Original web address: Swagger--Use/Usage/Example/Example_IT Cutting-edge Blog-CSDN Blog
Other web addresses
Introduction to swagger and two ways to use it _Programmed Ape-HZQ-CSDN Blog_swagger
Build a powerful RESTful API document using Swagger2 in Spring Boot - Short Book
Swagger - Short Book
GitHub - SpringForAll/spring-boot-starter-swagger (github: detailed tutorials)
brief introduction
Swagger is a very common tool for interface documentation. By annotating classes and methods, you can view interface information on the web.
Dependency and Configuration (Law 1: Official)
Introducing official dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
The first is the package acquired by the API, and the second is an ui interface given by the government. This interface can be customized and is official by default. It needs to be considered for security issues and ui routing settings.
The main class enables swagger
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableSwagger2
public class DemoSpringBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoSpringBootApplication.class, args);
}
}
Configure swagger
Swagger2Config.java
Be sure to note that the RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage is filled in correctly
package com.example.demo.conf;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ParameterBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.schema.ModelRef;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.service.Parameter;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Configuration
//In the production environment does not open, this method has problems, to find data to solve, so use the following Boolean values to achieve security control
//@Profile({"dev", "test"})
public class Swagger2Config {
private boolean swaggerShow = true;
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.enable(swaggerShow)
.groupName("demo.controller1(groupName)")
//.globalOperationParameters(getTocken())
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example.demo.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
// You can add interface descriptions for multiple packages. (@Bean's method name is arbitrary)
// In actual development, groupName should correspond to RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage one-to-one. (The same is used here for brevity)
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi2() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.enable(swaggerShow)
.groupName("demo.controller2(groupName)")
//.globalOperationParameters(getTocken())
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example.demo.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Swagger Of Demo(title)")
.description("Swagger Of Demo(description)")
//The line below can be commented out directly
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://blog.csdn.net/feiying0canglang/")
.contact(new Contact("xxx company", "https://blog.csdn.net/feiying0canglang/", "abcd@qq.com"))
.version("Swagger Of Demo(version)")
.build();
}
// public List getTocken() {
// List<Parameter> list = new ArrayList<>();
// ParameterBuilder tocken = new ParameterBuilder()
// .name("token")
// .description("authentication information")
// .modelRef(new ModelRef("string"))
// .parameterType("header")
// //Write token values here
// .defaultValue("xxxxxx")
// .required(true);
// list.add(tocken.build());
//
// return list;
// }
}As shown in the code above,
- Let Spring load this type of configuration through the @Configuration annotation.
- Then enable Swagger2 through the @EnableSwagger2 annotation.
- After creating a Bean for Docket through the createRestApi function, apiInfo() is used to create the basic information for the Api (which is displayed on the document page).
- The select() function returns an ApiSelectorBuilder instance that controls which interfaces are exposed to Swagger for presentation. This example uses the package path specified for the scan, which scans all Controller-defined API s under the package and generates document content (except for requests specified by @ApiIgnore).
Dependency and configuration (method 2:starter)
Other web addresses
https://github.com/SpringForAll/spring-boot-starter-swagger
Introducing dependencies
<dependency> <groupId>com.spring4all</groupId> <artifactId>swagger-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.9.0.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
Enable
Add the @EnableSwagger2Doc annotation to the application main class
@EnableSwagger2Doc
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}By default, all request mapping documents currently loaded by Spring MVC will be generated.
