Processes and threads
Process is the basic unit that can run independently and allocate resources in a computer system. It is composed of PCB (process control block), data segment and code segment. It is a basic unit that can run independently. The creation, scheduling and allocation of processes require large time and space overhead. Threads are introduced into the operating system, and threads are used as scheduling. The basic unit of allocation to improve the performance of multiprocessor systems
Threads are the smallest unit in which the operating system can schedule operations. Threads in the same process share all system resources in the process.
The difference between processes and threads:
- Each time a process is scheduled, context switching is needed to save the breakpoint information in PCB, which costs a lot. In thread scheduling, only a small number of registers need to be saved and set, and the switching cost is relatively small.
- As the basic unit of system resource allocation, process has certain resources, including disk and memory address space for storing program, data, I/O devices needed when it runs, open semaphores, etc. A set of registers and stacks that indicate the sequence of instructions to be executed, hold local variables, a few state parameters, return addresses, etc., allowing multiple threads to share memory address space and resources in the process.
Two ways to implement threads in java
In java, programs are allowed to run multiple threads concurrently, concurrency refers to the simultaneous occurrence of two or more events at the same time interval, and concurrency refers to the simultaneous execution of two or more events at the same time.
1. Inherit the Thread class and override the run() method
Thread represents the thread class. The run method is what we do when we start the thread. We should start the thread by using the start() method. To call the run method directly is equivalent to the ordinary method call. Next, we define a thread class to output 0 to 9 by inheriting the Thread class. Then we create two instances of the thread class in the main method. And start the thread, you can see that the thread execution is random. Thread scheduling details depend on the operating system. Preemptive thread scheduling gives each thread a time slice to run the thread. When the time slice is over, the system will save the status of the current thread, and then terminate the execution of the current thread and execute another thread. When the next time slice is over, the current thread of execution is terminated, and so on. Until all threads terminate.
1 public class FirstThread extends Thread{ 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) { 5 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"Printing"+i); 6 } 7 } 8 } 9 public class FirstDemo { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 Thread thread = new FirstThread(); 12 Thread thread2 = new FirstThread(); 13 thread.start(); 14 thread2.start(); 15 } 16 }
2. Implementing Runnable Interface
The Thread class has a constructor whose parameter is a Runnable object, which can create a thread with a given Runnable object.
1 public class FirstThread implements Runnable{ 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) { 5 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"Printing"+i); 6 } 7 } 8 } 9 public class FirstDemo { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 Thread thread = new Thread(new FirstThread()); 12 Thread thread2 = new Thread(new FirstThread()); 13 thread.start(); 14 thread2.start(); 15 } 16 }
Thread properties
Thread name (default Thread-serial number at thread initialization)
1 private String name; 2 3 // Set the name of the thread 4 public final synchronized void setName(String name) { 5 checkAccess(); // Check whether thread parameters are allowed to be changed 6 7 if (name == null) { 8 throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); 9 } 10 11 this.name = name; 12 if (threadStatus != 0) { // Judging the state of threads 13 setNativeName(name); 14 } 15 } 16 17 // Get the name of the thread 18 public final String getName() { 19 return name; 20 }
Thread priority (default is parent thread priority)
1 private int priority; 2 3 public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1; // Minimum priority of threads 4 5 public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5; // Default priority of threads 6 7 public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10; // Maximum priority of threads 8 9 // Setting Thread Priority 10 public final void setPriority(int newPriority) { 11 ThreadGroup g; 12 checkAccess(); // Security check 13 14 // Check whether the set priority is greater than the maximum priority or the minimum priority,If the parameter is thrown illegally 15 if (newPriority > MAX_PRIORITY || newPriority < MIN_PRIORITY) { 16 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 17 } 18 19 // Get the current thread group 20 if((g = getThreadGroup()) != null) { 21 // If the current set priority is greater than its maximum priority on the thread group 22 if (newPriority > g.getMaxPriority()) { 23 // Set the priority of the current thread to the maximum priority of the current thread group 24 newPriority = g.getMaxPriority(); 25 } 26 // Call local methods setPriority0 Setting Thread Priority 27 setPriority0(priority = newPriority); 28 } 29 } 30 31 // Get the priority of the current thread 32 public final int getPriority() { 33 return priority; 34 } 35
Is the thread a daemon thread (default is the value of the parent thread)
Daemon threads are threads that serve other threads. When only daemon threads are left in a program, the java virtual machine will quit the program. That is to say, daemon threads exist on the basis of user threads. The termination of user threads will cause the termination of daemon threads. Whatever the current state, daemon threads should be avoided when using daemon threads. A daemon-free thread accesses inherent resources, such as files, databases, etc. It interrupts in the middle of any operation.
