- Overindexing
- Insufficient index
- Index fragmentation rate
This paper also introduces some practical daily maintenance methods and tools from these three perspectives.
Overindexing
Over-indexing means that there are many non-aggregated indexes on each table, and some non-aggregated indexes are seldom used. Too many indexes will lead to the decrease of efficiency of data addition and deletion, the increase of database volume, and the increase of maintenance cost of index and statistical information. It is suggested that similar indexes should be checked regularly. It is better to have no more than 10 indexes on each table.Through the following two DMV s, the index utilization is checked periodically to determine whether the index is needed or not. The function sys.dm_db_index_operation_stats gives the operation of insert, update and delete on an index. The view sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats gives an overview of all methods of accessing the index.
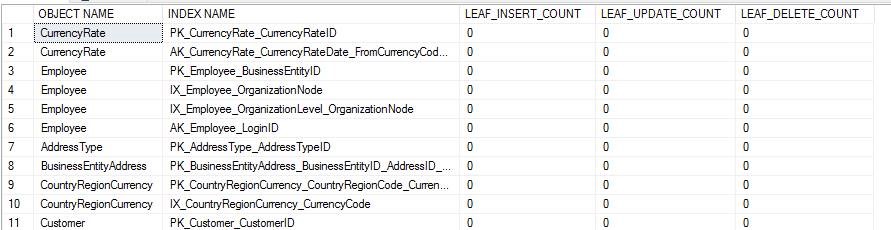
--sys.dm_db_index_operational_stats SELECT OBJECT_NAME(A.[OBJECT_ID]) AS [OBJECT NAME], I.[NAME] AS [INDEX NAME], A.LEAF_INSERT_COUNT, A.LEAF_UPDATE_COUNT, A.LEAF_DELETE_COUNT FROM SYS.DM_DB_INDEX_OPERATIONAL_STATS (NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL ) A INNER JOIN SYS.INDEXES AS I ON I.[OBJECT_ID] = A.[OBJECT_ID] AND I.INDEX_ID = A.INDEX_ID WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(A.[OBJECT_ID],'IsUserTable') = 1
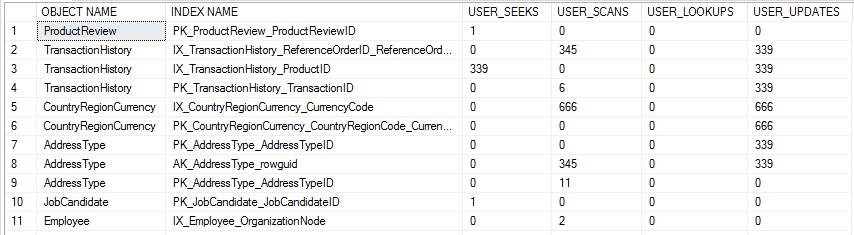
--sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats SELECT OBJECT_NAME(S.[OBJECT_ID]) AS [OBJECT NAME], I.[NAME] AS [INDEX NAME], USER_SEEKS, USER_SCANS, USER_LOOKUPS, USER_UPDATES FROM SYS.DM_DB_INDEX_USAGE_STATS AS S INNER JOIN SYS.INDEXES AS I ON I.[OBJECT_ID] = S.[OBJECT_ID] AND I.INDEX_ID = S.INDEX_ID WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(S.[OBJECT_ID],'IsUserTable') = 1
Insufficient index
Insufficient index refers to the lack of index or index, but not covering the required columns, the query effect is not good. The latter can also be summed up as inappropriate index. So let's see how we can find the missing index.SQL Server provides the following four DMV s for querying missing index. When the SQL Server restarts, the content in the system view will be updated, and this information needs to be saved regularly.
- sys.dm_db_missing_index_details Returns the details of the missing index.
- sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats Returns a summary of the missing index group.
- sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups Returns which missing indexes are in the missing index group.
- sys.dm_db_missing_index_columns Returns the column of the missing index in the table.
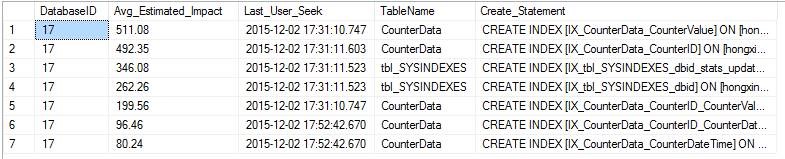
The following statement executes the following query on each library to view the recommended index, including the creation statement. However, before creating the index, it is necessary to synthesize the existing indexes in the scale and whether they can be merged.
Use DB SELECT dm_mid.database_id AS DatabaseID, dm_migs.avg_user_impact*(dm_migs.user_seeks+dm_migs.user_scans) Avg_Estimated_Impact, dm_migs.last_user_seek AS Last_User_Seek, OBJECT_NAME(dm_mid.OBJECT_ID,dm_mid.database_id) AS [TableName], 'CREATE INDEX [IX_' + OBJECT_NAME(dm_mid.OBJECT_ID,dm_mid.database_id) + '_' + REPLACE(REPLACE(REPLACE(ISNULL(dm_mid.equality_columns,''),', ','_'),'[',''),']','') + CASE WHEN dm_mid.equality_columns IS NOT NULL AND dm_mid.inequality_columns IS NOT NULL THEN '_' ELSE '' END + REPLACE(REPLACE(REPLACE(ISNULL(dm_mid.inequality_columns,''),', ','_'),'[',''),']','') + ']' + ' ON ' + dm_mid.statement + ' (' + ISNULL (dm_mid.equality_columns,'') + CASE WHEN dm_mid.equality_columns IS NOT NULL AND dm_mid.inequality_columns IS NOT NULL THEN ',' ELSE '' END + ISNULL (dm_mid.inequality_columns, '') + ')' + ISNULL (' INCLUDE (' + dm_mid.included_columns + ')', '') AS Create_Statement FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups dm_mig INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats dm_migs ON dm_migs.group_handle = dm_mig.index_group_handle INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_details dm_mid ON dm_mig.index_handle = dm_mid.index_handle WHERE dm_mid.database_ID = DB_ID() ORDER BY Avg_Estimated_Impact DESC GO
When creating index, it is recommended to do so in the following order.
