class:
Copy code 1234567891011 JAVApublic class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
// Get all webmvcconfigurers from the container
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
}
4. We can find a viewController we just set in this class as a reference and find that it calls a
Copy code 123 JAVAprotected void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addViewControllers(registry);
}
5. Let's go in and have a look
Copy code 12345678910 JAVApublic void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
Iterator var2 = this.delegates.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
// Call all WebMvcConfigurer related configurations together! Including those configured by ourselves and those configured by Spring
WebMvcConfigurer delegate = (WebMvcConfigurer)var2.next();
delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
}
}
Therefore, it is concluded that all WebMvcConfiguration will be used, not only Spring's own configuration class, but also our own configuration class will be called;
12.5 take over spring MVC
Official documents:
Copy code 12 JAVAIf you want to take complete control of Spring MVC you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
Full takeover: spring boot does not need to automatically configure spring MVC. We configure everything ourselves!
Just add a @ EnableWebMvc in our configuration class.
Let's take a look. If we take over spring MVC, the static resource mapping configured by SpringBoot will be invalid. We can test it;
Go to the home page without comments:
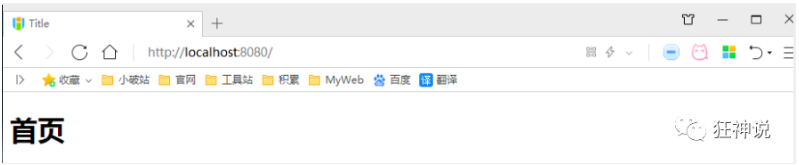
Annotate the configuration class: @ EnableWebMvc
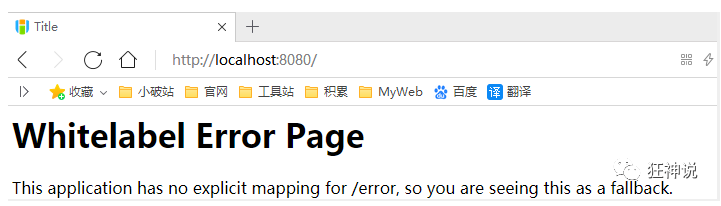
We found that all spring MVC auto configuration failed! Return to the original appearance;
Of course, it is not recommended to use spring MVC in our development
Thinking? Why is the automatic configuration invalid when an annotation is added! Let's look at the source code:
1. It is found that it imports a class. We can continue to look at it
Copy code 1
JAVA@Import({DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class})public @interface EnableWebMvc {}
2. It inherits a parent class WebMvcConfigurationSupport
Copy code 1
JAVApublic class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport { // ......}
3. Let's review the Webmvc autoconfiguration class
Copy code 1234567891011 JAVA@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
// This annotation means that the autoconfiguration class takes effect only when there is no component in the container
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
}
To sum up: @ EnableWebMvc has imported the WebMvcConfigurationSupport component;
The imported WebMvcConfigurationSupport is only the most basic function of spring MVC!