summary:
- The algorithm is mainly composed of header files < algorithm > < functional > < numeric >.
- < algorithm > is the largest of all STL header files, covering comparison, exchange, search, traversal, copy, modification, etc
- < numeric > is very small and only includes a few template functions that perform simple mathematical operations on the sequence
- < functional > defines some template classes to declare function objects.
1 common traversal algorithms
Algorithm Introduction:
- for_ each / / traverse the container
- transform / / move the container to another container
1.1 for_each
Function Description:
- Implement traversal container
Function prototype:
- for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func);
//The traversal algorithm traverses the container elements
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
// _ func function or function object
//Ordinary function
void print01(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
//functor
class print02
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
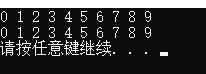
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);
cout << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}
1.2 transform
Function Description:
- Transport container to another container
Function prototype:
- transform( iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2,_func);
//beg1 source container start iterator
//end1 source container end iterator
//beg2 target container start iterator
//_ func function or function object
class Transform
{
public:
int operator()(int v)
{
return v + 100;
}
};
class MyPrint
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
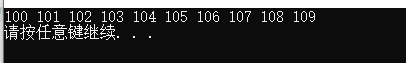
vector<int>vTarget; //Target container
vTarget.resize(v.size()); //The target container needs to open up space in advance
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());
cout << endl;
}
2. Common search algorithms
Algorithm Introduction:
- Find / / find elements
- find_ if / / find elements by criteria
- adjacent_find / / find adjacent duplicate elements
- binary_search / / binary search
- Count / / count the number of elements
- count_ if / / count the number of elements by condition
2.1 find
- Find the specified element, find the iterator that returns the specified element, and cannot find the return end iterator end()
Function prototype:
- find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
//Find the element by value, find the iterator that returns the specified position, and the iterator that returns the end position cannot be found
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
//value lookup element
Find built-in data types
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
//Find out if there is 5 this element in the container
vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "Can't find!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Found: " << *it << endl;
}
}
Find custom data types
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
//Overload = = let the underlying find know how to compare the person data type
bool operator==( const Person & p)
{
if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
//Find custom data types
void test02()
{
vector<Person>v;
//Create data
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
//Put into container
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
Person pp("bbb", 20);// Find out if there is the same as pp in the container
vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "Can't find" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Element name found:" << it->m_Name << " Age: " << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
2.2 find_if
- Find elements by criteria
Function prototype:
- find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
//Find the element by value, find the iterator that returns the specified position, and the iterator that returns the end position cannot be found
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
// _ pred function or predicate (an imitation function that returns bool type)
Find built-in data types
class GreaterFive
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "Can't find" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "The number found greater than 5 is: " << *it << endl;
}
}
Find custom data types
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class Greater20
{
public:
bool operator()(Person &p)
{
return p.m_Age > 20;
}
};
void test02()
{
vector<Person>v;
//Create data
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
//Find someone older than 20
vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "Can't find" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Name found: " << it->m_Name << " Age: " << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
2.3 adjacent_find
- Find adjacent duplicate elements
Function prototype:
- adjacent_ find(iterator beg, iterator end);
//Find adjacent repeating elements and return the iterator at the first position of adjacent elements
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(0);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(0);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(3);
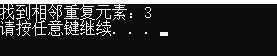
vector<int>::iterator pos = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());
if (pos == v.end())
{
cout << "No adjacent duplicate elements found" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Adjacent duplicate elements found:" << *pos << endl;
}
}
2.4 binary_search
- Finds whether the specified element exists
Function prototype:
- bool binary_ search(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
//Find the specified element and return true, otherwise false
//Note: not available in unordered sequences
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
//value lookup element
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
//v.push_back(2); If it is an unordered sequence, the result is unknown!
