Course objectives
- Master the basic grammatical structure of sed
- Familiar with sed common commands, such as print p, delete d, insert i, etc
Windows:

Linux:
vim vi gedit nano emacs
1, sed introduction
1. sed workflow
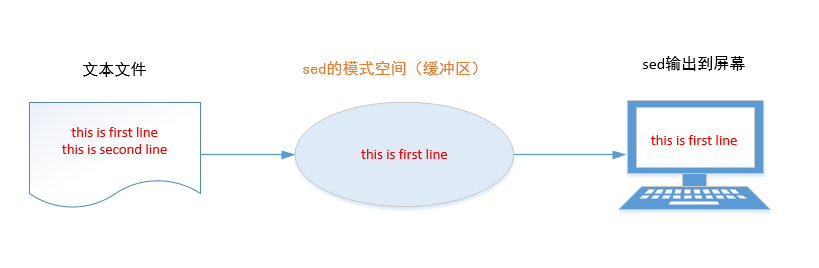
- First, sed saves the row currently being processed in a temporary buffer (also known as pattern space), then processes the row in the temporary buffer, and sends the row to the screen after completion.
- sed saves each line in a temporary buffer and edits the copy, so the original file will not be modified.
- Sed is mainly used to automatically edit one or more files; Simplify the repeated operation of documents; Write conversion program, etc.
2. sed usage
sed has two common syntax formats: command line mode and script mode.
2.1 command line format
- format
sed [option] 'sed Command of|Address location' filename Description: Reference shell script Variables in should use double quotation marks instead of the usual single quotation marks option: -e Make multiple edits, that is, apply multiple edits to the input line sed Command -n Cancel default output -f appoint sed The file name of the script -r Using extended regular expressions -i inplace,Edit in place (modify source file)
- Common commands and options
References:
[root@server shell06]# cat 2.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
298374837483
172.16.0.254
10.1.1.1
p Print line
d Delete row
[root@server ~]# sed -n 'p' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1p' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '2p' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1,5p' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '5,10p' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '$p' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '5p' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '5p' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '1d' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1d' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '1d' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '1,5d' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '$d' a.txt
i\ Inserts text before the current line. In case of multiple lines, except the last line, the end of each line shall be"\"Continuation vim->O
a\ Adds one or more rows after the current row. In case of multiple lines, except the last line, the end of each line shall be“\"Continuation vim-> o
c\ Replace the text in the current line with the new text after this symbol. In case of multiple lines, except the last line, the end of each line shall be"\"Continuation line full line replacement
[root@server ~]# sed '$a99999' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed 'a99999' a.txt
[root@server ~]# cat -n a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '5chello world' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed 'chello world' a.txt
[root@server ~]# cat -n a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '1,5chello world' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed 'i\
aaaaa\
bbbbb\
88888' 1.txt
# sed '$a\
yyyyy\
8888' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '/^user01/c888888' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '18chello world' 1.txt
Command 2:
r Read input line from file
w Writes the selected line to the file
[root@server ~]# sed '3r /etc/hosts' 2.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '$r /etc/hosts' 2.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '/root/w a.txt' 2.txt
[root@server ~]# sed '/[0-9]{4}/w a.txt' 2.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -r '/([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}/w b.txt' 2.txt
! Apply the command to all lines except the selected line, after the number of lines
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1!p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '4p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '4!p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# cat -n 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1,17p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1,17!p' 1.txt
s Replace one string with another
g Global replace within row
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's/root/ROOT/p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's/root/ROOT/gp' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's/^#//gp' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's@/sbin/nologin@itcast@gp' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's/\/sbin\/nologin/itcast/gp' a.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '10s#/sbin/nologin#itcast#p' a.txt
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:itcast
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's@/sbin/nologin@itcastheima@p' 2.txt
Note: the separator in search and replacement can be specified by yourself
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1,5s/^/#/p' a.txt Comment out lines 1-5 of the file
#root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
#bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
#daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
#adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
#lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
& Save the lookup string for reference in the replacement string \(\)
