Introductory Grammar
Table for example:
+----+--------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+ | id | name | url | alexa | country | +----+--------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+ | 1 | Google | https://www.google.cm/ | 1 | USA | | 2 | TaoBao | https://www.taobao.com/ | 13 | CN | | 3 | Tutorial rookie | http://www.runoob.com/ | 4689 | CN | | 4 | micro-blog | http://weibo.com/ | 20 | CN | | 5 | Facebook | https://www.facebook.com/ | 3 | USA | +----+--------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+
SELECT
-
Select all records from websites:
SELECT * FROM websites;
-
Select the name and country columns from websites:
SELECT name,country FROM websides;
SELECT DISTINCT
- Only select the only different value from the "country" column of the "Websites" table, that is, remove the duplicate value of the "country" column (de duplication):
SELECT DISTINCT country FROM websites;

WHERE
-
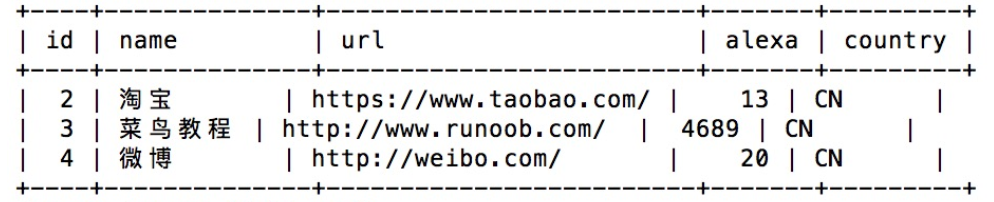
The following SQL statement selects all Websites whose country is "CN" from the "Websites" table:
SELECT * FROM websites WHERE country = 'CN'
-
Special operators in where:
- BETWEEN is within a certain range
Select * from emp where sal between 1500 and 3000;
- LIKE search for a pattern
Select * from emp where ename like 'M%';
- IN specifies multiple possible values for a column
Select * from emp where sal in (5000,3000,1500);
