Hello, I'm brother Cheng~
Today I share the window function foundation of SQL.
catalog:
1. What is the window function
2. Sorting function
3. Distribution function
4. Front and back functions
5. Head and tail function
6. Aggregate function
[note] there is a technical exchange group at the end of the text
Recommended articles
-
Someone made the Chinese version of Miss Wu Enda's machine learning and deep learning
-
Addicted, I recently gave the company a large visual screen (with source code)
-
So elegant, four Python automatic data analysis artifacts are really fragrant
1. What is the window function
Window function, also known as OLAP function (online analytical processing), can analyze and process database data in real time.
mysql has supported window function since version 8.0. Today, we take mysql as an example to introduce this window function.
Window actually refers to a record set, and window function is to execute the specified function method on the record set that meets some conditions. Common examples in daily work, such as seeking the ranking of students' single subject scores, seeking the top three, and so on.
The basic syntax of window functions is as follows:
<Window function> OVER (PARTITION BY <Column name for grouping> ORDER BY <Column name for sorting>)
For example, some aggregate functions such as SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MAX() and MIN(), as well as special window functions RANK(), deny ()_ RANK() and ROW_NUMBER() and so on.
2. Sorting function
Is to sort and display the ranking
RANK(),DENSE_RANK() and ROW_NUMBER()
Let's create a data table as follows:
DROP TABLE
IF
EXISTS school report;
CREATE TABLE school report ( Student number VARCHAR ( 8 ), full name VARCHAR ( 8 ), subject VARCHAR ( 8 ), score INT ) ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
INSERT INTO school report
VALUES
('1000', 'Xiao Ming', 'language' ,112 ),
('1000', 'Xiao Ming', 'mathematics' ,120 ),
('1000', 'Xiao Ming', 'English' ,92 ),
('1001', 'cloud', 'language' ,112 ),
('1001', 'cloud', 'mathematics' ,118 ),
('1001', 'cloud', 'English' ,99 ),
('1002', 'Curry', 'language' ,101 ),
('1002', 'Curry', 'mathematics' ,111 ),
('1002', 'Curry', 'English' ,90 ),
('1003', 'Talent', 'language' ,112 ),
('1003', 'Talent', 'mathematics' ,120 ),
('1003', 'Talent', 'English' ,112 ),
('1004', 'Xiaohua', 'language' ,112 ),
('1004', 'Xiaohua', 'mathematics' ,112 ),
('1004', 'Xiaohua', 'English' ,112 ),
('1005', 'Johnson', 'language' ,92 ),
('1005', 'Johnson', 'mathematics' ,120 ),
('1005', 'Johnson', 'English' ,92 );
This is a transcript, including student number, name, subject and score.
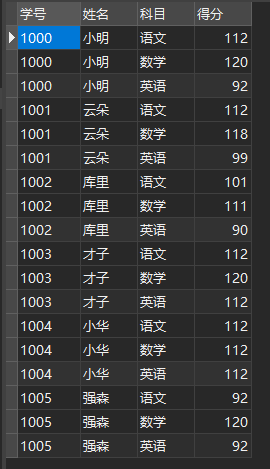
Transcript
In the face of the above data, we require students of all subjects to rank by score, so we can use the ranking function.
For example, RANK()
SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS RANK_ranking FROM school report
This operation is to group by account, and then sort by score (DESC is from large to small).
The results are as follows:
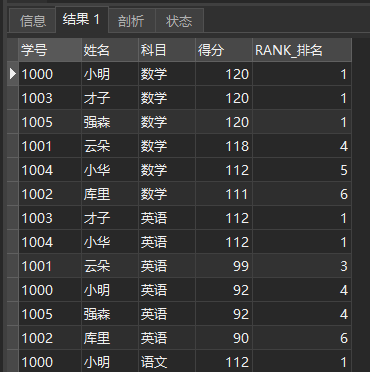
RANK()
It can be seen that rank does not exist in the same rank.
