Git instruction
1. Initialize warehouse
git init
2. Clone a project code
git clone [url]
3. Create a new branch and switch to it
git checkout -b [branch]
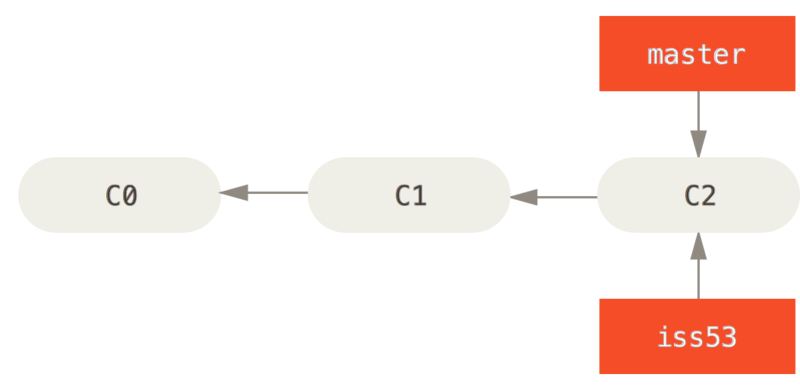
When handling a bug, you can first create a branch, then add - commit - merge, and finally delete the branch
Picture Description:
$ git checkout -b iss53 Switched to a new branch "iss53"
Explanation:
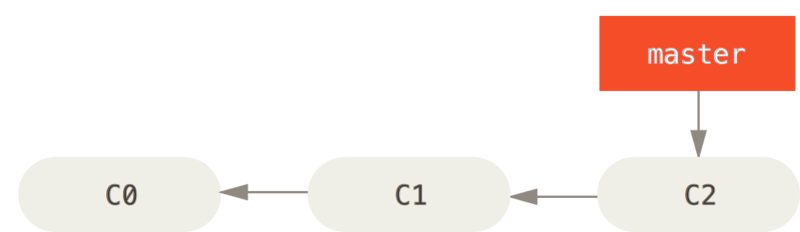
- The branch of Git is essentially just a variable pointer to the submitted object. The default branch name of Git is master. After multiple commit operations, you actually have a master branch pointing to the last commit object. The master branch automatically moves forward each time it is submitted.
- Git's master branch is not a special branch. It is no different from other branches. The reason why almost every warehouse has a master branch is that the git init command creates it by default, and most people are too lazy to change it.
4. View current branch
git branch
The git branch command will list all branches, and the current branch will be preceded by a * sign
master system_test * yunfei
5. View modified files
git status
6. Add all files in the current directory to the staging area
git add .
7. Submit staging area to warehouse area
git commit -m [message]
8. Push specified local branch to remote warehouse
git push origin dbase_bugfix That's it
9. Save file to staging area
# Save to cache
git stash save 'ID name of this temporary storage'