- AND and conditions
SELECT * FROM Websites WHERE country='CN' AND alexa > 50;
- OR or condition
SELECT * FROM Websites WHERE country='USA' OR country='CN';
ORDER BY
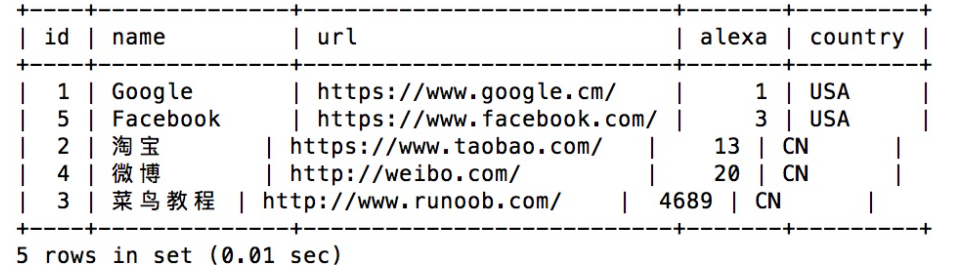
- Output the specified data in the order after arrangement (default ascending order)
SELECT * FROM Websites ORDER BY alexa;
- Descending order
SELECT * FROM Websites ORDER BY alexa DESC;
- Multiple columns (first by first name, then by second)
SELECT * FROM Websites ORDER BY country,alexa;
INSERT INTO
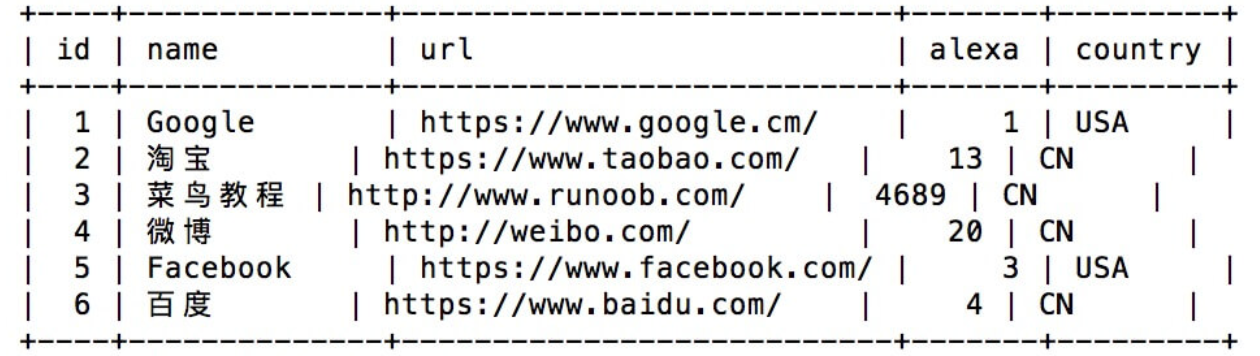
- Insert operation (insert a set of data)
INSERT INTO Websites (name, url, alexa, country) VALUES ('Baidu','https://www.baidu.com/','4','CN');
UPDATE
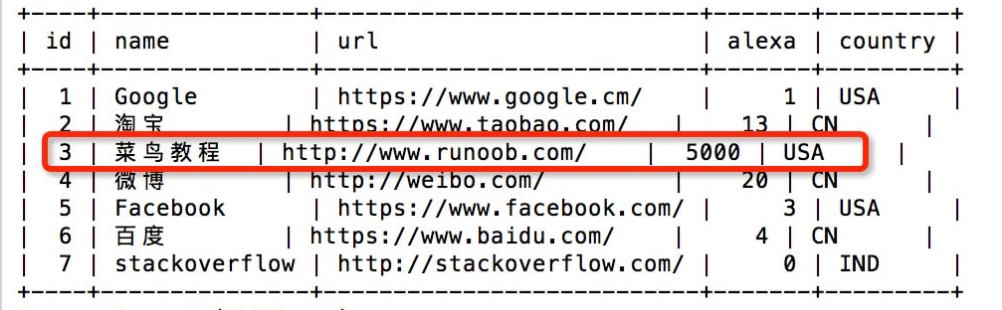
- Be sure to add where
UPDATE Websites SET alexa='5000', country='USA' WHERE name='Tutorial rookie';
DELETE
- Delete rows in table
DELETE FROM Websites WHERE name='Facebook' AND country='USA';

- Delete all tables
DELETE FROM table_name; //or DELETE * FROM table_name;
Advanced Grammar
Table used for demonstration:
mysql> SELECT * FROM Websites; +----+---------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+ | id | name | url | alexa | country | +----+---------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+ | 1 | Google | https://www.google.cm/ | 1 | USA | | 2 | TaoBao | https://www.taobao.com/ | 13 | CN | | 3 | Tutorial rookie | http://www.runoob.com/ | 5000 | USA | | 4 | micro-blog | http://weibo.com/ | 20 | CN | | 5 | Facebook | https://www.facebook.com/ | 3 | USA | | 7 | stackoverflow | http://stackoverflow.com/ | 0 | IND | +----+---------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+
mysql> SELECT * FROM access_log; +-----+---------+-------+------------+ | aid | site_id | count | date | +-----+---------+-------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | 45 | 2016-05-10 | | 2 | 3 | 100 | 2016-05-13 | | 3 | 1 | 230 | 2016-05-14 | | 4 | 2 | 10 | 2016-05-14 | | 5 | 5 | 205 | 2016-05-14 | | 6 | 4 | 13 | 2016-05-15 | | 7 | 3 | 220 | 2016-05-15 | | 8 | 5 | 545 | 2016-05-16 | | 9 | 3 | 201 | 2016-05-17 | +-----+---------+-------+------------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
SELECT TOP,LIMIT,ROWNUM
Select the first two records from the "Websites" table:
SELECT * FROM Websites LIMIT 2;
Select the first 50% of the records from the websites table:
SELECT TOP 50 PERCENT * FROM Websites;
SQL alias
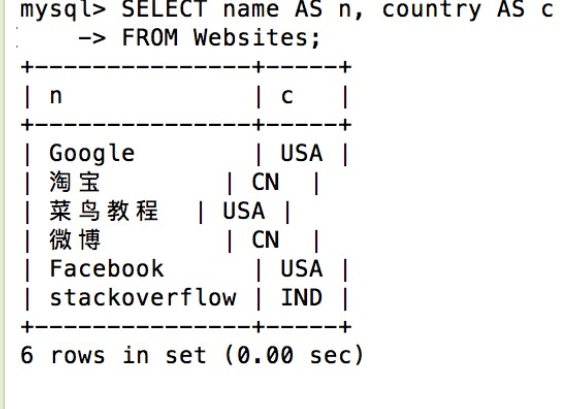
- The following SQL statement specifies two aliases, one is the alias of the name column and the other is the alias of the country column:
SELECT name AS n, country AS c FROM Websites
SQL connection (JOIN) -- import
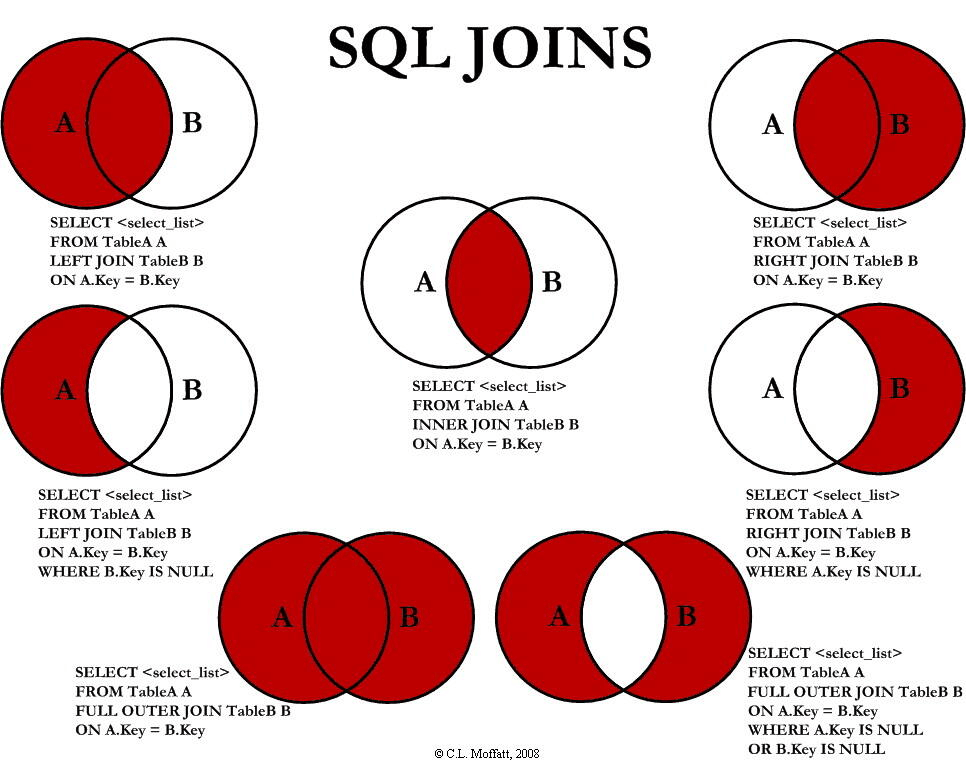
The SQL JOIN clause is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on the common fields between these tables.