1 private boolean daemon; 2 3 // Set whether the thread is a daemon thread 4 public final void setDaemon(boolean on) { 5 // Security check 6 checkAccess(); 7 8 // If the thread is active,Throws an exception that indicates that there is no proper state operation on the thread 9 if (isAlive()) { 10 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); 11 } 12 // Set whether a thread is a daemon thread 13 daemon = on; 14 } 15 // Determine whether the current thread is active 16 public final native boolean isAlive(); 17 18 // Determine whether the current thread is a daemon thread 19 public final boolean isDaemon() { 20 return daemon; 21 }
Status of threads
The state of a thread is represented by an internal static enumeration class
1 public enum State { 2 3 NEW, // New status 4 5 RUNNABLE, // Runnable state 6 7 BLOCKED, // Blocking state 8 9 WAITING, // Waiting state 10 11 TIMED_WAITING, // The state of waiting for a period of time. 12 13 TERMINATED; // Termination status 14 } 15 16 // Gets the status of the current thread 17 public State getState() { 18 // get current thread state 19 return sun.misc.VM.toThreadState(threadStatus); 20 }
Uncaptured exception handlers for threads
The run method of a thread does not throw any checked exception. If an exception is thrown at runtime, but the exception is not caught and handled, the thread is about to terminate. At this point, the thread and exception will be used as parameters to call the method of the Uncaptured exception handler, which is a class that implements the UncaughtException Handler interface. UncaughtException is a static inner class of Thread, and there is only one method inside it: void uncaughtException (Thread, Throwable); this method will be called when the thread terminates due to an uncovered exception. The ThreadGroup class implements this interface. The Thread class has two variables of UncaughtException Handler interface, one is silent. The recognized processor (decorated with static) is used by all threads and the other is only used by the current thread. By default, both variables are null, and the Uncaptured exception processor used by the thread is the processor of the thread group.
1 // For current threads 2 private volatile UncaughtExceptionHandler uncaughtExceptionHandler; 3 4 // Gets the Uncaptured exception handler for the current thread 5 public UncaughtExceptionHandler getUncaughtExceptionHandler() { 6 // If the current thread has no uncovered exception handler,Returns the processor of the thread group to which the thread belongs 7 return uncaughtExceptionHandler != null ? 8 uncaughtExceptionHandler : group; 9 } 10 // Setting the Uncaptured exception handler for the current thread 11 public void setUncaughtExceptionHandler(UncaughtExceptionHandler eh) { 12 checkAccess(); 13 uncaughtExceptionHandler = eh; 14 } 15 16 // For all threads 17 private static volatile UncaughtExceptionHandler defaultUncaughtExceptionHandler; 18 19 // Get the default Uncaptured exception handler 20 public static UncaughtExceptionHandler getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(){ 21 return defaultUncaughtExceptionHandler; 22 } 23 // Setting the default Uncaptured exception handler 24 public static void setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(UncaughtExceptionHandler eh) { 25 26 // Getting System Security Manager 27 SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); 28 if (sm != null) { 29 // Check whether requests with given permissions are allowed to execute,If not allowed,Throw out SecurityException abnormal 30 sm.checkPermission( 31 32 // Create a thread that terminates suddenly because of an uncovered exception,Set the runtime permission object of the default handler to be used 33 new RuntimePermission("setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler") 34 ); 35 } 36 // Setting the default Uncaptured exception handler 37 defaultUncaughtExceptionHandler = eh; 38 }
1 // ThreadGroup Realization Thread.Uncaughtexception Source code parsing of interface 2 public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) { 3 // If the thread group has a parent thread group,The processor that uses the parent thread group 4 if (parent != null) { 5 parent.uncaughtException(t, e); 6 } else { 7 8 // Get the default Uncaptured exception handler 9 Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler ueh = 10 Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(); 11 12 // Use it if there is a default exception handler 13 if (ueh != null) { 14 ueh.uncaughtException(t, e); 15 16 } 17 // Otherwise, determine if the exception causing thread termination is ThreadDeath Subclasses,If it is,Do nothing,Responsible for exporting thread name and stack information to standard error stream,ThreadDeath yes 18 else if (!(e instanceof ThreadDeath)) { 19 System.err.print("Exception in thread \"" 20 + t.getName() + "\" "); 21 e.printStackTrace(System.err); 22 } 23 } 24 }