[root@server ~]# sed -n '/root/p' a.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's/root/#&/p' a.txt
#root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
# sed -n 's/^root/#&/P 'passwd comment out lines starting with root
# sed -n -r 's/^root|^stu/#&/p' /etc/passwd Comment out lines that start with root or stu
# sed -n '1,5s/^[a-z].*/#&/P 'passwd comment out the lines starting with any lowercase letter in lines 1 ~ 5
# sed -n '1,5s/^/#/P '/ etc / passwd comment lines 1 to 5
perhaps
sed -n '1,5s/^/#/p' passwd Empty plus#
sed -n '1,5s/^#//P 'passwd replace the beginning with # with null
[root@server ~]# sed -n '/^root/p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's/^root/#&/p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n 's/\(^root\)/#\1/p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -nr '/^root|^stu/p' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -nr 's/^root|^stu/#&/p' 1.txt
= Print line number
# sed -n '/bash$/=' passwd prints the line number of the line ending in bash
# sed -ne '/root/=' -ne '/root/p' passwd
# sed -n '/nologin$/=;/nologin$/p' 1.txt
# sed -ne '/nologin$/=' -ne '/nologin$/p' 1.txt
Comprehensive application:
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1,5s/^/#&/p' 1.txt
#root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
#bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
#daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
#adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
#lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
[root@server ~]# sed -n '1,5s/\(^\)/#\1/p' 1.txt
#root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
#bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
#daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
#adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
#lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
Options:-e -r -i
-e Multieditor
-r Extended regularity
-i Modify original document
[root@server ~]# sed -ne '/root/p' 1.txt -ne '/root/='
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
1
[root@server ~]# sed -ne '/root/=' -ne '/root/p' 1.txt
1
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
At 1.txt Insert before line 5 in the file“ hello world";At 1.txt Insert "ha ha ha" under line 8 of the file
[root@server ~]# sed -e '5ihello world' -e '8a ha ha ha ha ha ha' 1 txt -e '5=; 8='
filter vsftpd.conf File with#Beginning and blank lines:
[root@server ~]# grep -Ev '^#|^$' /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
[root@server ~]# sed -e '/^#/d' -e '/^$/d' /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
[root@server ~]# sed '/^#/d;/^$/d' /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
[root@server ~]# sed -r '/^#|^$/d' /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
filter smb.conf Effective lines in file:
[root@server shell06]# sed -e '/^#/d' -e '/^;/d' -e '/^$/d' -e '/^\t$/d' -e '/^\t#/d' smb.conf
[root@server shell06]# sed -r '/^(#|$|;|\t#|\t$)/d' smb.conf
[root@server shell06]# sed -e '/^#/d' -e '/^;/d' -e '/^$/d' -e '/^\t$/d' -e '/^\t#/' smb.conf
[root@server ~]# grep '^[^a-z]' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -n '/^[^a-z]/p' 1.txt
Filter out files IP Address:
[root@server ~]# grep -E '([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}' 1.txt
192.168.0.254
[root@server ~]# sed -nr '/([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}/p' 1.txt
192.168.0.254
[root@server ~]# grep -o -E '([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}' 2.txt
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.255
255.255.255.0
[root@server ~]# sed -nr '/([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}/p' 2.txt
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.255
255.255.255.0
Filter out ifcfg-eth0 In file IP,Subnet mask, broadcast address
[root@server shell06]# grep -Eo '([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}' ifcfg-eth0
10.1.1.1
255.255.255.0
10.1.1.254
[root@server shell06]# sed -nr '/([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}/p' ifcfg-eth0|cut -d'=' -f2
10.1.1.1
255.255.255.0
10.1.1.254
[root@server shell06]# sed -nr '/([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}/p' ifcfg-eth0|sed -n 's/[A-Z=]//gp'
10.1.1.1
255.255.255.0
10.1.1.254
[root@server shell06]# ifconfig eth0|sed -n '2p'|sed -n 's/[:a-Z]//gp'|sed -n 's/ /\n/gp'|sed '/^$/d'
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.255
255.255.255.0
[root@server shell06]# ifconfig | sed -nr '/([0-9]{1,3}\.)[0-9]{1,3}/p' | head -1|sed -r 's/([a-z:]|[A-Z/t])//g'|sed 's/ /\n/g'|sed '/^$/d'
[root@server shell06]# ifconfig eth0|sed -n '2p'|sed -n 's/.*addr:\(.*\) Bcast:\(.*\) Mask:\(.*\)/\1\n\2\n\3/p'
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.255
255.255.255.0
-i Option to modify the original file directly
# sed -i 's/root/ROOT/;s/stu/STU/' 11.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -i '17{s/YUNWEI/yunwei/;s#/bin/bash#/sbin/nologin#}' 1.txt
[root@server ~]# sed -i '1,5s/^/#&/' a.txt
be careful:
-ni Do not use together
p Do not use the command again-i When using
- summary
Sed option 'sed command or regular expression or address location = =' = = file name
Addressing is used to determine which rows to edit. The form of an address can be a number, a regular expression, or a combination of the two. If no address is specified, sed will process all lines of the input file.