//Find if there are 9 elements in the container
//Note: containers must be ordered sequences
bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);
if (ret)
{
cout << "Element found" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "not found" << endl;
}
}

2.5 count
- Number of statistical elements
Function prototype:
- count(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
//Count the number of occurrences of the element
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
//Element of value statistics
Statistics built-in data type
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(40);
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 40);
cout << "40 The number of elements is: " << num << endl;
}
Statistics custom data type
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person & p)
{
if (this->m_Age == p.m_Age)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test02()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("Liu Bei", 35);
Person p2("Guan Yu", 35);
Person p3("Fei Zhang", 35);
Person p4("Zhao Yun", 30);
Person p5("Cao Cao", 40);
//Insert the person into the container
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
Person p("Zhuge Liang", 35);
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p);
cout << "The number of people of the same age as Zhuge Liang is:" << num << endl;
}
2.6 count_if
- Count the number of elements by condition
Function prototype:
- count_if(iterator beg,iterator end,_pred);
//Count the occurrence times of elements by conditions
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
// _ pred predicate
//Statistics built-in data type
class Greater20
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 20;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());
cout << "The number of elements greater than 20 is: " << num << endl;
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class AgeGreater20
{
public:
bool operator()(const Person & p)
{
return p.m_Age > 20;
}
};
//Statistics custom data type
void test02()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("Liu Bei", 35);
Person p2("Guan Yu", 35);
Person p3("Fei Zhang", 35);
Person p4("Zhao Yun", 40);
Person p5("Cao Cao", 20);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
//Count the number of persons over 20 years old
int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), AgeGreater20());
cout << "The number of persons over 20 years old is:" << num << endl;
}
3. Common sorting algorithms
Algorithm Introduction:
- Sort / / sort the elements in the container
- random_ shuffle / / shuffle the elements within the specified range to randomly adjust the order
- Merge / / merge container elements and store them in another container
- reverse / / reverses the elements of the specified range
3.1 sort
- Sort the elements in the container
Function prototype:
- sort(iterator beg, iterator end,_Pred);
//Find the element by value, find the iterator that returns the specified position, and the iterator that returns the end position cannot be found
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
//. _ Pred predicate
//Ascending by sort sort(v.begin(), v.end()); for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint); cout << endl; //Change to descending order sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>()); for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint); cout << endl;
3.2 random_shuffie
- Shuffle, randomly adjust the order of elements in the specified range
Function prototype:
- random_ shuffle(iterator beg, iterator end);
//Randomly adjust the order of elements within the specified range
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
void myPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));// Add random number seed
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
//Shuffle the order using shuffle algorithm
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);
cout << endl;
}
3.3 merge
- The two container elements are merged and stored in another - container
Function prototype:
- merge(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
//Container elements are merged and stored in another container
//Note: the two containers must be ordered
//beg1 container 1 start iterator
//end1 container 1 end iterator
//beg2 container 2 start iterator
//end2 container 2 end iterator
//dest destination container start iterator
//Common sorting algorithm merge
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+1);
}
//Target container
vector<int>vTarget;
//Allocate space to the target container in advance
vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), myPrint);
cout << endl;
}
3.4 reverse
- Invert the elements in the container
Function prototype:
- reverse(iterator beg,iterator end);
//Inverts the elements of the specified range
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
4. Common copy and replacement algorithms
Algorithm Introduction:
- Copy / / copy the elements of the specified range in the container to another container
- replace / / modify the old element of the specified range in the container to a new element
- replace_if / / replace the qualified elements in the specified range in the container with new elements
- Swap / / swap elements of two containers
4.1 copy
- Copies the specified range of elements in a container to another container
Function prototype:
- copy(iterator beg, iterator end, iterator dest);
//Find the element by value, find the iterator that returns the specified position, and the iterator that returns the end position cannot be found
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
//dest target start iterator
