Standard library os package learning in GoLang
1.io.EOF error
io.EOF is triggered when there is no readable content. For example, if a file Reader object is empty, or the file pointer points to the end after reading several times, calling Read will trigger EOF
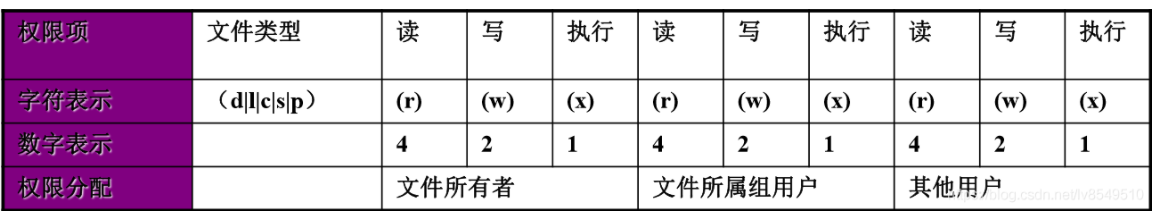
2.perm parameter permission


3.os. O_ Constants such as rdonly
const (
O_RDONLY int = syscall.O_RDONLY // Open file in read-only mode
O_WRONLY int = syscall.O_WRONLY // Open file in write only mode
O_RDWR int = syscall.O_RDWR // Open file in read-write mode
O_APPEND int = syscall.O_APPEND // Append data to the end of the file when writing
O_CREATE int = syscall.O_CREAT // If it does not exist, a new file will be created
O_EXCL int = syscall.O_EXCL // And o_ For use with create, the file must not exist
O_SYNC int = syscall.O_SYNC // Open file for synchronizing I/O
O_TRUNC int = syscall.O_TRUNC // If possible, empty the file when opening
)
4.os.File structure
type File struct {
*file // os specific
}
//Note: file is still in the os package, but it is not used because it is lowercase
type file struct {
pfd poll.FD
name string
dirinfo *dirInfo // nil unless directory being read
appendMode bool // whether file is opened for appending
}
5.os.File{}.Close() method
After operating on the file, be sure to close the file. Close closes the file f so that the file cannot be used for reading and writing. It returns possible errors
func (f *File) Close() error {
if f == nil {
return ErrInvalid
}
return f.file.close()
}
6.os.File{}.Write() method
Write byte type information to the file;
Write writes len(b) byte data to the file;
It returns the number of bytes written and any errors that may be encountered. If the return value is n= Len (b), this method will return a non nil error
func (f *File) Write(b []byte) (n int, err error) {}
7.os.File{}.WriteString() method
Write string information to the file. WriteString is similar to write, but accepts a string parameter
func (f *File) WriteString(s string) (n int, err error) {}
8.os.File{}.WriteAt() method
WriteAt writes len(b) byte data at the specified position (relative to the file start position);
It returns the number of bytes written and any errors that may be encountered;
If the return value is n= Len (b), this method will return a non nil error.
func (f *File) WriteAt(b []byte, off int64) (n int, err error){}
9.os.File{}.Read() method
The Read method reads up to len(b) bytes of data from f and writes it to B;
It returns the number of bytes read and any errors that may be encountered;
The file termination flag reads 0 bytes and the return value err is Io EOF
func (f *File) Read(b []byte) (n int, err error) {}
10.os.File{}.ReadAt() method
ReadAt reads len(b) byte data from the specified position (relative to the file start position) and writes it to B;
It returns the number of bytes read and any errors that may be encountered;
When n < len (b), this method will always return an error;
If it is because the end of the file is reached, the return value err will be io EOF.
