Now, the microservice projects developed use more distributed locks, so some records are made for the self-determined implementation of distributed locks.
*In the actual project, you can use the RLock lock of the Redisson framework directly.
Create a springboot redis project
springboot-redis-demo
Add dependency package
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId> <artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>3.2.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-integration</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.integration</groupId> <artifactId>spring-integration-redis</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
Add configuration item application.properties
spring.cache.type=redis spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.database=0 spring.redis.password=111111 spring.redis.timeout=0 spring.redis.ssl=false spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=300 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=300 spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=1 #spring.redis.cluster.nodes=127.0.0.1:6080 #spring.redis.cluster.max-redirects=10 #spring.redis.sentinel.master=127.0.0.1:6080 #spring.redis.sentinel.nodes=192.168.1.248:26379,192.168.1.249:26379,192.168.1.250:26379 #spring.data.redis.repositories.enabled=true
Create redis configuration class
Add @ EnableFeignClients annotation to configuration class
@Configuration @EnableCaching public class RediseConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport { @Autowired private RedisProperties redisProperties; @Autowired private RedisProperties.Pool redisPropertiesPool; @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "poolConfig") public JedisPoolConfig poolConfig() { JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig(); jedisPoolConfig.setBlockWhenExhausted(true); jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(redisPropertiesPool.getMaxActive()); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(redisPropertiesPool.getMaxIdle()); jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(redisPropertiesPool.getMinIdle()); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(redisPropertiesPool.getMaxWait());// 100000 jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true); jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnReturn(true); //Connection scan on Idle jedisPoolConfig.setTestWhileIdle(true); //Indicates the number of milliseconds to sleep between two scans of idle object monitor jedisPoolConfig.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(30000); //Represents the maximum number of objects per scan for idle object monitor jedisPoolConfig.setNumTestsPerEvictionRun(10); //Indicates the minimum time for an object to stay in the idle state before it can be scanned and expelled by the idle object monitor; this item only makes sense when the time between evaluation runsmillis is greater than 0 jedisPoolConfig.setMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(60000); return jedisPoolConfig; } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "jedisPool") public JedisPool jedisPool(JedisPoolConfig poolConfig) { return new JedisPool(poolConfig, redisProperties.getHost(), redisProperties.getPort(), redisProperties.getTimeout().getNano(), redisProperties.getPassword()); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisConnectionFactory") public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory(JedisPoolConfig poolConfig) { RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisStandaloneConfiguration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration(); //Set the host or ip address of the redis server redisStandaloneConfiguration.setHostName(redisProperties.getHost()); redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPort(redisProperties.getPort()); redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPassword(redisProperties.getPassword()); redisStandaloneConfiguration.setDatabase(redisProperties.getDatabase()); //Get the default connection pool construction //It should be noted here that editconnectionfactoryj has no (RedisStandaloneConfiguration, JedisPoolConfig) constructor for the Standalone mode, for which //We instantiate a constructor with the builder method of the JedisClientConfiguration interface, and we have to convert the type JedisClientConfiguration.JedisPoolingClientConfigurationBuilder jpcf = (JedisClientConfiguration.JedisPoolingClientConfigurationBuilder) JedisClientConfiguration.builder(); //Modify our connection pool configuration jpcf.poolConfig(poolConfig); //Constructing jedis client configuration through a constructor JedisClientConfiguration jedisClientConfiguration = jpcf.build(); return new JedisConnectionFactory(redisStandaloneConfiguration, jedisClientConfiguration); } @Primary @Bean public CacheManager cacheManager(@Qualifier("redisConnectionFactory") RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(); //. entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)) / / set the cache validity for one hour //. disablecacheingnullvalues(); / / do not cache null values return RedisCacheManager.builder(RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory)) .cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration).build(); } /** * Instantiate RedisTemplate object * @return */ @Bean(name = "redisTemplate") @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate") public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer(); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = this.jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer); template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); template.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer); template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); template.afterPropertiesSet(); return template; } @Bean(name = "stringRedisTemplate") @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "stringRedisTemplate") public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer(); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = this.jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer); template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); template.