Configuration example
swagger.enabled=true swagger.title=spring-boot-starter-swagger swagger.description=Starter for swagger 2.x swagger.version=1.4.0.RELEASE swagger.license=Apache License, Version 2.0 swagger.licenseUrl=https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html swagger.termsOfServiceUrl=https://github.com/dyc87112/spring-boot-starter-swagger swagger.contact.name=didi swagger.contact.url=http://blog.didispace.com swagger.contact.email=dyc87112@qq.com swagger.base-package=com.didispace swagger.base-path=/** swagger.exclude-path=/error, /ops/** swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].name=name one swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].description=some description one swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].modelRef=string swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].parameterType=header swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].required=true swagger.globalOperationParameters[1].name=name two swagger.globalOperationParameters[1].description=some description two swagger.globalOperationParameters[1].modelRef=string swagger.globalOperationParameters[1].parameterType=body swagger.globalOperationParameters[1].required=false // Unuse default predefined response messages and use custom response messages swagger.apply-default-response-messages=false swagger.global-response-message.get[0].code=401 swagger.global-response-message.get[0].message=401get swagger.global-response-message.get[1].code=500 swagger.global-response-message.get[1].message=500get swagger.global-response-message.get[1].modelRef=ERROR swagger.global-response-message.post[0].code=500 swagger.global-response-message.post[0].message=500post swagger.global-response-message.post[0].modelRef=ERROR
Configuration Instructions
Default configuration:
- swagger.enabled=Is it enabled swagger,Default: true - swagger.title=Title - swagger.description=describe - swagger.version=Edition - swagger.license=Licence - swagger.licenseUrl=Licence URL - swagger.termsOfServiceUrl=Terms of Service URL - swagger.contact.name=Maintainer - swagger.contact.url=Maintainer URL - swagger.contact.email=Maintainer email - swagger.base-package=swagger Base package for scanning, default: full scan - swagger.base-path=Basis to be handled URL Rule, default:/** - swagger.exclude-path=Need to be excluded URL Rule, default: empty - swagger.host=Document's host Information, default: empty - swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].name=Parameter Name - swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].description=Descriptive Information - swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].modelRef=Specify parameter type - swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].parameterType=Specify parameter storage location,Optional header,query,path,body.form - swagger.globalOperationParameters[0].required=Specifies whether the parameter must be passed, true,false
Write code
Controller does not have many methods, but many of them are annotated with @ApiImplicitParam. If there are more methods and most of them are related to the User class, is there any way to optimize them?
The answer is yes. You can annotate the User class and its fields so that @ApiImplicitParam is not used for most methods in Controller.
Method 1: Note to Controller
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.bean.User;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.*;
//If not, the default is "user-controller". Just write tags, and the value of tags is displayed on the page.
//@Api(tags = User Controller)
@Api(
tags = {"User Controller a(tags)", "User Controller b(tags)"},
value = "User Management Controller(value)",
)
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/users") // Configure here so that the following maps are all under / users and can be removed
public class UserController {
static Map<Long, User> users = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Long, User>());
@ApiOperation(value="Get User List", notes="")
@RequestMapping(value={""}, method=RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> getUserList() {
List<User> r = new ArrayList<User>(users.values());
return r;
}
@ApiOperation(value="Create User", notes="according to User Object Creation User")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "User Detailed Entities user",
required = true, dataTypeClass = User.class)
@RequestMapping(value="", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String postUser(@RequestBody User user) {
users.put(user.getId(), user);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="Get user details", notes="according to url Of id To get user details")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "user ID", required = true, dataTypeClass = Long.class)
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return users.get(id);
}
@ApiOperation(value="Update user details", notes="according to url Of id Specify the update object and update it according to the incoming user Information Update User Details")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "user ID", required = true, dataTypeClass = Long.class),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "User Detailed Entities user", required = true, dataTypeClass = User.class)
})
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody User user) {
User u = users.get(id);
u.setName(user.getName());
u.setAge(user.getAge());
users.put(id, u);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="delete user", notes="according to url Of id To specify the deletion object")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "user ID", required = true, dataTypeClass = Long.class)
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method= RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
users.remove(id);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="Delete all users", notes="")
@RequestMapping(value="", method= RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteAllUser() {
users.clear();
return "success";
}
}Method 2: Comment to Entity
Controller
UserController.java
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.bean.User;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.*;
//No, the default name is "user controller". Typically, just tags are enough.
