In general, use the listener ConfigChangeListener that implements apollo to get the configuration in real time through onChange method.
However, if the timeliness requirements for configuration changes are not high, and you just want to use the new configuration when using the configuration, you can get the configuration directly from the environment without implementing the listener.
Article directory
apollo mechanism
graphic
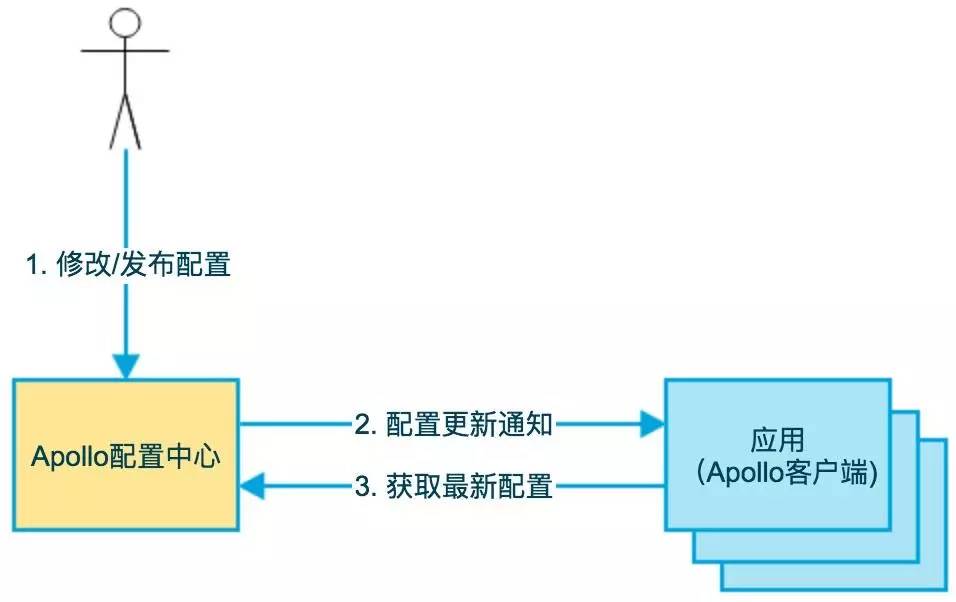
code analysis
Let's use the old friend refresh method to reveal it.
First, through AbstractApplicationContext.refresh():
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
After many hardships, we found the PropertySourcesProcessor, executed its postProcessBeanFactory method, and entered initializePropertySources().
Main process
1. Create Config
2. Package Config with CompositePropertySource and insert environment
private void initializePropertySources() {
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
// Once the apollo configuration has been initialized, it will return directly
return;
}
// Create a PropertySource to load all configurations
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
......
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
int order = iterator.next();
for (String namespace : NAMESPACE_NAMES.get(order)) {
// Get a config, if not, a config will be created (subsequent analysis, very important)
Config config = ConfigService.getConfig(namespace);
// Use CompositePropertySource to wrap config as a PropertySource, and then add the value environment
composite.addPropertySource(configPropertySourceFactory.getConfigPropertySource(namespace, config));
}
}
// clean up
NAMESPACE_NAMES.clear();
// If there are Apollo bootstrap property sources, make sure that the Apollo bootstrap property sources are in the first place and the above composite is set after it. Otherwise, the composite is set in the first place
if (environment.getPropertySources()
.contains(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
ensureBootstrapPropertyPrecedence(environment);
environment.getPropertySources()
.addAfter(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, composite);
} else {
// After setting the composite to the first one, even if we do not apply the listener method, we can get the configuration directly from the environment through getProperty even if we are notified of the configuration change
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(composite);
}
}
So, after understanding the two parts, let's taste the mechanism in detail. A config, why can you know the change of apollo in real time?
Create remotecononfigrepository
As mentioned earlier, if you can't get config from ConfigService.getConfig(namespace), you will create a config. The remotecononfigrepository is created. Look at its construction methods. In addition to various attribute assignments, three methods will be called, which are very important.