Thread Group
Thread group is a set of unified managed threads. In addition to the initial thread group, each thread group has a parent thread group. Thread group can also contain other thread groups, allowing threads to access information about their own thread group, but not the parent thread group or any other thread group of their thread group. In this case, the thread groups created belong to the main thread group. There are two ways to construct the thread group
Thread Group Properties
1 private final ThreadGroup parent; // Parent Thread Group,Once specified, non-modifiable 2 String name; // Thread group name 3 int maxPriority; // Maximum Priority of Thread Groups 4 boolean destroyed; // Are Thread Groups Destroyed 5 boolean daemon; // Is a thread group a daemon thread group? 6 boolean vmAllowSuspension; // Automatic suspension of virtual machine 7 8 int nUnstartedThreads = 0; // Number of Unstarted Threads in Thread Group 9 int nthreads; // The number of threads contained in this thread group 10 Thread[] threads[]; // Threads included in this thread group 11 12 int ngroups; // Subthread Group Counter 13 ThreadGroup[] groups; // Thread groups included in this thread group
1 Constructor call order from top to bottom 2 3 //Use the specified thread group name to construct the thread group 4 public ThreadGroup(String name) { 5 // Gets the parent thread group of the current thread group 6 this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name); 7 } 8 9 //Specify threads when creating a parent thread group,And the name is name Thread group 10 public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) { 11 // Check the parent thread group 12 this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name); 13 } 14 15 16 //Check Thread Group Security 17 private static Void checkParentAccess(ThreadGroup parent) { 18 parent.checkAccess(); 19 return null; 20 } 21 //Security check 22 public final void checkAccess() { 23 SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); 24 if (security != null) { 25 security.checkAccess(this); 26 } 27 } 28 29 private ThreadGroup(Void unused, ThreadGroup parent, String name) { 30 // Setting Thread Group Name 31 this.name = name; 32 // Maximum priority is the maximum priority of the parent thread group 33 this.maxPriority = parent.maxPriority; 34 // Is it the daemon thread combination parent thread group consistent? 35 this.daemon = parent.daemon; 36 // Virtual Machine Parameters 37 this.vmAllowSuspension = parent.vmAllowSuspension; 38 this.parent = parent; 39 parent.add(this); 40 } 41 // Add the specified thread group 42 private final void add(ThreadGroup g) { 43 synchronized (this) { 44 // If the thread group has been destroyed,throw 45 if (destroyed) { 46 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); 47 } 48 // Determine whether the subthread array of this thread group is empty or full 49 // If empty,Create an array of sub-threads,Initial capacity is 4,Adds a specified thread group to the array,Counter plus one; 50 // If the subthread array is full,Array capacity doubled,Save the specified thread group into an array,Counter plus one 51 // If the subthread array is not full,Adds a specified thread group to the array,Counter plus one 52 if (groups == null) { 53 groups = new ThreadGroup[4]; 54 } else if (ngroups == groups.length) { 55 groups = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroups * 2); 56 } 57 groups[ngroups] = g; 58 ngroups++; 59 } 60 }
Other methods
1 // Remove the specified thread group 2 private void remove(ThreadGroup g) { 3 synchronized (this) { 4 // Determine whether the thread group is dead 5 if (destroyed) { 6 return; 7 } 8 // Loop traversal subthread array,Find the thread group to delete,If found,Subthread group counter minus one 9 // Move the element behind the thread group element forward,Empty the last element,Break 10 for (int i = 0; i < ngroups; i++) { 11 if (groups[i] == g) { 12 ngroups -= 1; 13 System.arraycopy(groups, i + 1, groups, i, ngroups - i); 14 groups[ngroups] = null; 15 break; 16 } 17 } 18 19 // Wake up all waiting threads on this object 20 if (nthreads == 0) { 21 notifyAll(); 22 } 23 // If this thread group satisfies the following conditions at the same time,Destroy the thread group and its subgroups 24 // 1. Is the daemon thread group 25 // 2. The number of threads included is 0 26 // 3. The number of unstarted threads is 0 27 // 4. The number of threads included is 0 28 if (daemon && (nthreads == 0) && (nUnstartedThreads == 0) && (ngroups == 0)) { 29 destroy(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 34 // Adds a specified thread to the thread group 