Fastjson source address: https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson
Fastjson Chinese Wiki: https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/Quick-Start-CN

I. introduce dependency
1) FastJson is a toolkit for java background processing json format data
2) FastJson mainly uses the following three classes for parsing json format strings:
(1) JSON: fastJson parser, which is used for the conversion between JSON format strings, JSON objects and JavaBeans.
(2) JSONObject: the json object provided by fastJson.
(3) JSONArray: fastJson provides json array objects.3) maven introduces dependency
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.47</version>
</dependency>II. Test demo
Note: JSON string has format requirements. It must be a key value pair, not an arbitrary string.
public class User implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int id;
private String username;
private String pazzword;
private String sex;
private Date birthday;
private Integer status; //0: inactive, 1: active
private Long ordinal; //Serial number
//get / set
}1. javaBean,list,array to json string
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(object);
/**
* javaBean,list,array convert to json string
*
* @param obj
* @return
*/
public static String obj2json(Object obj) {
return JSON.toJSONString(obj);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(100);
user.setUsername("Li Si");
user.setPazzword("lisi123");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setSex("male");
user.setStatus(1);
user.setOrdinal(10L);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(101);
user2.setUsername("Wang Wu");
user2.setPazzword("wangwu123");
user2.setBirthday(new Date());
user2.setSex("female");
user2.setStatus(1);
user2.setOrdinal(11L);
System.out.println("=javaBean=\n" + obj2json(user));
ArrayList<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(user);
list.add(user2);
System.out.println("=list=\n" + obj2json(list));
Object[] array = new Object[2];
array[0] = user;
array[1] = user2;
System.out.println("=array=\n" + obj2json(array));
} 
2. Convert json string to javaBean object
T t = JSON.parseObject(jsonString, T.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "{\"birthday\":1554885019427,\"id\":100,\"ordinal\":10,\"pazzword\":\"lisi123\",\"sex\":\"male\",\"status\":1,\"username\":\"Li Si\"}";
String jsonStr2 = "{\"birthday\":1554885019427,\"id\":100,\"ordinal\":10,\"pazzword\":\"lisi123\",\"sex\":\"male\",\"status11\":1}";
User user3 = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr, User.class);
System.out.println("=user=\n" + user3);
System.out.println("=user=\n" + JSON.parseObject(jsonStr2, User.class));
} 
Note: when javaBean object has no corresponding field in json string, the value is null
3. From json string to JSONObject
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(jsonString);
String jsonStr = "{\"birthday\":1554885019427,\"id\":100,\"ordinal\":10,\"pazzword\":\"lisi123\",\"sex\":\"male\",\"status\":1,\"username\":\"Li Si\"}";
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr);
System.out.println(jsonObject);
System.out.println(jsonObject.get("sex")); 
Note: JSONObject can obtain values through key value pairs
III. handling of complex jsonStr
There was a small business function used before
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Map<String, Object>> nodesList = new ArrayList<>();
String jsonStr = "{\r\n" +
" \"title\":\"Event flow chart\",\r\n" +
" \"nodes\":{\r\n" +
" \"1553438226938\":{\"name\":\"start\",\"left\":267,\"top\":88,\"type\":\"start round mix\",\"width\":28,\"height\":28,\"alt\":true},\r\n" +
" \"1553438229007\":{\"name\":\"End\",\"left\":277,\"top\":412,\"type\":\"end round mix\",\"width\":28,\"height\":28,\"alt\":true},\r\n" +
" \"1553438231623\":{\"name\":\"Node 1\",\"left\":\"237\",\"top\":\"169\",\"type\":\"task\",\"width\":\"104\",\"height\":\"28\",\"alt\":true,\"model\":\"node\",\"xm\":\"Zhang San\",\"xb\":\"male\"},\r\n" +