Let's look at RANK() and DENSE_RANK() and ROW_NUMBER() the difference between the three:
SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS RANK_ranking , DENSE_RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS DENSE_RANK_ranking , ROW_NUMBER() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS ROW_NUMBER_ranking FROM school report
The results are compared as follows:
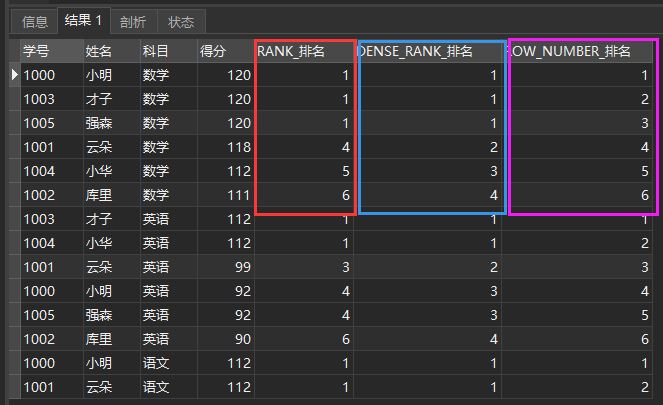
Difference comparison
It can be seen that the functions of these three are as follows:
| function | explain |
|---|---|
| ROW_NUMBER | Assign a sequence number to each row in the table. You can specify grouping (or not) and sorting fields (continuous and non repetitive) |
| DENSE_RANK | Assign a sequence number to each row in each group according to the sorting field. When the ranking value is the same, the sequence number is the same, and there is no gap in the sequence number (such as 1,1,1,2,3) |
| RANK | Assign a sequence number to each row in each group according to the sorting field. When the ranking value is the same, the sequence number is the same, but there is a gap in the sequence number (such as 1,1,1,4,5) |
If we want to get the students ranking first in each subject and their scores, we can add a condition to judge. Note that sub query is used here.
SELECT * FROM ( SELECT *, DENSE_RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS DENSE_RANK_ranking FROM school report ) a WHERE DENSE_RANK_ranking = 1;
The query results are as follows:
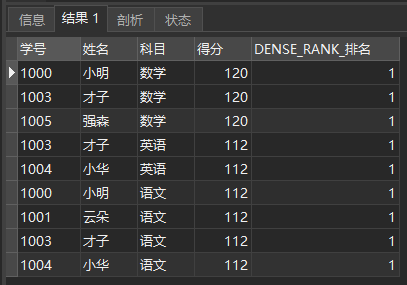
DENSE_RANK_ Ranked first
Another NTILE(n) divides the ordered data in the partition into N levels and records the number of levels
For example, it is divided into two grades according to the score ranking of student number partition
SELECT *, NTILE(2) OVER ( PARTITION BY Student number ORDER BY score DESC ) AS NTILE_ FROM school report
The query results are as follows:
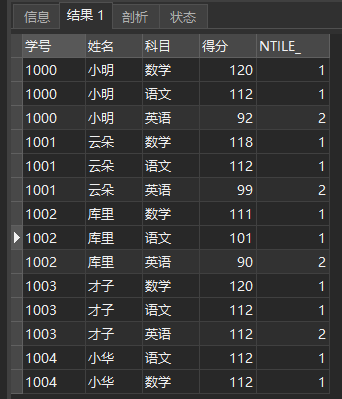
NTILE(2)
NTILE(n) is widely used in data analysis. For example, due to the large amount of data, it is necessary to evenly distribute the data to N parallel processes for calculation respectively. At this time, NTILE(n) can be used to group the data (because the number of records is not necessarily divided by n, the data may not be completely average), and then redistribute the data of different bucket numbers.
3. Distribution function
The distribution function has two PERCENT_RANK() and cube_ DIST()
**PERCENT_RANK() * * is used to calculate each row according to the formula (rank-1) / (rows-1). Where rank is the sequence number generated by RANK() function, and rows is the total number of records in the current window.
SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS RANK_ranking , PERCENT_RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS PERCENT_RANK_ FROM school report
The query results are as follows:
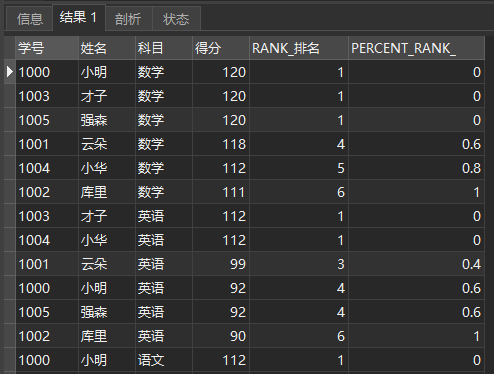
PERCENT_RANK()
CUME_ The purpose of dist() is the number of rows in the group less than or equal to the current rank value / the total number of rows in the group.