35 void add(Thread t) { 36 synchronized (this) { 37 if (destroyed) { 38 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); 39 } 40 if (threads == null) { 41 threads = new Thread[4]; 42 } else if (nthreads == threads.length) { 43 threads = Arrays.copyOf(threads, nthreads * 2); 44 } 45 threads[nthreads] = t; 46 nthreads++; 47 // To prevent thread groups from being destroyed,Decreasing number of unstarted threads 48 nUnstartedThreads--; 49 } 50 } 51 52 // Remove the specified thread 53 private void remove(Thread t) { 54 synchronized (this) { 55 if (destroyed) { 56 return; 57 } 58 for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { 59 if (threads[i] == t) { 60 System.arraycopy(threads, i + 1, threads, i, --nthreads - i); 61 threads[nthreads] = null; 62 break; 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 68 // Get the name of the thread group 69 public final String getName() { 70 return name; 71 } 72 73 // Get the maximum priority of the thread group 74 public final int getMaxPriority() { 75 return maxPriority; 76 } 77 78 // Get the parent thread group of the thread group 79 public final ThreadGroup getParent() { 80 if (parent != null) 81 parent.checkAccess(); 82 return parent; 83 } 84 85 // Determine whether the thread group is a daemon thread group 86 public final boolean isDaemon() { 87 return daemon; 88 } 89 90 // Determine whether the thread group is destroyed 91 public synchronized boolean isDestroyed() { 92 return destroyed; 93 } 94 95 // Set the maximum priority for this thread group 96 public final void setMaxPriority(int pri) { 97 int ngroupsSnapshot; 98 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 99 100 synchronized (this) { 101 checkAccess(); 102 // Determine whether a given priority meets the requirements,Non-conforming direct return 103 if (pri < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || pri > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) { 104 return; 105 } 106 107 // If the current thread group does not have a parent thread group,The maximum priority is a given value 108 // Otherwise, determine the maximum priority and specified priority of the parent thread group,Take the minimum value as the maximum priority of the thread group 109 maxPriority = (parent != null) ? Math.min(pri, parent.maxPriority) : pri; 110 111 // Get a snapshot of the thread subthread group(If it exists 112 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 113 if (groups != null) { 114 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 115 } else { 116 groupsSnapshot = null; 117 } 118 } 119 // Traversing through all subthread groups of the thread group,Recursively sets the maximum priority to the specified value 120 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 121 groupsSnapshot[i].setMaxPriority(pri); 122 } 123 } 124 125 // Set whether the thread group is a daemon thread 126 public final void setDaemon(boolean daemon) { 127 checkAccess(); 128 this.daemon = daemon; 129 } 130 131 // Test whether this thread group is the ancestor of the specified thread group 132 public final boolean parentOf(ThreadGroup g) { 133 for (; g != null; g = g.parent) { 134 if (g == this) { 135 return true; 136 } 137 } 138 return false; 139 } 140 141 // Destroy this thread group and its subgroups 142 public final void destroy() { 143 int ngroupsSnapshot; 144 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 145 synchronized (this) { 146 checkAccess(); 147 // If the thread group has been destroyed or there are active threads in the thread group,Throw an exception 148 if (destroyed || (nthreads > 0)) { 149 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); 150 } 151 // Get a snapshot of the subthread group(If it exists) 152 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 153 if (groups != null) { 154 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 155 } else { 156 groupsSnapshot = null; 157 } 158 159 // If the thread group has a parent thread group,Empty all attributes 160 if (parent != null) { 161 destroyed = true; 162 ngroups = 0; 163 groups = null; 164 nthreads = 0; 165 threads = null; 166 } 167 } 168 // Loop through subthread groups,Recursive processing for each subthread group 169 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i += 1) { 170 groupsSnapshot[i].destroy(); 171 } 172 173 // If a thread group has a parent thread group,Remove the thread group from the parent thread group 174 if (parent != null) { 175 parent.remove(this); 176 } 177 } 178 179 // Get the number of threads active in this thread group 180 public int activeCount() { 181 int result; 182 int ngroupsSnapshot; 183 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 184 synchronized (this) { 185 if (destroyed) { 186 return 0; 187 } 188 result = nthreads; 189 