INNER JOIN
INNER JOIN keywordreturns a row when there is at least one match in the table (returns all overlaps)
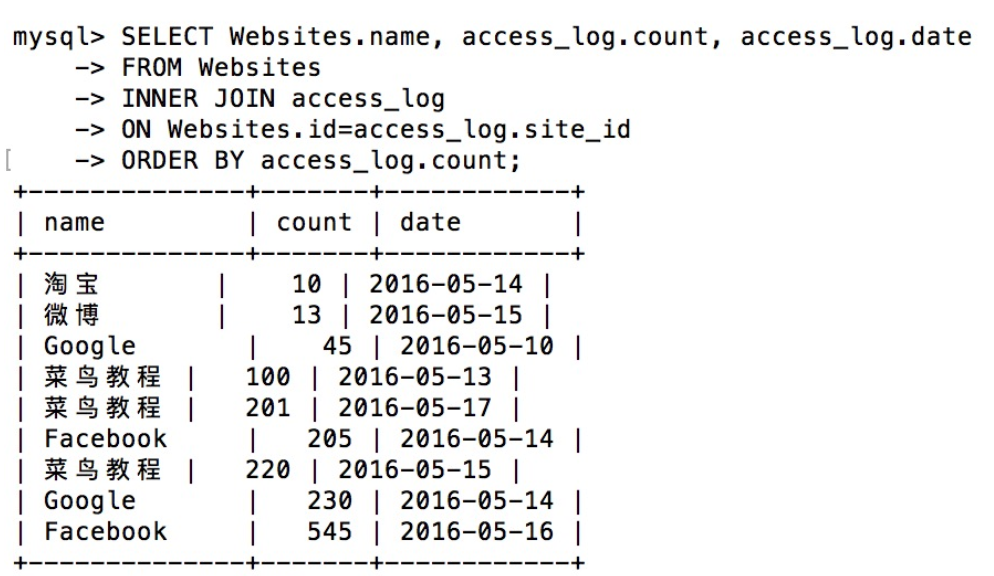
- Return access records of all websites
SELECT Websites.name, access_log.count, access_log.date FROM Websites INNER JOIN access_log ON websites.id = access_log.site_id order by access_log.count
Operation results:
LEFT JOIN
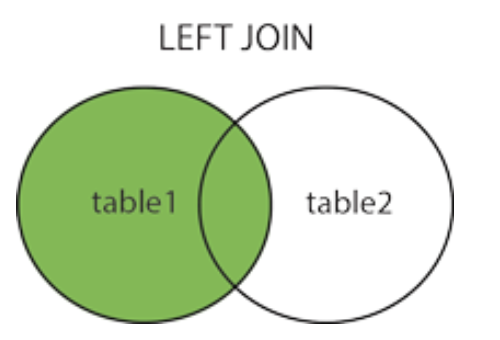
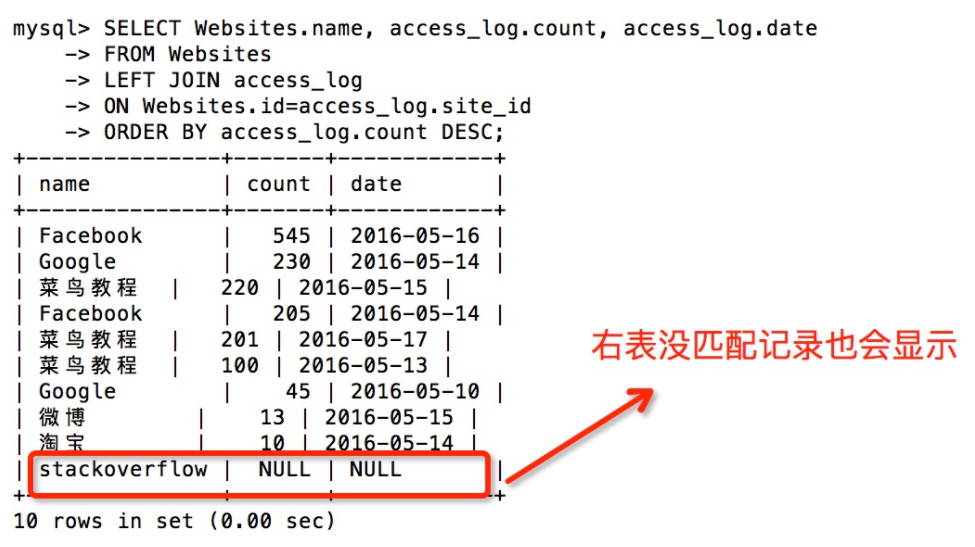
- Take Websites as the left table, access_log as the right table
SELECT Websites.name, access_log.count, access_log.date FROM Websites LEFT JOIN access_log ON Websites.id=access_log.site_id ORDER BY access_log.count DESC;
RIGHT JOIN
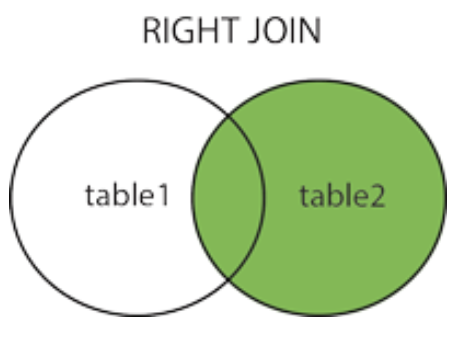
- In contrast to LEFT JOIN, if there is no match on the left, the value of the attribute related to the left table is empty
FULL JOIN
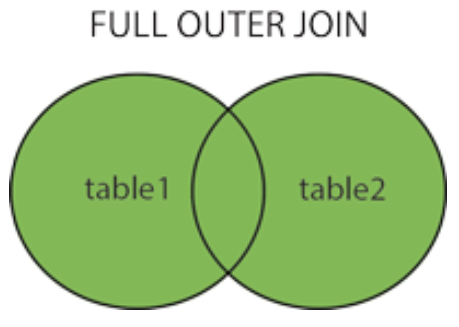
- FULL JOIN combines the common results of LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN
UNION operator
The UNION operator is used to combine the result sets of two or more SELECT statements.
Each SELECT statement within a UNION must have the same number of columns. Columns must also have similar data types. At the same time, the order of columns in each SELECT statement must be the same.
Demo database:
mysql> SELECT * FROM Websites; +----+--------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+ | id | name | url | alexa | country | +----+--------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+ | 1 | Google | https://www.google.cm/ | 1 | USA | | 2 | TaoBao | https://www.taobao.com/ | 13 | CN | | 3 | Tutorial rookie | http://www.runoob.com/ | 4689 | CN | | 4 | micro-blog | http://weibo.com/ | 20 | CN | | 5 | Facebook | https://www.facebook.com/ | 3 | USA | | 7 | stackoverflow | http://stackoverflow.com/ | 0 | IND | +----+---------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+
