Teach you how to import the third-party library of Go language
1, Get using go get
The go command go get allows us to quickly and easily download or update the go language pack and its dependent files from the network, compile and install them.
- First enter go --help in command line mode to view the following information.
Go is a tool for managing Go source code.
Usage:
go <command> [arguments]
The commands are:
bug start a bug report
build compile packages and dependencies
clean remove object files and cached files
doc show documentation for package or symbol
env print Go environment information
fix update packages to use new APIs
fmt gofmt (reformat) package sources
generate generate Go files by processing source
get add dependencies to current module and install them
install compile and install packages and dependencies
list list packages or modules
mod module maintenance
run compile and run Go program
test test packages
tool run specified go tool
version print Go version
vet report likely mistakes in packages
Use "go help <command>" for more information about a command.
Additional help topics:
buildconstraint build constraints
buildmode build modes
c calling between Go and C
cache build and test caching
environment environment variables
filetype file types
go.mod the go.mod file
gopath GOPATH environment variable
gopath-get legacy GOPATH go get
goproxy module proxy protocol
importpath import path syntax
modules modules, module versions, and more
module-get module-aware go get
module-auth module authentication using go.sum
module-private module configuration for non-public modules
packages package lists and patterns
testflag testing flags
testfunc testing functions
Use "go help <topic>" for more information about that topic.
We can see get add dependencies to current module and install them
That's what we're going to use today.
Then view its help information: go get --help
usage: go get [-d] [-f] [-t] [-u] [-v] [-fix] [-insecure] [build flags] [packages] Run 'go help get' for details.
Find the library we want to get.
Copy link https://github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql
Use go get GitHub com/go-sql-driver/mysql
Result error:
go: missing Git command. See https://golang.org/s/gogetcmd package github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql: exec: "git": executable file not found in %PATH%
Git is installed here. Bloggers have git installed, but it needs to be configured here.
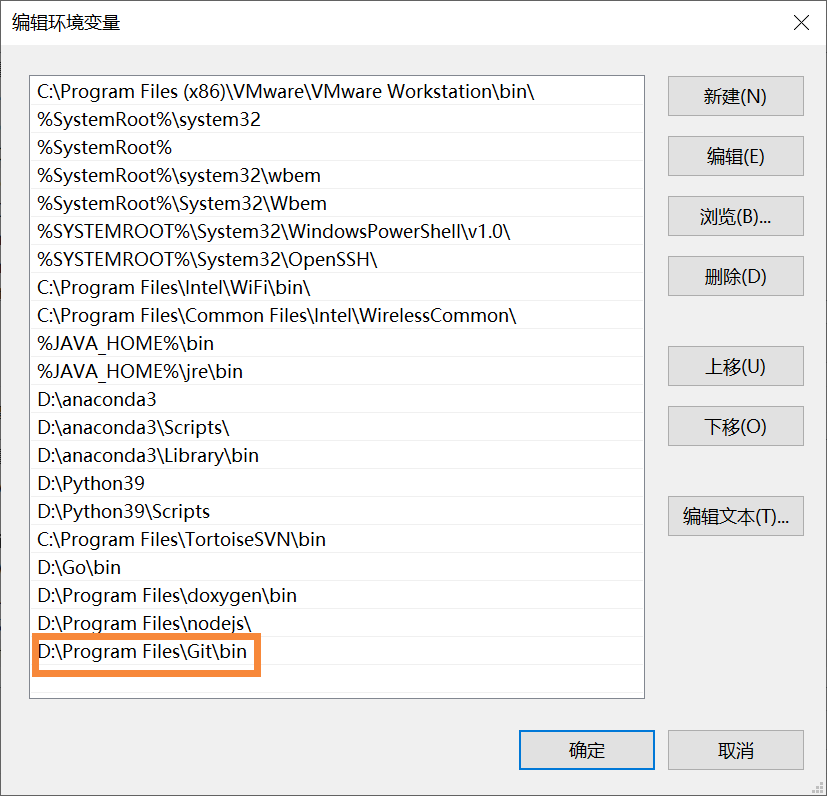
Add the PATH of Git's bin directory in the PATH of the system variable.
Then run go get GitHub com/go-sql-driver/mysql
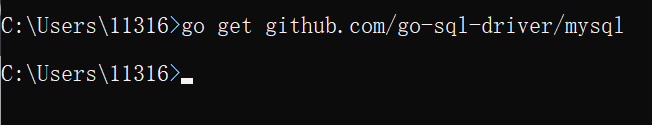
It works now.
This GitHub COM / GO SQL driver / MySQL is called the remote import path. In fact, go get is called the remote dynamic import GO package. In fact, what go get does is to find the code package from the warehouse of the distributed version control system, compile and install it.
| Warehouse name | VCS | VCS | VCS |
|---|---|---|---|
| BitBucket | Mercurial | Git | |
| GitHub | Git | ||
| Google Code Project Hosting | Git | Mercurial | Subversion |
| Launchpad | Bazaar |
Generally, the first element in the remote import path of the code package is the main domain name of the code hosting website. During static analysis, the go get command will match the remote import path of the code package with the primary domain name of the preset code hosting site. If the match is successful, a normal return value or error message is returned after the preliminary check of the remote import path of the code package. If the matching is not successful, the remote import path of the code package will be dynamically analyzed.
2, Download GO library directly
Download the Go library from github or elsewhere.
Then view GOPATH in the system variable.
Then open the src directory of GOPATH
Copy the file in.
Then it was successfully obtained.
3, Parameter introduction
usage: go get [-d] [-f] [-t] [-u] [-v] [-fix] [-insecure] [build flags] [packages] Run 'go help get' for details.
Then we can take a look at the introduction of parameters in go help get.
The -d flag instructs get to stop after downloading the packages; that is, it instructs get not to install the packages. The -f flag, valid only when -u is set, forces get -u not to verify that each package has been checked out from the source control repository implied by its import path. This can be useful if the source is a local fork of the original. The -fix flag instructs get to run the fix tool on the downloaded packages before resolving dependencies or building the code. The -insecure flag permits fetching from repositories and resolving custom domains using insecure schemes such as HTTP. Use with caution. The -t flag instructs get to also download the packages required to build the tests for the specified packages. The -u flag instructs get to use the network to update the named packages and their dependencies. By default, get uses the network to check out missing packages but does not use it to look for updates to existing packages. The -v flag enables verbose progress and debug output.
In short:
- -d stop working after downloading and do not install the library
- -The f parameter is only useful when the - U parameter is used. It forces - u not to verify whether each import ed package has been obtained, which is very useful for local fork packages.
- -Fix this - fix parameter means that the fix tool is run before resolving dependencies or building code.
- -Secure this parameter allows the use of a repository to be obtained and resolved through a custom domain that is not secure, such as HTTP.
- -Tthis parameter allows you to download the package required to test the package when downloading the package.
- -The u parameter allows get to use the network to update the package
And their dependence. By default, get uses the network to check for missing packets, but does not use it to find updates to existing packets. - -v enable detailed progress and debugging information output.