Query the proportion of less than or equal to the current score
SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS RANK_ranking , CUME_DIST() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS CUME_DIST_ FROM school report
The query results are as follows:
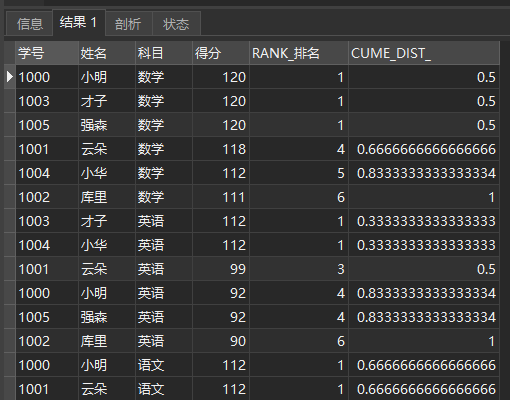
CUME_DIST()
It can be seen that in mathematics subjects, 0.5, that is, 50% of friends score 120, and more than 66.66% of students score 118 or above.
4. Front and back functions
Query the data in the front and back N rows of the specified field in the current row, LAG() and LEAD()
LAG(expr[,N[,default]]) in the first N lines. For example, we look at the scores of the top 3 students in each subject.
SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS RANK_ranking , LAG(score, 3) OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC) AS LAG_ FROM school report
The query results are as follows:
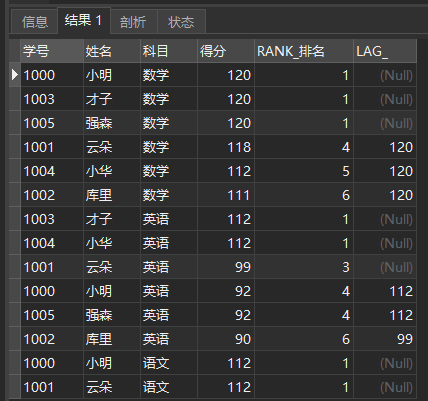
Lag (score, 3)
It can be seen that the three lines of each section are NULL values at present, because the first three lines do not have the values of the previous three lines. The first three of rank 4 are rank 1 and the corresponding score is 120.
This can be used for some cases such as month on month comparison. Here, we can calculate the score difference between the current student and the top student. The operation is as follows:
SELECT *, LAG_ - score FROM ( SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS RANK_ranking, LAG(score, 1 ) OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS LAG_ FROM school report ) a
The query results are as follows:
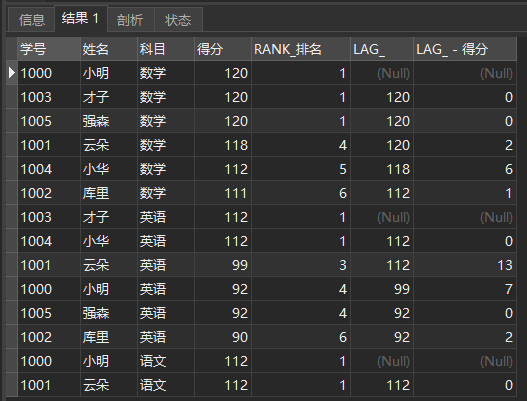
**LEAD(expr[,N[,default]] * *) is the next N names, which will not be repeated here.
5. Head and tail function
Query the first or last data of the specified field FIRST_VALUE(expr) and LAST_VALUE(expr)
Query the 1st score of each account
SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS RANK_ranking, FIRST_VALUE(score) OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS FIRST_VALUE_score FROM school report
The query results are as follows:
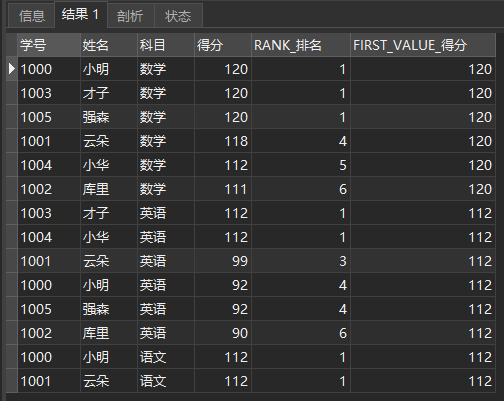
FIRST_ Value (score)
We can calculate the gap between each student and the first place (the gap between each student and the first place is introduced in the front and back functions above):
SELECT *, FIRST_VALUE_score - score FROM ( SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS RANK_ranking, FIRST_VALUE(score) OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS FIRST_VALUE_score FROM school report ) a
The query results are as follows:
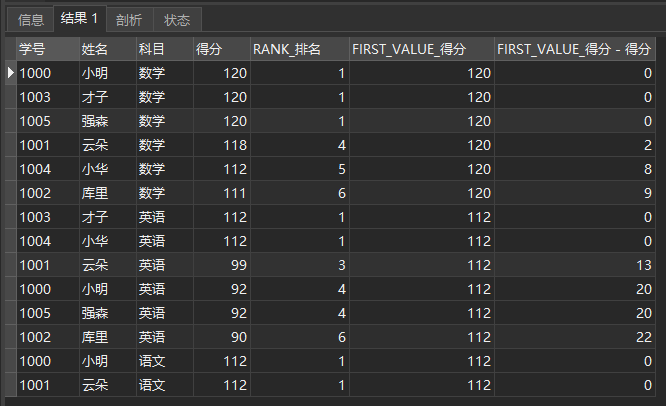
LAST_VALUE(expr) is the last one. I won't repeat it here.