x appoint x Line number sed -n '5p' 1.txt x,y appoint x reach y Line number sed -n '1,5p' 1.txt /key/ Query rows containing keywords sed -n '/root/p' 1.txt /key1/,/key2/ Match contains rows between two keywords sed -n '/^adm/,/^mysql/p' 1.txt /key/,x Start from the line matching the keyword to the second line of the file x Rows between rows (including the row where the keyword is located) sed -n '/^lp/,7p' x,/key/ From the first x The line from the beginning of the line to the line matching the keyword x,y! Not included x reach y that 's ok [root@server ~]# sed -n '/bash$/!p' 1.txt be careful: sed The regular expression used is enclosed in a slash"/"Mode between. //The following command is to find lines that start with lp or mail
- Explanation of other commands
y command This command is associated with UNIX/Linux Medium tr Similar to the command, characters are converted from left to right in a one-to-one manner. Regular expression metacharacter pair y The command does not work. And s Like the separator of the command, the slash can be replaced with other characters. s/xxx/xxx/ y/xxx/xxx/ # sed '39,41y/stu/STU/' /etc/passwd # sed '39,41y/stu:x/STU@%/' /etc/passwd q sign out # sed '5q' 1.txt # sed '/mail/q' 1.txt # sed -r '/^yunwei|^mail/q' 1.txt [root@server ~]# sed -n '/bash$/p;10q' 1.txt ROOT:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
2.2 script format
- usage
# sed -f scripts.sed file // Use scripts to process files Recommended use ./sed.sh file The first line of the script says #!/bin/sed -f 1,5d s/root/hello/g 3i777 5i888 a p
- matters needing attention
1) The script file is a sed Command line list for.'commands' 2) There must be no spaces, tabs at the end of each line( tab)Or other text. 3) If there are multiple commands on a line, they should be separated by semicolons. 4) Commands that do not need and can not be protected with quotation marks 5) #Behavior comments beginning with
- Example
# cat passwd stu3:x:509:512::/home/user3:/bin/bash stu4:x:510:513::/home/user4:/bin/bash stu5:x:511:514::/home/user5:/bin/bash # cat sed.sh #!/bin/sed -f 2a\ ****************** 2,$s/stu/user/ $a\ we inster new line s/^[a-z].*/#&/ [root@server ~]# cat 1.sed #!/bin/sed -f 3a********************** $chelloworld 1,3s/^/#&/ [root@server ~]# sed -f 1.sed -i 11.txt [root@server ~]# cat 11.txt #root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash #bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin #daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin ********************** adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin helloworld
3. Comprehensive application of SED and regularization
1,Regular expressions must begin with ''/"Front and rear specification interval
For example: sed '/root/d' file
For example: sed '/^root/d' file
2,If the matching is an extended regular expression, you need to use-r Selected to expand sed
grep -E
sed -r
+ ? () {n,m} | \d
be careful:
If special characters appear in regular expressions(^$.*/[]),Leading is required "\" No. do escape
eg: sed '/\$foo/p' file
3,GNU sed
For example: sed '5,7d' file Delete lines 5 to 7
For example: sed '/root/,/ftp/d' file
Delete the first matching string"root"To the first matching string"ftp"Loop execution not found for all rows
4,Combination mode
For example: sed '1,/foo/d' file Delete the first line to the first matching string"foo"All rows of
For example: sed '/foo/,+4d' file Delete from matching string foo"The line from the beginning to the next four lines
For example: sed '/foo/,~3d' file Delete from matching string foo"Start deleting multiple lines up to 3 (in file)
For example: sed '1~5d' file Delete from the first line delete every five lines
For example: sed -nr '/foo|bar/p' file Display configuration string"foo"or"bar"Line of
For example: sed -n '/foo/,/bar/p' file Show matching from foo reach bar Line of
For example: sed '1~2d' file Delete odd rows
For example: sed '0-2d' file Delete even rows sed '1~2!d' file
5,exceptional case
For example: sed '$d' file Delete last line
For example: sed '1d' file Delete the first line
6,other:
sed 's/.//' a.txt Delete the first character in each line
sed 's/.//2' a.txt Delete the second character in each line
sed 's/.//N' a.txt Starting from the nth line in the file, delete the nth character in each line (n > 2)
sed 's/.$//' a.txt Delete the last character in each line
[root@server ~]# cat 2.txt
1 a
2 b
3 c
4 d
5 e
6 f
7 u
8 k
9 o
[root@server ~]# sed '/c/,~2d' 2.txt
1 a
2 b
5 e
6 f
7 u
8 k
9 o
4. Classroom exercises
- Replace any number with an empty or tab character
- Remove numbers, colons and slashes from lines 1-5 of the file
- Replace the matching root keyword with hello itcast and save it to test Txt file