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer); template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); template.afterPropertiesSet(); return template; } private Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer() { ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper(); om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY); om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class); jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om); return jackson2JsonRedisSerializer; } /** * Data operation on hash type * @param redisTemplate * @return */ @Bean public HashOperations<String, String, Object> hashOperations(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) { return redisTemplate.opsForHash(); } /** * Data operation on redis string type * @param redisTemplate * @return */ @Bean public ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) { return redisTemplate.opsForValue(); } /** * Data operation on linked list type * @param redisTemplate * @return */ @Bean public ListOperations<String, Object> listOperations(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) { return redisTemplate.opsForList(); } /** * Data operations on unordered collection types * @param redisTemplate * @return */ @Bean public SetOperations<String, Object> setOperations(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) { return redisTemplate.opsForSet(); } /** * Data operations on ordered collection types * @param redisTemplate * @return */ @Bean public ZSetOperations<String, Object> zSetOperations(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) { return redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); } @Bean @Override public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() { return new KeyGenerator() { @Override public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(target.getClass().getName()); sb.append(method.getName()); for (Object obj : params) { sb.append(obj.toString()); } return sb.toString(); } }; } @Bean public RedisLockRegistry redisLockRegistry(@Qualifier("redisConnectionFactory") RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { return new RedisLockRegistry(redisConnectionFactory, "redis_locks", 6000L); } @Bean public Jedis jedis(@Qualifier("jedisPool") JedisPool jedisPool) { return jedisPool.getResource(); } }
Create RedisLockUtil tool class
@Slf4j public class RedisLockUtil implements Lock { private Jedis jedis = SpringUtils.getBean("jedis"); private static String REDIS_LOCK_KEY = "REDIS_LOCK_KEY_"; private static String REQUEST_ID = "redis_lock_id_"; /** * Lock timeout to prevent threads from waiting indefinitely after entering the lock */ private int EXPIRE_TIME_MSECS = 60 * 1000; private static final Long RELEASE_SUCCESS = 1L; public RedisLockUtil(String key){ this.REDIS_LOCK_KEY = this.REDIS_LOCK_KEY + key; } public RedisLockUtil(String key, String val){ this.REDIS_LOCK_KEY = this.REDIS_LOCK_KEY + key; this.REQUEST_ID = this.REQUEST_ID + val; } @Override public boolean tryLock() { try { if (jedis.exists(REDIS_LOCK_KEY)) { Long setNx = jedis.setnx(REDIS_LOCK_KEY, REQUEST_ID); if (setNx == 1) { return Boolean.TRUE; } } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("redis tryLock Exception", e); } return Boolean.FALSE; } @Override public void lock() { try { if (!tryLock()) { SetParams params = new SetParams(); params.px(EXPIRE_TIME_MSECS).nx(); jedis.set(REDIS_LOCK_KEY, REQUEST_ID, params); log.info(">>>>>>redis lock: {}", jedis.get(REDIS_LOCK_KEY)); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("redis lock Exception", e); } } @Override public boolean unlock() { try { if (jedis.exists(REDIS_LOCK_KEY)) { String delLock = "if redis.call('get',KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call('del',KEYS[1]) else return 0 end"; Object result = jedis.eval(delLock, Collections.singletonList(REDIS_LOCK_KEY), Collections.singletonList(REQUEST_ID)); if (RELEASE_SUCCESS.equals(result)) { return true; } } else { return true; } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("redis unlock Exception", e); } return false; } @Override public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { return false; } @Override public Condition newCondition() { return null; } @Override public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException { } }
To ensure that the automatic release time for adding locks when a lock is acquired is atomic
SetParams params = new SetParams();
params.px(EXPIRE_TIME_MSECS).nx();
jedis.set(REDIS_LOCK_KEY, REQUEST_ID, params);
xn: it means SET IF NOT EXIST, that is, when the key does not exist, set operation will be performed; if the key already exists, no operation will be performed;
px: it means to add an expiration time of MSECS to the key.
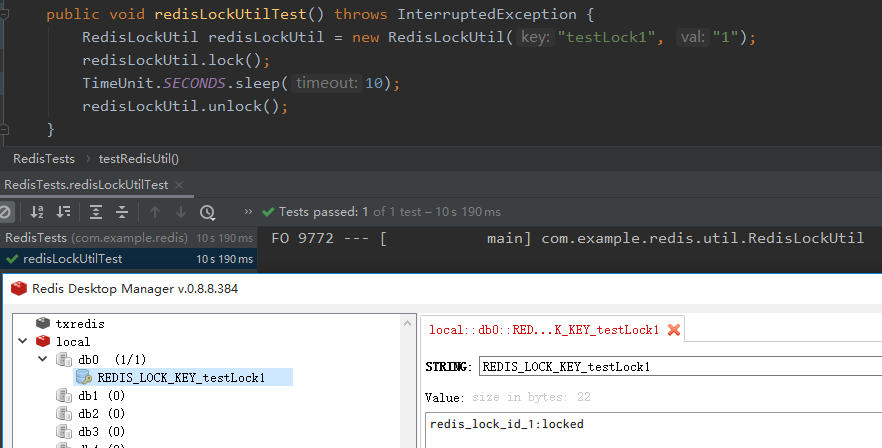
Create unit test test class
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootRedisDemoApplication.class) public class RedisTests { @Autowired private RedisUtils redisUtil; @Test public void redisLockUtilTest() throws InterruptedException { RedisLockUtil redisLockUtil = new RedisLockUtil("testLock1", "1"); redisLockUtil.lock(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); redisLockUtil.unlock(); } }
test result
You can see the status of the lock in redis when it is locked
Source code example: https://gitee.com/lion123/springboot-redis-demo
*What happens when the redis distributed lock expires but the business is not finished?
Directly use the RLock of the Redisson framework. After the successful acquisition of the redisson RLock lock, a scheduled task (a background thread) will be registered to check the expiration time of the lock every 10 seconds (the default life time of the locked key is 30 seconds). If the current thread still holds the lock key, the life time of the lock key will be continuously extended.