func (f *File) ReadAt(b []byte, off int64) (n int, err error) {}
11.os.Open function read only file
The Open function is used to Open a file knowledge in order to read a scene that does not need to be written;
Open opens a file for reading. If the operation is successful, the method of the returned file object can be used to read data; The corresponding file descriptor has O_RDONLY mode. If an error occurs, the underlying type of the error is * PathError
11.1 open files only
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
/*func Open(name string) (*File, error) {
return OpenFile(name, O_RDONLY, 0)
}*/
// Open main in the current directory in read-only mode Go file
file, err := os.Open("./main.go")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("open file failed!, err:", err)
return
}
// Close file
file.Close()
//Note: after running this code, the system will not have any output
}
11.2 opening and reading files
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
)
func main() {
// Open file
file, err := os.Open("./xxx.txt")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("open file err :", err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
// Defines the byte array read by the receive file
var buf [128]byte
var content []byte
for {
//Note: the original content in the slice will be cleared and rewritten every time
//The Read method reads up to len(b) bytes of data from the file and writes it to buf;
n, err := file.Read(buf[:]) //[:] represents the original slice, that is, convert the [128]byte array into a slice with a length of 128
if err == io.EOF {
// End of reading
break
}
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("read file err ", err)
return
}
content = append(content, buf[:n]...)
}
fmt.Println(string(content))
}
12.os.OpenFile function
Open the file named name. flag is the opening method, such as read-only, read-write, etc. perm is the permission
func OpenFile(name string, flag int, perm FileMode) (*File, error) {}
13.os. The create function creates a file
13.1 create and write without files
Create a new file according to the provided file name and return a file object. The default permission is 0666
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
/*func Create(name string) (*File, error) {
return OpenFile(name, O_RDWR|O_CREATE|O_TRUNC, 0666)
}
*/
// You don't need to create it manually. The system will build it by itself
file, err := os.Create("./xxx.txt")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
file.WriteString("ab\n")
file.Write([]byte("cd\n"))
}
}
13.2 create and write files:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
// We built a XXX in advance Txt file and write the content in it; After running the code, the system will clear out the contents of the file before writing
file, err := os.Create("./xxx.txt")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
file.WriteString("ab\n")
file.Write([]byte("cd\n"))
}
}
13.3 copying documents
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
)
func main() {
// open the source file
srcFile, err := os.Open("./xxx.txt")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// create a new file
dstFile, err2 := os.Create("./abc2.txt")
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Println(err2)
return
}
// Buffer read
buf := make([]byte, 1024)
for {
// Read data from source file
n, err := srcFile.Read(buf)
if err == io.EOF {
fmt.Println("Read complete")
break
}
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
break
}
//Write it out
dstFile.Write(buf[:n])
}
srcFile.Close()
dstFile.Close()
}
14.os. The hostname function gets the hostname
func Hostname() (name string, err error) {
return hostname()
}
15.os.Getwd function gets the current directory
func Getwd() (dir string, err error) {}
16. os.Getpid function gets the current process ID
func Getpid() int { return syscall.Getpid() }
17. os.Getppid function gets the current process ID
func Getppid() int { return syscall.Getppid() }
18.os. The exit function exits the current process
func Exit(code int) {}
19.os.Mkdir function creates a directory, but cannot create multiple levels
func Mkdir(name string, perm FileMode) error {}
20.os. The mkdirall function creates a multi-level directory
func MkdirAll(path string, perm FileMode) error {}
21.os. The remove function can only delete an empty directory or a file
func Remove(name string) error {}
22.os. The removeAll function can force the deletion of directories and files in the directory collection
func RemoveAll(path string) error {
return removeAll(path)
}
23.os.Rename function renames a file
func Rename(oldpath, newpath string) error {
return rename(oldpath, newpath)
}
24.os.Chmod function modifies file permissions
func Chmod(name string, mode FileMode) error { return chmod(name, mode) }
25.os. The chown function modifies the file owner
func Chown(name string, uid, gid int) error {
26.os.Getenv function gets the value of the environment variable
func Getenv(key string) string {}
27.os.Setenv function sets the environment variable
func Setenv(key, value string) error {}