" \"1553438232544\":{\"name\":\"Node 2 left\",\"left\":\"107\",\"top\":\"251\",\"type\":\"task\",\"width\":\"104\",\"height\":\"28\",\"alt\":true,\"model\":\"node\",\"xm\":\"Li Si\",\"xb\":\"female\"},\r\n" +
" \"1553438233100\":{\"name\":\"Node 2 right\",\"left\":\"382\",\"top\":\"251\",\"type\":\"task\",\"width\":\"104\",\"height\":\"28\",\"alt\":true,\"model\":\"node\",\"xm\":\"Wang Wu\",\"xb\":\"male\"},\r\n" +
" \"1553438235571\":{\"name\":\"Node 3\",\"left\":\"242\",\"top\":\"333\",\"type\":\"task\",\"width\":\"104\",\"height\":\"28\",\"alt\":true,\"model\":\"node\",\"xm\":\"Zhao Liu\",\"xb\":\"Unknown\"}\r\n" +
" },\r\n" +
" \"lines\":{\r\n" +
" \"1553438237966\":{\"type\":\"sl\",\"from\":\"1553438226938\",\"to\":\"1553438231623\",\"name\":\"\",\"dash\":false},\r\n" +
" \"1553438238928\":{\"type\":\"sl\",\"from\":\"1553438231623\",\"to\":\"1553438233100\",\"name\":\"\",\"dash\":false},\r\n" +
" \"1553438240303\":{\"type\":\"sl\",\"from\":\"1553438231623\",\"to\":\"1553438232544\",\"name\":\"\",\"dash\":false},\r\n" +
" \"1553438241365\":{\"type\":\"sl\",\"from\":\"1553438232544\",\"to\":\"1553438235571\",\"name\":\"\",\"dash\":false},\r\n" +
" \"1553438243677\":{\"type\":\"sl\",\"from\":\"1553438233100\",\"to\":\"1553438235571\",\"name\":\"\",\"dash\":false},\r\n" +
" \"1553438245066\":{\"type\":\"sl\",\"from\":\"1553438235571\",\"to\":\"1553438229007\",\"name\":\"\",\"dash\":false}\r\n" +
" },\r\n" +
" \"areas\":{},\r\n" +
" \"initNum\":13\r\n" +
"}";
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr);
String jsonNodesStr = jsonObject.getString("nodes");
String jsonLinesStr = jsonObject.getString("lines");
//jsonStr -- Object -- Map
Map<String, Object> nodesMap = (Map<String, Object>) JSON.parse(jsonNodesStr);
Map<String, Object> linesMap = (Map<String, Object>) JSON.parse(jsonLinesStr);
for (Entry<String, Object> entry : linesMap.entrySet()) {
// Get useful information of a single node according to the lineId relationship of lines and add it to the auditList
acquireNodeByLineId(nodesList,nodesMap,linesMap,entry.getKey());
}
// Reorder the auditList in node size order
Collections.sort(nodesList, new Comparator<Map<String,Object>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map<String, Object> o1, Map<String, Object> o2) {
String lineToId = String.valueOf(o1.get("lineToId"));
String lineToId2 = String.valueOf(o2.get("lineToId"));
return lineToId.compareTo(lineToId2);
}
});
System.out.println(jsonObject.get("title"));
for (Map<String, Object> map : nodesList) {
System.out.println("nodesList == "+ map.toString());
}
}
/**
* Get useful information of a single node according to the lineId relationship of lines and add it to the list object
* @param auditorList
* @param nodesMap
* @param linesMap
* @param lineId
* @return
*/
private static void acquireNodeByLineId(List<Map<String, Object>> nodesList, Map<String, Object> nodesMap, Map<String, Object> linesMap, String lineId) {
String jsonLineStr = String.valueOf(linesMap.get(lineId));
String lineFromId = JSON.parseObject(jsonLineStr).getString("from");
String lineToId = JSON.parseObject(jsonLineStr).getString("to");
//Get information about a single node
String jsonNodeStr = String.valueOf(nodesMap.get(lineToId));
String nodeName = JSON.parseObject(jsonNodeStr).getString("name");
String nodeXm = JSON.parseObject(jsonNodeStr).getString("xm");
String nodeXb = JSON.parseObject(jsonNodeStr).getString("xb");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
if(!nodeName.equals("End")) {
map.put("nodename", nodeName);
map.put("nodexm", nodeXm);
map.put("nodexb", nodeXb);
map.put("lineFromId", lineFromId);
map.put("lineToId", lineToId);
nodesList.add(map);
}
} 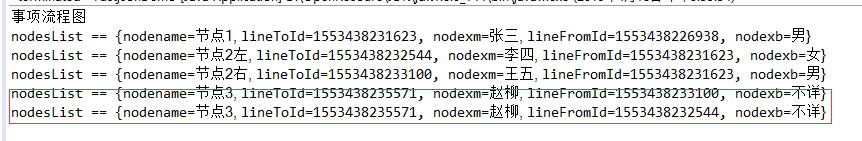

There will be no various situations in a single process line. Because it is a multi process line, there will be an additional node 3. Later, the NodeList data can be further processed according to the requirements