mysql> SELECT * FROM apps; +----+------------+-------------------------+---------+ | id | app_name | url | country | +----+------------+-------------------------+---------+ | 1 | QQ APP | http://im.qq.com/ | CN | | 2 | micro-blog APP | http://weibo.com/ | CN | | 3 | TaoBao APP | https://www.taobao.com/ | CN | +----+------------+-------------------------+---------+
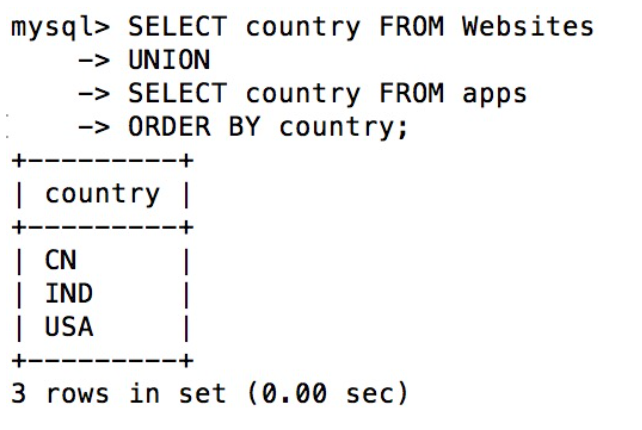
UNION
SELECT country FROM Websites UNION SELECT country FROM apps ORDER BY country;
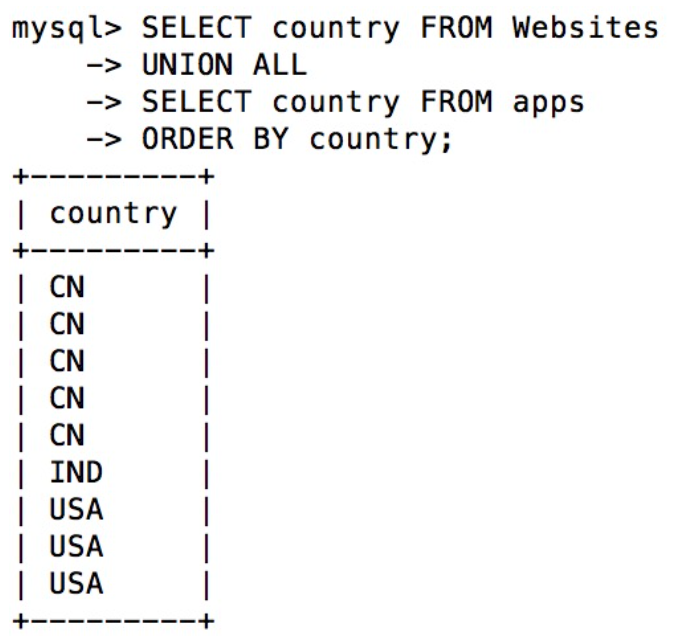
UNION ALL
Like UNION, it just doesn't need to be repeated
SELECT country FROM Websites UNION ALL SELECT country FROM apps ORDER BY country;
SQL UNION ALL with WHERE
SELECT country, name FROM Websites WHERE country='CN' UNION ALL SELECT country, app_name FROM apps WHERE country='CN' ORDER BY country;

SELECT INTO
The SELECT INTO statement copies data from one table and then inserts the data into another new table.
example:
- Create a backup copy of Websites:
SELECT * INTO WebsiteBackup2016 FROM Websites;
- Only copy some columns and insert them into the new table:
SELECT name, url INTO WebsitesBackup2016 FROM Websites;
- Only copy Chinese websites and insert them into the new table:
SELECT * INTO WebsitesBackup2016 FROM Websites WHERE country ='CN'
- Copy the data of multiple tables and insert it into the new table
SELECT Websites.name, access_log.count, access_log.date INTO WebsitesBackup2016 FROM Websites LEFT JOIN access_log ON Websites.id=access_log.site_id;
- The SELECT INTO statement can be used to create a new empty table through another mode. You only need to add a WHERE clause that causes the query to return no data:
SELECT * INTO newtable FROM table1 WHERE 1=0;
INERT INTO SELECT
(use the two tables at the beginning of this chapter)
The INSERT INTO SELECT statement copies data from a table and then inserts the data into an existing table. Any existing rows in the target table will not be affected.