# View the list of staging areas
git stash list
# View recent staging saved content
git stash show
git stash show stash@{index}
# Delete the record specified in the staging area
git stash drop stash@{index}
# Empty cache
git stash clear
Restore files from scratch
# Restore recently staged content
git stash pop
# Restore the specified draft (pop will delete the contents of the staging area)
git stash pop stash@{index}
git stash apply stash@{0}
10. Cancel submission (– hard is mandatory submission and can be omitted)
git reset --hard HEAD
# Step back
git reset --hard HEAD^
# Back N steps
git reset --hard HEAD~2
# Undo specified record submission
git log
git reset --hard commit_id (Hash index value)
# Undo specified file submission
git reset HEAD README.MD ((specify file name)
git reflog (View non details)
git reset HEAD@{1} (Note that the number 1 is the version that needs to be undone)
Press q to exit git log in English
11. Download the latest changes on the remote branch (git fetch)
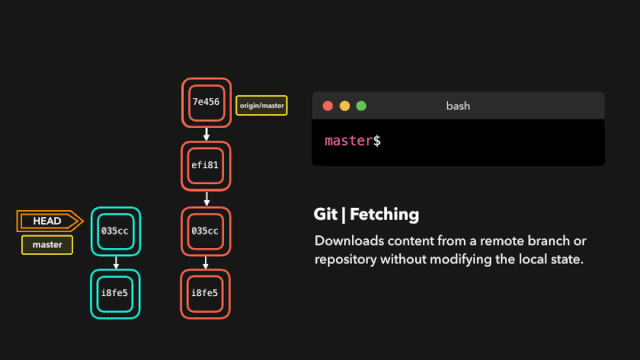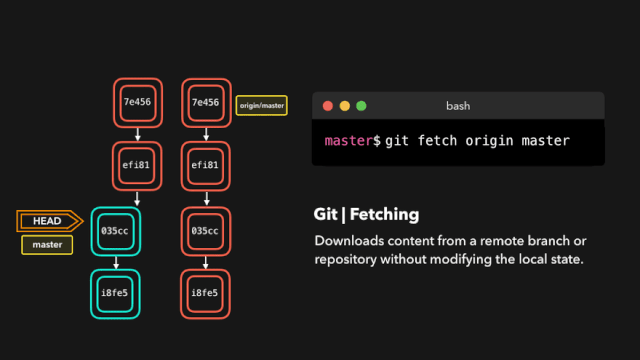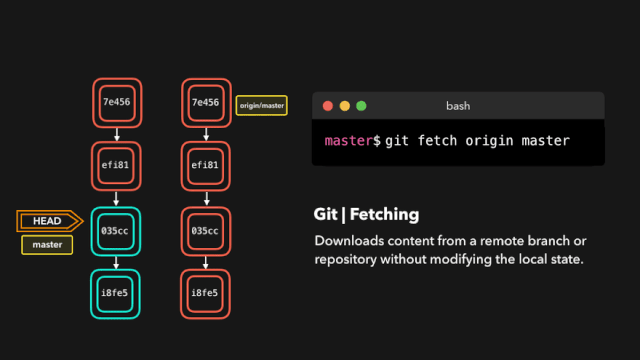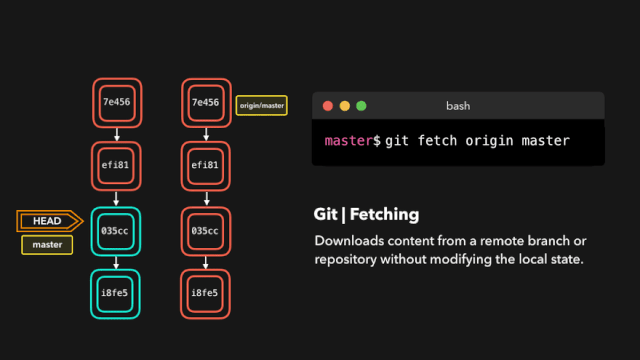
$ git fetch <Remote host name> <Branch name> For example: retrieve origin Host master Branch as follows: git fetch origin master
12. Changes from one branch are merged into the current branch
The git rebase instruction copies all the latest submissions of the current branch, and then adds these submissions to the specified branch submission record.