- Delete vsftpd conf,smb.conf,main.cf all comment lines and blank lines in the configuration file (do not directly modify the original file)
- Use the sed command to intercept your own ip address
- Use sed command to intercept ip address, broadcast address and subnet mask at one time
- Comment out 2-3 lines of the file and match to lines starting with root or ftp
1,Replace any number in the file with an empty or tab character 2,Remove file 1-5 Number, colon, slash in line 3,matching root Replace the line of the keyword with hello itcast,And save to test.txt In the file 4,delete vsftpd.conf,smb.conf,main.cf All comment lines and blank lines in the configuration file (do not directly modify the original file) 5,use sed Command to intercept your own ip address # ifconfig eth0|sed -n '2p'|sed -n 's/.*addr://pg'|sed -n 's/Bcast.*//gp' 10.1.1.1 # ifconfig eth0|sed -n '2p'|sed 's/.*addr://g'|sed 's/ Bcast:.*//g' 6,use sed Command one-time interception ip Address, broadcast address, subnet mask # ifconfig eth0|sed -n '2p'|sed -n 's#.*addr:\(.*\) Bcast:\(.*\) Mask:\(.*\)#\1\n\2\n\3#p' 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.255 255.255.255.0 7,Comment out 2 of the document-3 Line and match to root Begin or begin with ftp First line # sed -nr '2,3s/^/#&/p;s/^ROOT|^ftp/#&/p' 1.txt #ROOT:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash #bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin #3daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin # sed -ne '1,2s/^/#&/gp' a.txt -nre 's/^lp|^mail/#&/gp' # sed -nr '1,2s/^/#&/gp;s/^lp|^mail/#&/gp' a.txt
2, Homework after class
1. Write a script to initialize the system
1) Automatically modify the host name (for example, if the ip is 192.168.0.88, the host name is changed to server88.itcast.cc)
a. Change file non interactive sed
/etc/sysconfig/network
b. Intercept the ip of the host and assign it to a variable ip; Then put the ip variable with The last bit of the split is assigned to another variable ip1
2) Automatically configure available yum sources
3) Automatically turn off firewall and selinux
2. Write a script to build ftp service. The requirements are as follows:
1) Local user login to local is not supported_ enable=NO
2) Anonymous users can upload, create and delete anon_upload_enable=YES anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES
3) Anonymous users are limited to 500KBps anon_max_rate=500000
For reference only:
#!/bin/bash
ipaddr=`ifconfig eth0|sed -n '2p'|sed -e 's/.*inet addr:\(.*\) Bcast.*/\1/g'`
iptail=`echo $ipaddr|cut -d'.' -f4`
ipremote=192.168.1.10
#Modify host name
hostname server$iptail.itcast.com
sed -i "/HOSTNAME/cHOSTNAME=server$iptail.itcast.com" /etc/sysconfig/network
echo "$ipaddr server$iptail.itcast.cc" >>/etc/hosts
#Turn off firewall and selinux
service iptables stop
setenforce 0 >/dev/null 2>&1
sed -i '/^SELINUX=/cSELINUX=disabled' /etc/selinux/config
#Configure yum source (generally intranet source)
#test network
ping -c 1 $ipremote > /dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo "Your network is blocked. Please check your network first"
exit 1
else
echo "network ok."
fi
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/server.repo << end
[server]
name=server
baseurl=ftp://$ipremote
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
end
#Install software
read -p "Please enter the software to be installed, separated by spaces:" soft
yum -y install $soft &>/dev/null
#Backup profile
conf=/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
\cp $conf $conf.default
#Modify the configuration file as required
sed -ir '/^#|^$/d' $conf
sed -i '/local_enable/c\local_enable=NO' $conf
sed -i '$a anon_upload_enable=YES' $conf
sed -i '$a anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES' $conf
sed -i '$a anon_other_write_enable=YES' $conf
sed -i '$a anon_max_rate=512000' $conf
#Start service
service vsftpd restart &>/dev/null && echo"vsftpd Service started successfully"
#Test verification
chmod 777 /var/ftp/pub
cp /etc/hosts /var/ftp/pub
#Test Download
cd /tmp
lftp $ipaddr <<end
cd pub
get hosts
exit
end
if [ -f /tmp/hosts ];then
echo "Anonymous user downloaded successfully"
rm -f /tmp/hosts
else
echo "Anonymous user download failed"
fi
#Test upload, create directory, delete directory, etc
cd /tmp
lftp $ipaddr << end
cd pub
mkdir test1
mkdir test2
put /etc/group
rmdir test2
exit
end
if [ -d /var/ftp/pub/test1 ];then
echo "Directory created successfully"
if [ ! -d /var/ftp/pub/test2 ];then
echo "File deleted successfully"
fi
else
if [ -f /var/ftp/pub/group ];then
echo "File uploaded successfully"
else
echo "Upload, create directory and delete directory Department ok"
fi
fi
[ -f /var/ftp/pub/group ] && echo "Upload file succeeded"