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>v2;
v2.resize(v1.size());
copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);
cout << endl;
}
4.2 replace
- Modifies the old element of the specified range in the container to a new element
Function prototype:
- replace(iterator beg, iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);
//Replace the old element in the interval with a new element
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
//oldvalue old element
//newvalue new element
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
cout << "Before replacement:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint());
cout << endl;
//Replace 20 with 2000
replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20, 2000);
cout << "After replacement:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myprint);
cout << endl;
}
4.3 replace_if
- Replace the qualified elements in the interval with the specified elements
Function prototype:
- replace_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _ pred, newvalue);
//Replace the element according to the condition, and replace the qualified element with the specified element
//beg start iterator
//End end iterator
// _ pred predicate
//New element replaced by newvalue
class MyPrint
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
};
class Greater30
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val >= 30;
}
};
//Common copy and replace algorithms replace_if
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
cout << "Before replacement: " << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint());
cout << endl;
//Replace 30 or more with 3000
replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater30(),3000);
cout << "After replacement: " << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint());
cout << endl;
}
4.4 swap
- Swap elements of two containers
Function prototype:
- swap(container C1,container c2);
//Swap elements of two containers
//c1 container 1
//c2 container 2
5 common arithmetic generation algorithms
- The arithmetic generation algorithm belongs to a small algorithm. When used, the header file included is #include < numeric >
Algorithm Introduction:
- Calculate / / calculate the cumulative sum of container elements
- fill / / add element to container
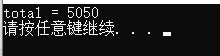
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
//Parameter 3 initial cumulative value
int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);
cout << "total = " << total << endl;
}
void myPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.resize(10);
//Post refill
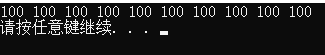
fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);
cout << endl;
}
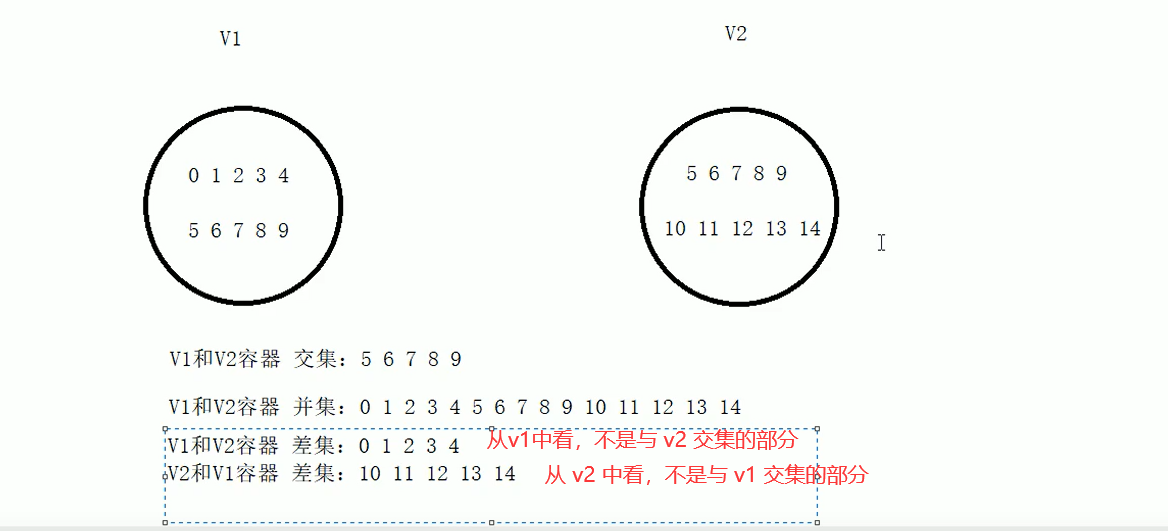
6 common set algorithms
Algorithm Introduction:
- set_ intersection / / find the intersection of two containers
- set_ union / / find the union of two containers
- set_ difference / / find the difference set of two containers
6.1 set_ intersection
- set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2,iterator dest);
//Find the intersection of two sets
//Note: the two sets must be an ordered sequence
//beg1 container 1 start iterator
//end1 container 1 end iterator
//beg2 container 2 start iterator
//end2 container 2 end iterator
//dest destination container start iterator
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i); // 0 ~ 9
v2.push_back(i + 5); // 5 ~ 14
}
vector<int>vTarget;
//The target container needs to open up space in advance
//In the most special case, a large container contains a small container. Open up space and take the size of the small container
vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));
//Get intersection
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(),
v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint);// End with the position of the iterator returned.
cout << endl;
}
6.2 set_union
- set_union(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
//Find the union of two sets
//Note: the two sets must be an ordered sequence
//beg1 container 1 start iterator
//end1 container 1 end iterator
//beg2 container 2 start iterator
//end2 container 2 end iterator
//dest destination container start iterator
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
vector<int>vTarget;
//The target container opens up space in advance
//In the most special case, two containers do not intersect. Union is the addition of two containers
vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(),
v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint);
cout << endl;
}
6.3 set_difference
- set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2,iterator dest);
//Find the difference set of two sets
//Note: the two sets must be an ordered sequence
//beg1 container 1 start iterator
//end1 container 1 end iterator
//beg2 container 2 start iterator
//end2 container 2 end iterator
//dest destination container start iterator
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+5);
}
//Create target container
vector<int>vTarget;
//Make room for the target container
//In the most special case, the two containers do not intersect, and the larger size of the two containers is taken as the target container to open up space
vTarget.resize( max(v1.size(),v2.size()) );
cout << "v1 and v2 The difference set of is:" << endl;
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(),
v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint);
cout << endl;
cout << "v2 and v1 The difference set of is:" << endl;
itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint);
cout << endl;
}