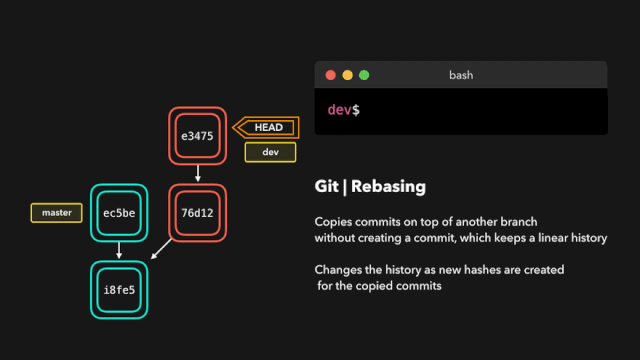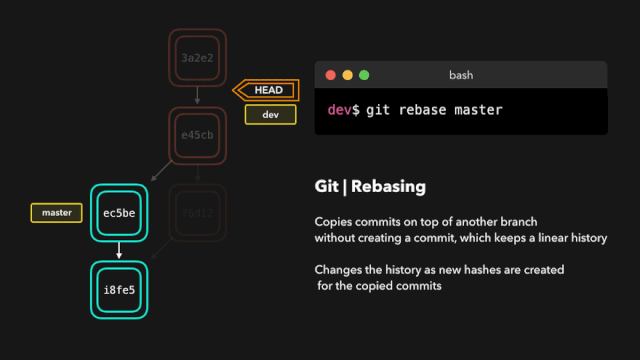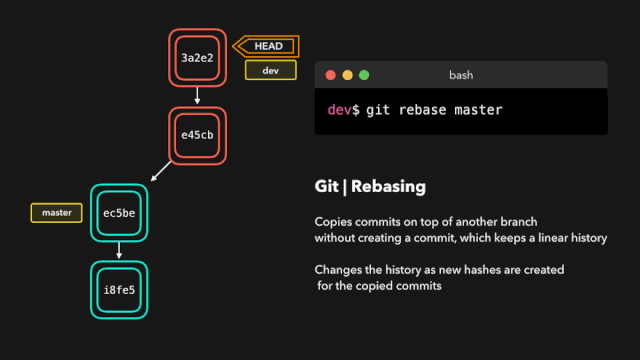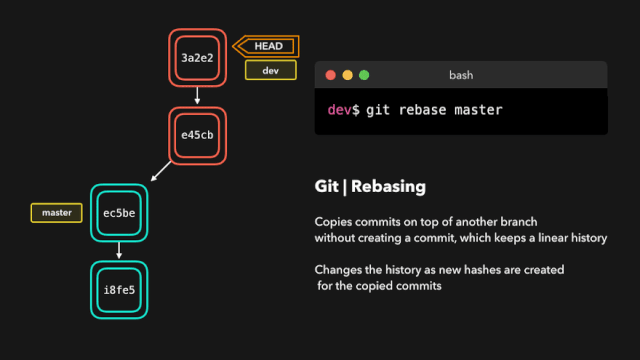
Refer to 1 for details
Refer to 2 for details
Suppose Git currently has only one branch master. The developer's workflow is
- git clone master branch
- Create a local development branch in your local checkout -b local
- Develop and test on local development branches
- After the phased development is completed (including functional code and unit test), you can prepare to submit the code
-
First, switch to the master branch, and git pull pulls the latest branch status
-
Then switch back to the local branch
-
Merge multiple local submissions into one through git rebase -i to simplify the submission history. When there are multiple local submissions, if this step is not performed, conflicts will be resolved multiple times in git rebase master (in the worst case, each submission will resolve a conflict accordingly)
-
git rebase master synchronizes the latest branch of the master to the local. This process may require manual conflict resolution (only one conflict resolution if the previous step is performed)
-
Then switch to the master branch, and git merge merges the contents of the local branch into the master branch
-
git push uploads the submission of the master branch
-
- Local development branches can be managed flexibly
git checkout master git pull git checkout local git rebase -i HEAD~2 //Merge submission - 2 means merging two git rebase master---->Conflict resolution--->git rebase --continue git checkout master git merge local git push
reference resources
1,https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42780289/article/details/98049574
2,https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI0MDQ4MTM5NQ==&mid=2247492813&idx=1&sn=886c2e6a4773fcdcaadb3e6034c07a52&chksm=e91881d1de6f08c7d8fc94dcd0f571442e665d1b6a99ab42fc72608aa7cff0adcda7b8f9324e&token=253868916&lang=zh_CN#rd
3,https://www.jianshu.com/p/6960811ac89c4
4,Four area common commands
5,git most commonly used commands