- Copy the data in "apps" and insert it into "Websites":
INSERT INTO Websites(name,country) SELECT app_name,country FROM apps;
- Only reply QQ APP to "Websites":
INSERT INTO Websites(name, country) SELECT app_name, country FROM apps WHERE id=1;
CREATE DATABASE
CREATE DATABASE is used to create a database
CREATE DATABASE my_db // Create a file named my_bd database
CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE table_name//Table name ( column_name1 data_type(size),//Column name | data type column_name2 data_type(size), column_name3 data_type(size), .... );
for example
CREATE TABLE Persons ( PersonID int, LastName varchar(255), FirstName varchar(255), Address varchar(255), City varchar(255) );
- When creating a database, you can add SQL Constraints after each column to be created to constrain data rules:
CREATE TABLE table_name ( column_name1 data_type(size) [constraint_name], column_name2 data_type(size) [constraint_name], column_name3 data_type(size) [constraint_name], .... );
Here, [constraint_name] has:
NOT NULL
A column cannot store NULL values. NULL values are not accepted
For example:
ALTER TABLE persons MODIFY Age int NOT NULL;//Add a NOT NULL constraint to a built table ALTER TABLE Persons MODIFY Age int NULL;//Delete the NOT NULL constraint in a built table
ALTER TABLE persons
UNIQUE
A column must have a unique value??????????
PRIMARY KEY
Combination of NOT NULL and UNIQUE. Ensuring that a column (or a combination of two or more columns) has a UNIQUE identification helps to find a specific record in the table more easily and quickly.
FOREIGN KEY
Ensure the referential integrity of the data in one table matching the values in another table.
CHECK
Ensure that the values in the column meet the specified conditions.
DEFAULT
Specifies the default value when no value is assigned to the column.