And NTH_VALUE(expr, n) queries the nth value of the ordered row of the specified field
For example, query the data ranking No. 4
SELECT *, RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS RANK_ranking, NTH_VALUE(score,4) OVER ( PARTITION BY subject ORDER BY score DESC ) AS NTH_VALUE_score FROM school report
The query results are as follows:
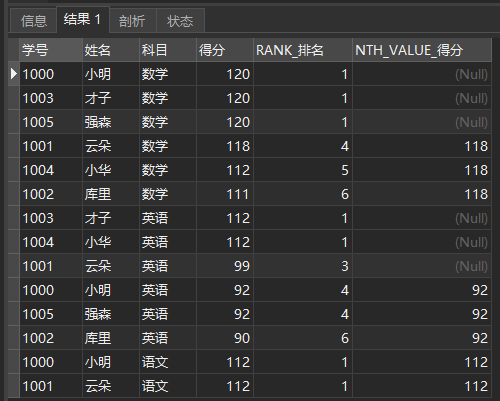
NTH_ Value (score, 4)
6. Aggregate function
Aggregate functions (SUM(), AVG(), MAX(), MIN(), COUNT()) are dynamically applied to each record in the window, and various aggregate function values in the specified window can be dynamically calculated.
Therefore, here we construct a data table with time field.
DROP TABLE
IF
EXISTS Chinese transcript;
CREATE TABLE Chinese transcript ( Student number VARCHAR ( 8 ), full name VARCHAR ( 8 ), time DATE, score INT ) ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
INSERT INTO Chinese transcript
VALUES
('1000', 'Xiao Ming', '2022-01-02' ,102 ),
('1001', 'cloud', '2022-01-04' ,112 ),
('1002', 'Curry', '2022-01-07' ,101 ),
('1003', 'Talent', '2022-01-07' ,118 ),
('1004', 'Xiaohua', '2022-01-08' ,112 ),
('1005', 'Johnson', '2022-01-09' ,92 );
This is a Chinese transcript, including student number, name, time and score.
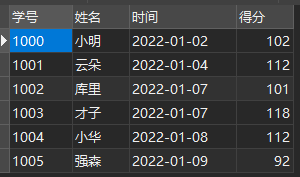
Chinese transcript
For example, if we want to query the highest score of Chinese at each deadline, we can operate as follows:
SELECT *, MAX(score) OVER ( ORDER BY time ) AS MAX_ FROM Chinese transcript
The query results are as follows:
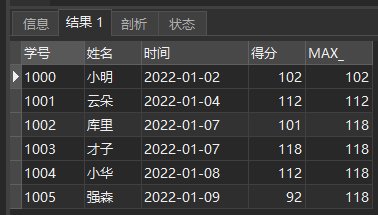
Max (score)
The above is the basic introduction of this time. The actual operation of daily work should be more complex. However, we will always find that the complexity is made up of many basic splices. If we lay a good foundation, we can become very strong!
Give me some praise, watch it, and then let's cheer together~
Technical exchange
Welcome to reprint, collect, gain, praise and support!

At present, the interview technology exchange group has been opened, and the group has more than 2000 friends. The best way to add notes is: source + Interest direction, which is convenient to find like-minded friends
- Method ① send the following pictures to wechat, long press to identify, and the background replies: add group;
- Mode ②. Add micro signal: dkl88191, remarks: from CSDN
- WeChat search official account: Python learning and data mining, background reply: add group
