Summary of python list method
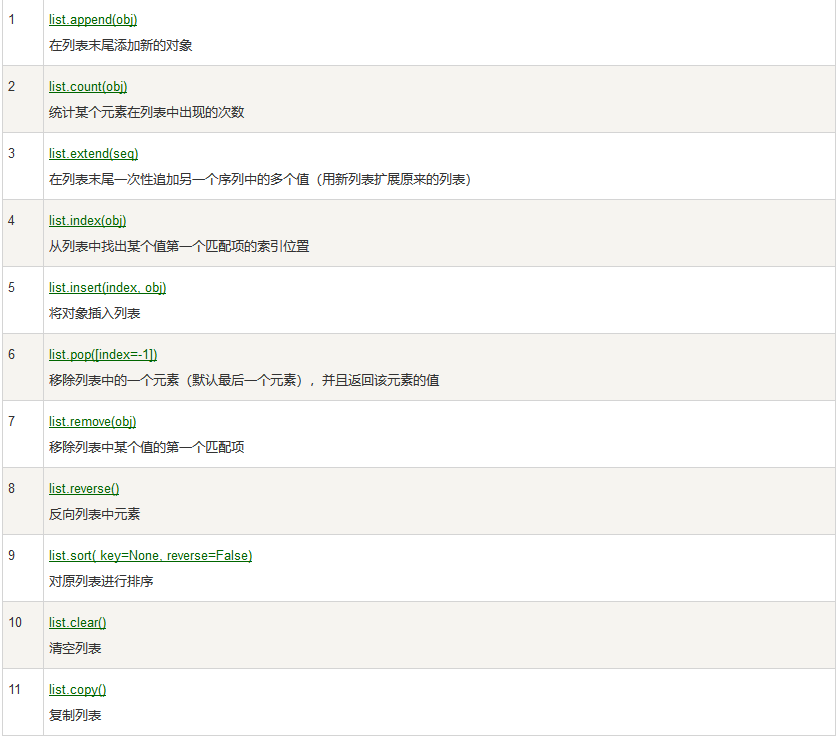
List.append() method
purpose
The append() method is used to add a new object at the end of the list.
grammar
list.append(obj)
parameter
- obj: the object added to the end of the list.
Return value
There is no return value for this method, but the original list will be modified.
Example
list1 = ['hello', 'world', 'python'] list1.append('pycharm') print ("After updating list1 : ", list1)
Output result
After update, LIST1: ['Hello ',' world ',' Python ',' pycharm ']
List.count() method
purpose
The count() method is used to count the number of times an element appears in the list.
grammar
list.count(obj)
parameter
- obj: objects counted in the list.
Return value
Returns the number of times an element appears in the list.
Example
List1 = ['hello', 'python', 323, 'hello', 'python', 323]; print ("323 Element number : ", List1.count(323)) print ("python Element number : ", List1.count('python'))
Output results:
323 number of elements: 2 Number of python elements: 2
List.extend() method
purpose
The extend() function is used to append multiple values in another sequence at the end of the list at one time (extending the original list with a new list).
grammar
list.extend(seq)
parameter
- -seq: list of elements, which can be list, tuple, set or dictionary. If it is a dictionary, only the key will be added to the end of the original list as an element in turn.
Return value
The method does not return a value, but adds new list content to the existing list.
Example
list1 = ['hello', 'world', 'python'] list2=list(range(3)) # Create a list of 0-2 list1.extend(list2) # Extended list print ("Expanded list:", list1)
Output result
Expanded list: ['Hello ',' world ',' Python ', 0, 1, 2,]
Do not use data type instance
# Language list language = ['French', 'English', 'German'] # tuple language_tuple = ('Spanish', 'Portuguese') # aggregate language_set = {'Chinese', 'Japanese'} # Add tuple element to end of list language.extend(language_tuple) print('New list: ', language) # Add collection elements to the end of the list language.extend(language_set) print('New list: ', language)
Output result
New list: ['french ',' English ',' German ',' Spanish ',' Portugal '] New list: ['french ',' English ',' German ',' Spanish ',' Portuguese ',' Japanese ',' Chinese ']
List.index() method
purpose
The index() function is used to find the index position of the first match of a value from the list.
grammar
list.index(x[, start[, end]])
parameter
- x -- the object to find.
- start -- optional, the starting position of the search.
- End -- optional, the end position of the search.