@Api( value = "User Management Controller(value)",
tags = {"User Controller a(tags)", "User Controller b(tags)"},
//tags = User Controller
)
//@Api(tags = User Controller)
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/users") // Configure here so that the following maps are all under / users and can be removed
public class UserController {
static Map<Long, User> users = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Long, User>());
@ApiOperation(value="Get User List", notes="")
@RequestMapping(value={""}, method=RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> getUserList() {
List<User> r = new ArrayList<User>(users.values());
return r;
}
@ApiOperation(value="Create User", notes="according to User Object Creation User")
@RequestMapping(value="", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String postUser(@RequestBody User user) {
users.put(user.getId(), user);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="Get user details", notes="according to url Of id To get user details")
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return users.get(id);
}
@ApiOperation(value="Update user details", notes="according to url Of id Specify the update object and update it according to the incoming user Information Update User Details")
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody User user) {
User u = users.get(id);
u.setName(user.getName());
u.setAge(user.getAge());
users.put(id, u);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="delete user", notes="according to url Of id To specify the deletion object")
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method= RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
users.remove(id);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="Delete all users", notes="")
@RequestMapping(value="", method= RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteAllUser() {
users.clear();
return "success";
}
}Entity
User.java
package com.example.demo.bean;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@ApiModel(value = "User Detailed Entities user(value)", description = "user id,Name, age(description)")
public class User {
//Typically, this would be: @ApiModelProperty("User ID(value)")
@ApiModelProperty(name = "id(name)", value = "user ID(value)", required = true, dataType = "Long")
private Long id;
private String name;
private Long age;
}Document Viewing Test
Run the project. Access after success: http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
This page is available
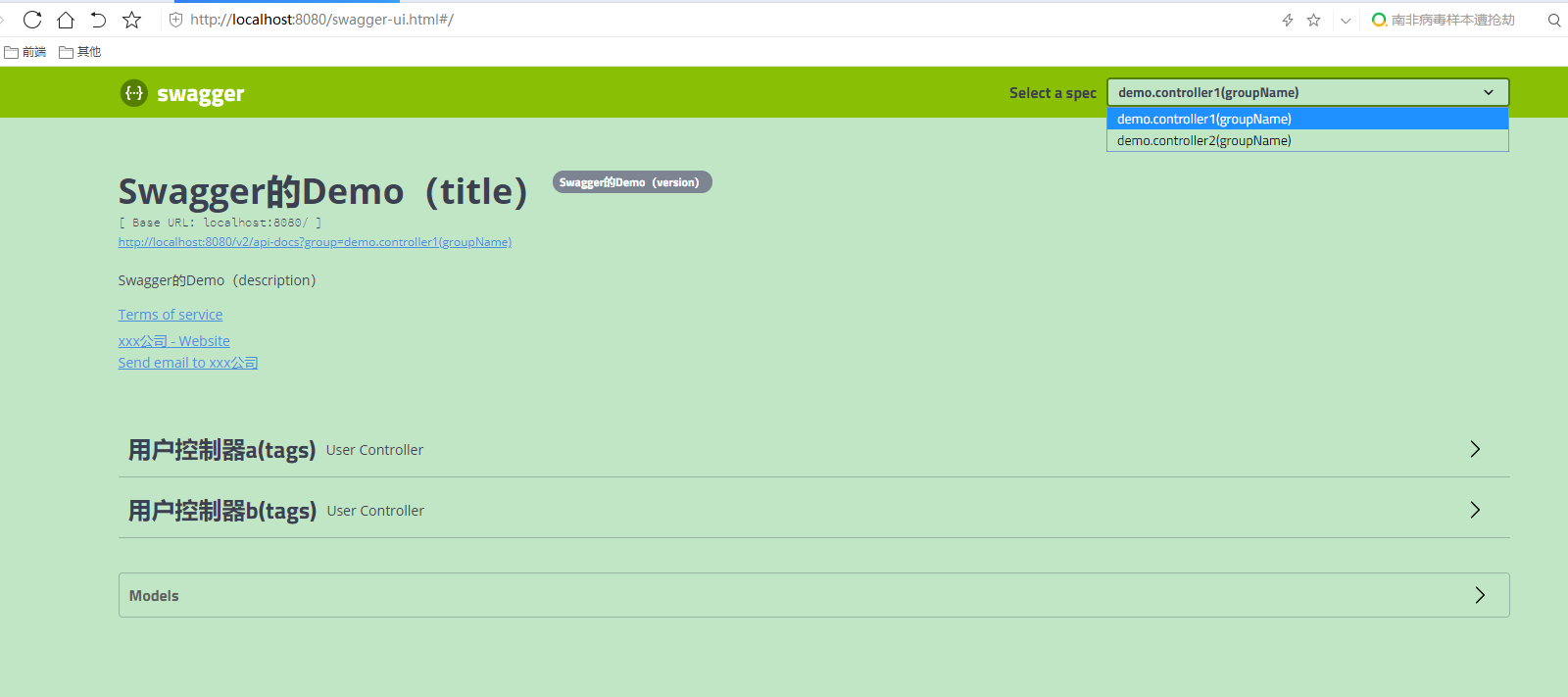
Click "Terms of service": to jump to the web address we specified, here is " IT Cutting-edge Blog_CSDN Blog"
Click on User Controller a(tags): to view the interface
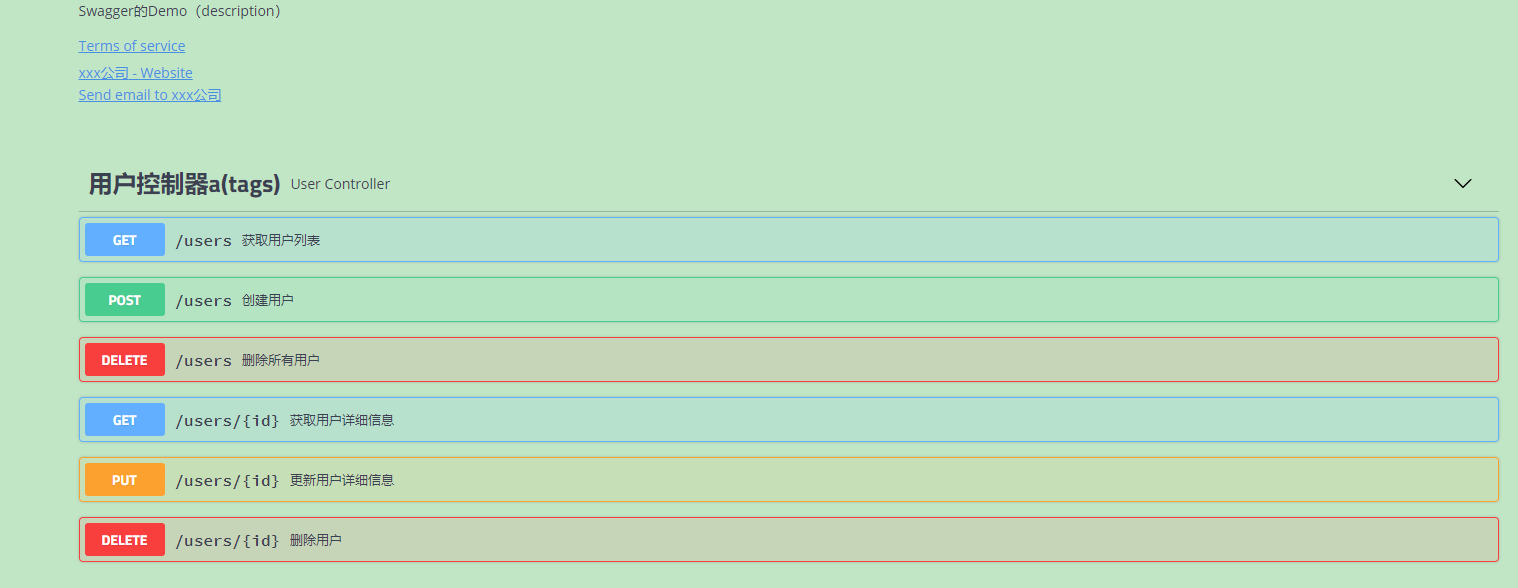
Click "http://localhost/v2/api-docs?group=demo.controller1(groupName)":
You can get the bottom content
(I'm using Firefox, which automatically parses JSON, but it doesn't work with 360 Speed browsers)




Interface Actual Test
Swagger provides not only interface viewing but also direct testing.