- To rank equal data at the top
- Ranking unequal data after equal data rows
- Column include data in the include clause of the create index statement
- To determine the order of equal rows of data, rank the rows selectively, ranking the rows with the highest selectivity at the top
Index fragmentation rate
When data is added, deleted and modified, the database automatically maintains the index. But over time, these operations can cause data discontinuity. This can have an impact on lookup performance.
First, observe the severity of index fragments.
Internal Fragmentation: There is a lot of free space in the data page;
External Fragmentation:
- Pages or sections placed on hard disks are discontinuous, i.e. data tables or indexes are scattered across multiple ranges, and pages that store data tables or indexes are not stored continuously according to instances.
- The order of logical data is different from that of instances on the hard disk.
create index idCreditCard on CreditCard(CreditCardID) with drop_existing DBCC showcontig(CreditCard,idCreditCard)
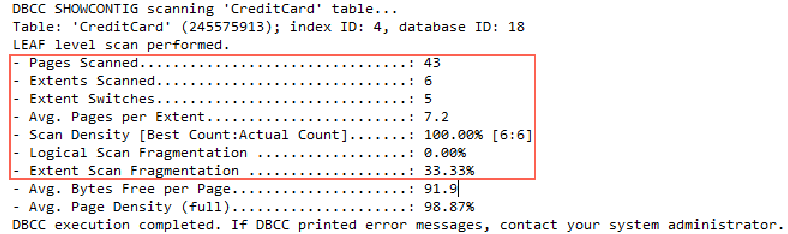
The parameters in the red box reflect the external discontinuity. The index idCreditCard uses 43 pages and 6 zones. The cursor scan area is converted five times, averaging 7.2 pages per zone, with a scanning density of 100%, a logical scan fragment of 0, and a fragmentation rate of 33.33%(= the number of zones skipped during reading/the total number of zones used).
The last two parameters, Avg. Bytes Free per Page and Avg. Page Density (full), reflect the internal discontinuity. The larger the average number of free bytes per page, the more serious the internal discontinuity is.
Data discontinuity can be observed by defining a temporary table.
--BDCC Showcontig to show the fragmentation of table or index create table #fraglist ( objectName char (255), objectID int, IndexName char(255), IndexID int, Lvl int, countPages int, countRows int, MinRecSize int, MaxRecSize int, AvgRecSize int, ForRecSize int, Extents int, ExtentSwitches int, AvgFreeBytes int, AvgPageDensity int, ScanDensity decimal, BestCount int, ActualCount int, LogicalFrag decimal, ExtentFrag decimal ) insert #fraglist exec('DBCC showcontig(CreditCard,idCreditCard) with tableresults') select * from #fraglist
2. Adoption sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats Observation of data discontinuity
View the index discontinuity of the Department table:
select a.index_id,name,avg_fragmentation_in_percent from sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(),object_id(N'HumanResources.Department'),null,null,null) as a join sys.indexes as b on a.object_id=b.object_id and a.index_id=b.index_id;
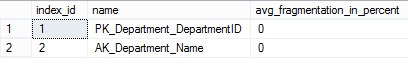
View fragmentation of all indexes in the database
use DB; SELECT OBJECT_NAME(ind.OBJECT_ID) AS TableName, ind.name AS IndexName, indexstats.index_type_desc AS IndexType, indexstats.avg_fragmentation_in_percent FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats(DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL) indexstats INNER JOIN sys.indexes ind ON ind.object_id = indexstats.object_id AND ind.index_id = indexstats.index_id WHERE indexstats.avg_fragmentation_in_percent > 5 ORDER BY indexstats.avg_fragmentation_in_percent DESC
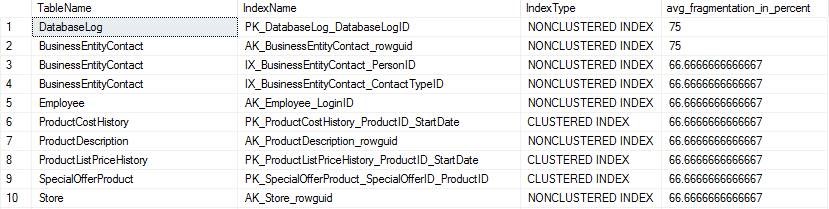
3. Decide whether to reorganize or rebuild the index according to the status of data fragments.
When the index fragmentation is greater than 5%, less than or equal to 30%, reorganize the index is recommended; when the index fragmentation rate is greater than 30%, rebuild the index is recommended. Rebuild Index consumes performance, and it is recommended to do it in off-hours. At the same time, it is recommended to rebuild index in online way to reduce the number of lock applications.
- Reorganization index:
ALTER INDEX IX_Employee_OrganizationalLevel_OrganizationalNode ON HumanResources.Employee REORGANIZE ;
- Reconstruct the index:
ALTER INDEX IX_TransactionHistory_TransactionDate ON Production.TransactionHistory REBUILD Partition = 5 WITH ( ONLINE = ON ( WAIT_AT_LOW_PRIORITY (MAX_DURATION = 10 minutes, ABORT_AFTER_WAIT = SELF )));
- Maintenance plan rebuilding index