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 190 if (groups != null) { 191 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 192 } else { 193 groupsSnapshot = null; 194 } 195 } 196 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 197 result += groupsSnapshot[i].activeCount(); 198 } 199 return result; 200 } 201 202 // Get the number of threads that are active in this thread group 203 public int activeGroupCount() { 204 int ngroupsSnapshot; 205 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 206 synchronized (this) { 207 if (destroyed) { 208 return 0; 209 } 210 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 211 if (groups != null) { 212 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 213 } else { 214 groupsSnapshot = null; 215 } 216 } 217 int n = ngroupsSnapshot; 218 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 219 n += groupsSnapshot[i].activeGroupCount(); 220 } 221 return n; 222 } 223 224 // Export information about this thread group to the standard output stream 225 public void list() { 226 list(System.out, 0); 227 } 228 229 void list(PrintStream out, int indent) { 230 int ngroupsSnapshot; 231 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 232 synchronized (this) { 233 for (int j = 0; j < indent; j++) { 234 out.print(" "); 235 } 236 out.println(this); 237 indent += 4; 238 for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { 239 for (int j = 0; j < indent; j++) { 240 out.print(" "); 241 } 242 out.println(threads[i]); 243 } 244 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 245 if (groups != null) { 246 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 247 } else { 248 groupsSnapshot = null; 249 } 250 } 251 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 252 groupsSnapshot[i].list(out, indent); 253 } 254 } 255 256 // Returns a string description of this class:Class name+Thread group name+Maximum priority 257 public String toString() { 258 return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + getName() + ",maxpri=" + maxPriority + "]"; 259 } 260 261 // All threads and sub-threads in interrupt threads group 262 public final void interrupt() { 263 int ngroupsSnapshot; 264 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 265 synchronized (this) { 266 checkAccess(); 267 // Interrupt the included thread 268 for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { 269 threads[i].interrupt(); 270 } 271 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 272 if (groups != null) { 273 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 274 } else { 275 groupsSnapshot = null; 276 } 277 } 278 // Traversing subthread groups,Recursive processing of each subthread group 279 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 280 groupsSnapshot[i].interrupt(); 281 } 282 } 283 284 // Copies all active threads of the thread group into the specified array. If a second parameter exists,The second parameter is true Represents active threads that contain subgroups,The default number of active threads in a subgroup, 285 // When a given array is insufficient to accommodate the number of active threads in that thread group,Ignore additional threads,therefore,Better call activeCount Method to determine if less than list Length 286 public int enumerate(Thread list[]) { 287 checkAccess(); 288 return enumerate(list, 0, true); 289 } 290 291 public int enumerate(Thread list[], boolean recurse) { 292 checkAccess(); 293 return enumerate(list, 0, recurse); 294 } 295 296 private int enumerate(Thread list[], int n, boolean recurse); 297 298 // Copies all active subgroups of the thread group into the specified array. If a second parameter exists,The second parameter is true Represents an active subgroup in a containing subgroup,Default contains all active subgroups in subgroups, 299 // When the given array is insufficient to accommodate the active subarray of the thread group,Ignore additional subgroups,therefore,Better call activeGroupCount Method to determine if less than list Length 300 301 public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[]) { 302 checkAccess(); 303 return enumerate(list, 0, true); 304 } 305 306 public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[], boolean recurse) { 307 checkAccess(); 308 return enumerate(list, 0, recurse); 309 } 310 311 private int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[], int n, boolean recurse); 312 313 // allow Java The virtual machine is suspended because of insufficient memory 314 @Deprecated 315 public boolean allowThreadSuspension(boolean b); 316 317 // Stop all threads in this thread group,Unsafe 318 @Deprecated 319 public final void stop(); 320 321 // Suspend all threads in this thread group. Easy to cause deadlock 322 @Deprecated 323 public final void suspend(); 324 325 // Continue all threads in this thread group. Easy to cause deadlock 326 @Deprecated 327 public final void resume(); 328 329 }