Continue above. Click Create User
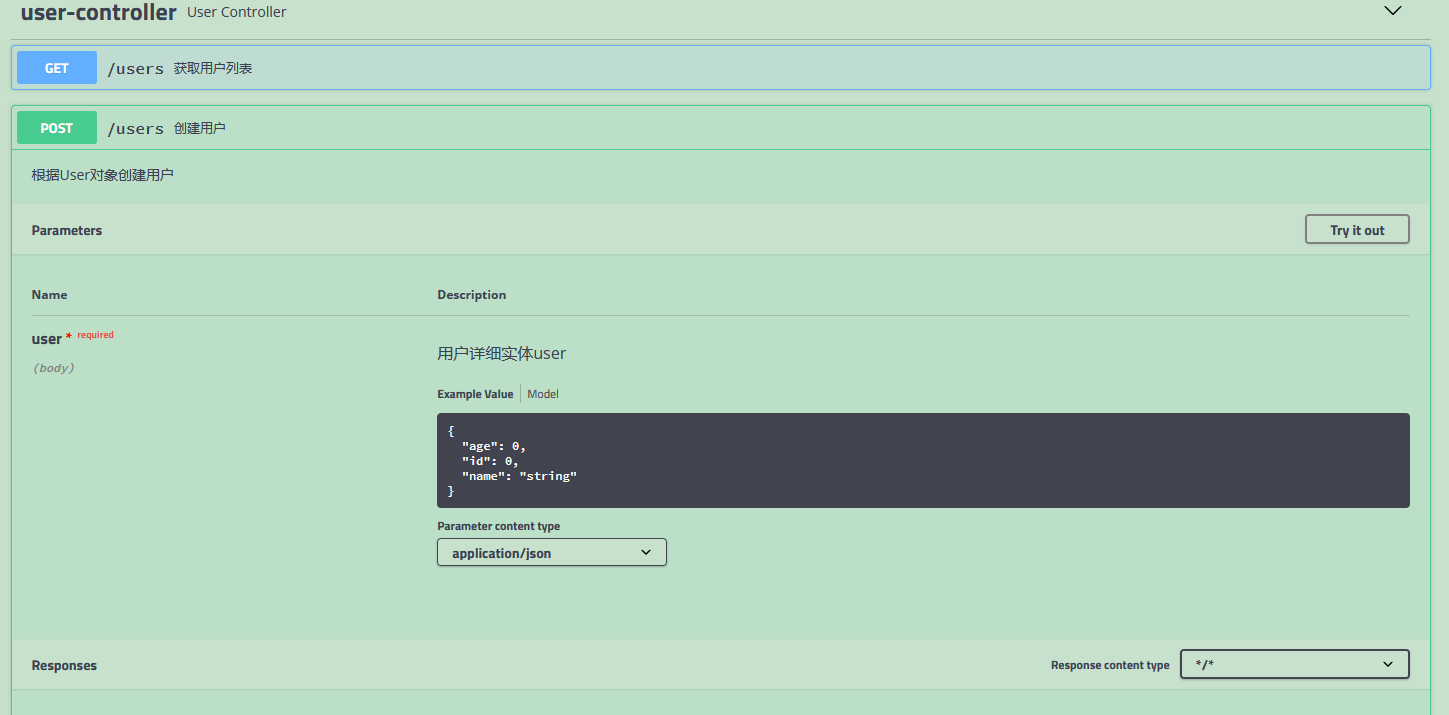
Click "Try it out"

After clicking, the following interface appears. The numbers and strings pointed to by the arrows can be changed. Modify them here. Click "Execute" at the bottom

A successful response appears
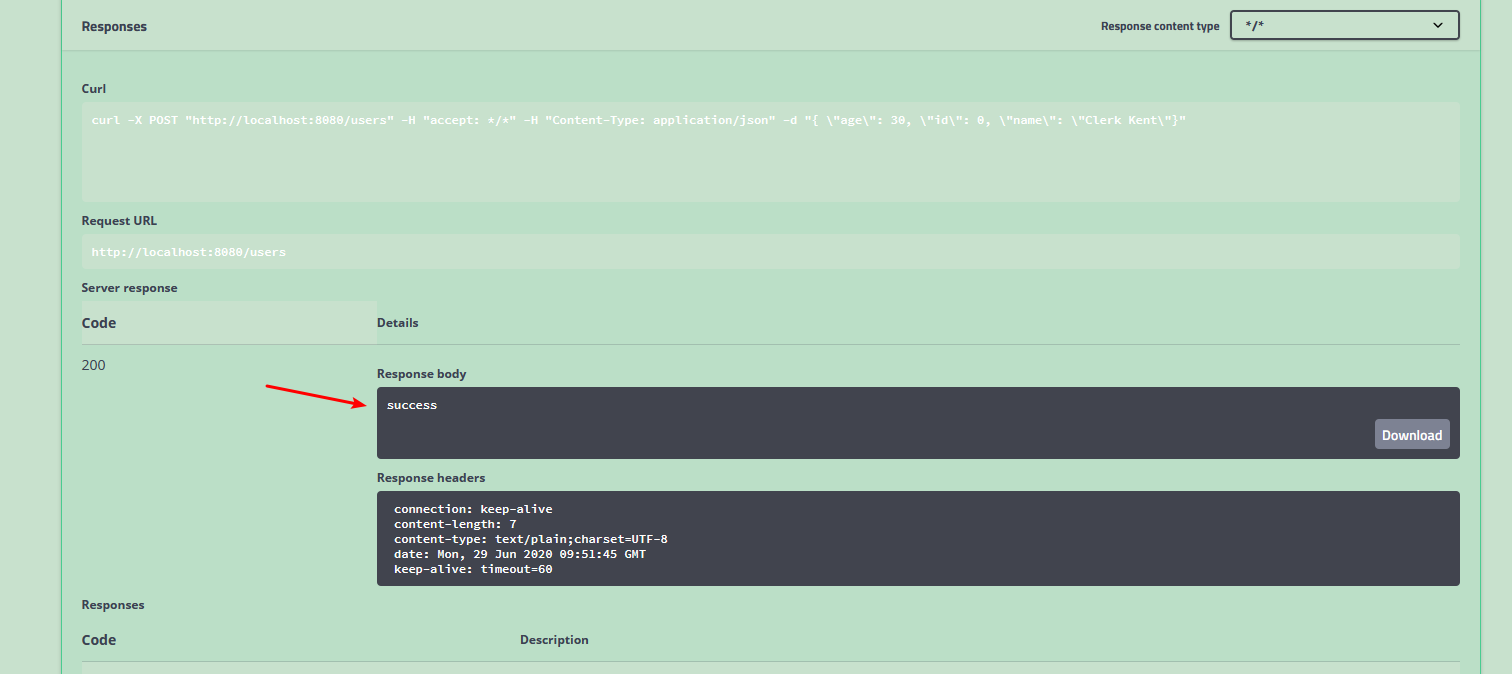
Same operation, operation "Get User List", results as follows

Problem solving
Upload Files
Wrong Writing
@PostMapping(value = "/upload-image")
@ApiOperation(value = "Picture Upload", notes = "Picture Upload")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "deviceId", value = "deviceId", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "attach", value = "Upload Files", required = true, dataType = "File"),
})
public JsonResult imageUpload(String deviceId,
MultipartFile file) {
}Correct Writing
@PostMapping(value = "/upload-image", headers="content-type=multipart/form-data")
@ApiOperation(value = "Picture Upload", notes = "Picture Upload")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "deviceId", value = "deviceId", required = true, dataType = "String")
})
public JsonResult imageUpload(String deviceId,
@ApiParam(name = "attach", value = "Upload Files", required = true)
MultipartFile file) {
}Of course, if form-data is already agreed upon with the front end, there is no need to add: headers="content-type=multipart/form-data"