Return value
This method returns the index location of the lookup object, and throws an exception if the object is not found.
Example
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao'] print ('Runoob Index value is', list1.index('Runoob')) print ('Taobao Index value is', list1.index('Taobao'))
Output result
Runoob index value is 1 Taobao index value is 2
Example 2
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'Facebook', 'QQ'] # Search from specified location print ('Runoob Index value is', list1.index('Runoob',1))
Output result
Runoob index value is 1
List.insert() method
purpose
The insert() function inserts the specified object into the specified location in the list.
grammar
list.insert(index, obj)
parameter
- Index – the index location where the object obj needs to be inserted.
- obj – the object to insert into the list.
Return value
The method does not return a value, but inserts the object at the location specified in the list.
Example
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao'] list1.insert(1, 'Baidu') print ('List after element insertion : ', list1)
Output result
After inserting elements in the list: ['google ',' Baidu ',' runoob ',' Taobao ']
List.pop() method
purpose
The pop() function removes an element from the list (the last element by default) and returns the value of that element.
grammar
list.pop([index=-1])
parameter
- Index – optional parameter. To remove the index value of a list element, it cannot exceed the total length of the list. The default value is index=-1. Delete the last list value.
Return value
This method returns the element object removed from the list.
Example
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao'] list1.pop() print ("The list is now : ", list1) list1.pop(1) print ("The list is now : ", list1)
Output result
The list is now: ['google ',' runoob '] The list is now: ['Google ']
Give an example
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao'] list_pop=list1.pop(1) print ("Deleted items are :", list_pop) print ("The list is now : ", list1)
Output result
The deleted element is: Runoob The list is now: ['google ',' Taobao ']
List.remove() method
purpose
The remove() function removes the first match for a value in the list.
grammar
list.remove(obj)
parameter
- obj: the object to be removed from the list.
Return value
The method does not return a value but removes the first match for a value in the list.
Example
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'Baidu'] list1.remove('Taobao') print ("The list is now : ", list1) list1.remove('Baidu') print ("The list is now : ", list1)
Output result
The list is now: ['google ',' runoob ',' Baidu '] The list is now: ['google ',' runoob ']
List.reverse() method
purpose
The reverse() function is used to reverse the elements in the list.
grammar
list.reverse()
parameter
nothing
Return value
The method does not return a value, but sorts the elements of the list in reverse.
Example
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'Baidu'] list1.reverse() print ("After list reversal: ", list1)
Output result
After the list is reversed: ['baidu ',' Taobao ',' runoob ',' Google ']
List.sort() method
purpose
The sort() function is used to sort the original list. If you specify parameters, the comparison function specified by the comparison function is used.
grammar
list.sort( key=None, reverse=False)
parameter
- key - the element mainly used for comparison. There is only one parameter. The specific function parameter is taken from the iteratable object. Specify an element in the iteratable object to sort.
- Reverse - collation, reverse = True descending, reverse = False ascending (default).
Return value
This method does not return a value, but sorts the objects in the list.
Example
aList = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'Facebook'] aList.sort() print ( "List : ", aList)
Output result
List : ['Facebook', 'Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao']
Descending instance
# list vowels = ['e', 'a', 'u', 'o', 'i'] # Descending order vowels.sort(reverse=True) # Output result print ( 'Descending output:', vowels )
Output result
Output in descending order: ['u ',' o ',' I ',' e ',' a ']
Specify the output instance of element sorting in the list
# Get the second element of the list def takeSecond(elem): return elem[1] # list random = [(2, 2), (3, 4), (4, 1), (1, 3)] # Specify the second element sort random.sort(key=takeSecond) # Output class print ('Sort list:', random)
Output result
Sort list: [(4, 1), (2, 2), (1, 3), (3, 4]]
List.clear() method
purpose
The clear() function is used to clear the list, similar to del a [:].
grammar
list.clear()
parameter
nothing
Return value
The method has no return value.
Example
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'Baidu'] list1.clear() print ("After the list is cleared : ", list1)
Output result
After the list is cleared: []
List.copy() method
purpose
The copy() function copies the list, similar to a [:].
grammar
list.copy()
parameter
nothing
Return value
Returns the new list after replication.
Example
list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'Baidu'] list2 = list1.copy() print ("list2 list: ", list2)
Output result
list2 list: ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'Baidu']