Thread threads
1 // Public constructors essentially call four parameters first init Method,Then call the private of six parameters init Method to construct Thread objects 2 3 public Thread() { 4 // Set the name of the thread when calling a parametric construct,Then call the private of the four parameters init Method,from init Method to call six parameters init Method 5 init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); 6 } 7 8 // Constructing a new Thread object,Use the specified runtime object 9 public Thread(Runnable target) { 10 // Set the name of the thread,Calling four parameters init Method,from init Method to call six parameters init Method 11 init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); 12 } 13 14 // Construct a specified thread group,Using the specified running object Thread object 15 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) { 16 init(group, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); 17 } 18 19 // Constructing a specified thread name Thread object 20 public Thread(String name) { 21 init(null, null, name, 0); 22 } 23 24 // Constructing a specified thread group and name Thread object 25 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) { 26 init(group, null, name, 0); 27 } 28 29 // Construct an object with the specified running object and name Thread object 30 public Thread(Runnable target, String name) { 31 init(null, target, name, 0); 32 } 33 34 // Construct a group of specified threads,Running object and name Thread object 35 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) { 36 init(group, target, name, 0); 37 } 38 39 // Construct a group of specified threads,Running object,Name and stack size Thread object 40 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, 41 long stackSize) { 42 init(group, target, name, stackSize); 43 } 44 45 // This constructor is not public,He will create a 46 Thread(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) { 47 init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0, acc, false); 48 } 49 50 // The public constructor calls this method first 51 private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, 52 long stackSize) { 53 init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true); 54 } 55 56 private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,boolean inheritThreadLocals) { 57 // If the given thread name is null Throw a null pointer exception 58 if (name == null) { 59 throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); 60 } 61 // Set the thread name 62 this.name = name; 63 // Get the parent thread 64 Thread parent = currentThread(); 65 // Getting the Security Manager 66 SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); 67 68 // If the thread group where the thread is not specified 69 if (g == null) { 70 // If the security manager exists,Returns the thread group of the current thread using the security manager method 71 if (security != null) { 72 g = security.getThreadGroup(); 73 } 74 75 // If the thread group still does not belong to it,Use the thread group of the parent thread as the thread group of that thread 76 if (g == null) { 77 g = parent.getThreadGroup(); 78 } 79 } 80 // Determine whether the current thread has permission to modify this g Thread group,The time of this method ThreadGroup Of 81 g.checkAccess(); 82 83 // Check for permissions 84 if (security != null) { 85 // Verify that the instance can be constructed 86 if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) { 87 security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);// Verify that there are specified run-time permissions 88 } 89 } 90 // Increase the number of threads that are not started in the thread group. 91 g.addUnstarted(); 92 93 // Setting Thread Related Properties,Get the related attributes of the parent thread as the related attributes of the thread(If not specified) 94 this.group = g; 95 this.daemon = parent.isDaemon(); 96 this.priority = parent.getPriority(); 97 if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass())) 98 this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader(); 99 else 100 this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader; 101 this.inheritedAccessControlContext = 102 acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext(); 103 this.target = target; 104 setPriority(priority); 105 if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) 106 this.inheritableThreadLocals = 107 ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals); 108 this.stackSize = stackSize; 109 tid = nextThreadID(); 110 }
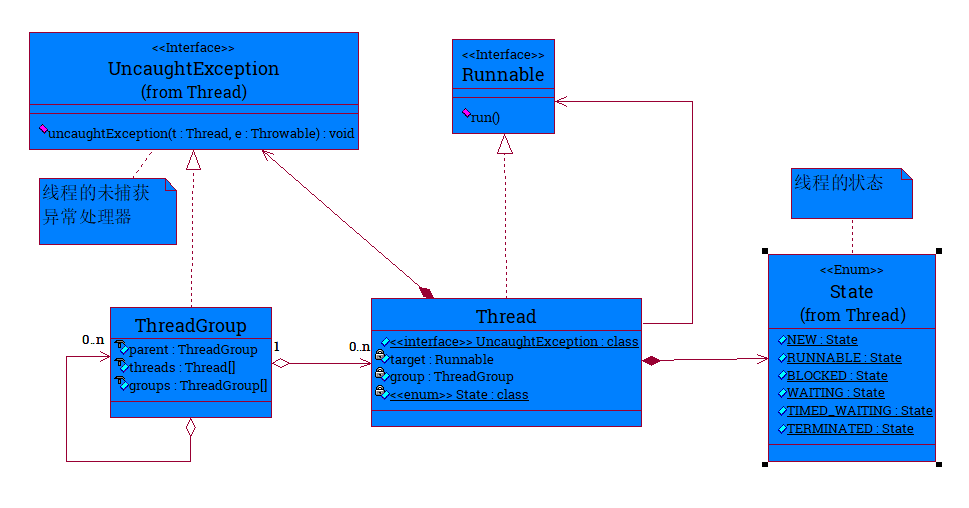
Class diagrams between ThreadGroup,Thread,Thread.State,Thread.UncaughtException