public RemoteConfigRepository(String namespace) {
m_namespace = namespace;
m_configCache = new AtomicReference<>();
m_configUtil = ApolloInjector.getInstance(ConfigUtil.class);
m_httpUtil = ApolloInjector.getInstance(HttpUtil.class);
m_serviceLocator = ApolloInjector.getInstance(ConfigServiceLocator.class);
remoteConfigLongPollService = ApolloInjector.getInstance(RemoteConfigLongPollService.class);
m_longPollServiceDto = new AtomicReference<>();
m_remoteMessages = new AtomicReference<>();
m_loadConfigRateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(m_configUtil.getLoadConfigQPS());
m_configNeedForceRefresh = new AtomicBoolean(true);
m_loadConfigFailSchedulePolicy = new ExponentialSchedulePolicy(m_configUtil.getOnErrorRetryInterval(),
m_configUtil.getOnErrorRetryInterval() * 8);
gson = new Gson();
// First synchronization apollo
this.trySync();
// Scheduled refresh configuration (304 is returned in most cases, which can prevent long polling failure)
this.schedulePeriodicRefresh();
// Long polling refresh configuration (the main way to get configuration in real time)
this.scheduleLongPollingRefresh();
}
First synchronization apollo
@Override
protected synchronized void sync() {
Transaction transaction = Tracer.newTransaction("Apollo.ConfigService", "syncRemoteConfig");
try {
ApolloConfig previous = m_configCache.get();
// Send a get request to get the current apollo configuration information according to the apollo address, appId, maxRetries and other information you set
ApolloConfig current = loadApolloConfig();
// Update local apollo configuration information
if (previous != current) {
logger.debug("Remote Config refreshed!");
m_configCache.set(current);
// The task of refreshing the configuration may call this method, get the configuration, and notify the listener of the client
this.fireRepositoryChange(m_namespace, this.getConfig());
}
if (current != null) {
Tracer.logEvent(String.format("Apollo.Client.Configs.%s", current.getNamespaceName()),
current.getReleaseKey());
}
transaction.setStatus(Transaction.SUCCESS);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
transaction.setStatus(ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
transaction.complete();
}
}
Enable scheduled refresh configuration
private void schedulePeriodicRefresh() {
logger.debug("Schedule periodic refresh with interval: {} {}",
m_configUtil.getRefreshInterval(), m_configUtil.getRefreshIntervalTimeUnit());
m_executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Tracer.logEvent("Apollo.ConfigService", String.format("periodicRefresh: %s", m_namespace));
logger.debug("refresh config for namespace: {}", m_namespace);
// trySync is the same method as the first sync above
trySync();
Tracer.logEvent("Apollo.Client.Version", Apollo.VERSION);
}
//The default interval is 5 minutes
}, m_configUtil.getRefreshInterval(), m_configUtil.getRefreshInterval(),
m_configUtil.getRefreshIntervalTimeUnit());
}
Enable long polling refresh configuration
public boolean submit(String namespace, RemoteConfigRepository remoteConfigRepository) {
boolean added = m_longPollNamespaces.put(namespace, remoteConfigRepository);
m_notifications.putIfAbsent(namespace, INIT_NOTIFICATION_ID);
if (!m_longPollStarted.get()) {
// Open pull
startLongPolling();
}
return added;
}
private void doLongPollingRefresh(String appId, String cluster, String dataCenter) {
final Random random = new Random();
ServiceDTO lastServiceDto = null;
while (!m_longPollingStopped.get() && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
if (!m_longPollRateLimiter.tryAcquire(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
// Wait for 5 seconds.
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
// Obtain all kinds of information, initiate requests, and check whether the configuration in apollo has changed
......
// If the configuration changes, take the initiative to obtain the new configuration, and call the onChange method of the implementation class of ConfigChangeListener
if (response.getStatusCode() == 200 && response.getBody() != null) {
updateNotifications(response.getBody());
updateRemoteNotifications(response.getBody());
transaction.addData("Result", response.getBody().toString());
notify(lastServiceDto, response.getBody());
}
......
} finally {
transaction.complete();
}
}
}
The notify method will eventually enter the firerepository change
fireRepositoryChange
This method is mentioned in the sync() method introduced earlier. This method will be executed by two types of refresh configuration tasks to inform each listener of configuration changes.
1. Get new configuration
2. Statistics of changes in various configurations
3. Notify each listener
protected void fireRepositoryChange(String namespace, Properties newProperties) {
// Traverse all listeners
for (RepositoryChangeListener listener : m_listeners) {
try {
// Pass the latest configuration information to the listener
listener.onRepositoryChange(namespace, newProperties);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Tracer.logError(ex);
logger.error("Failed to invoke repository change listener {}", listener.getClass(), ex);
}
}
}
@Override
public synchronized void onRepositoryChange(String namespace, Properties newProperties) {
if (newProperties.equals(m_configProperties.get())) {
return;
}
ConfigSourceType sourceType = m_configRepository.getSourceType();
Properties newConfigProperties = new Properties();
newConfigProperties.putAll(newProperties);
// Sort out the configuration information and determine the type of configuration change
Map<String, ConfigChange> actualChanges = updateAndCalcConfigChanges(newConfigProperties, sourceType);
//check double checked result
if (actualChanges.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Call onChange method of each ConfigChangeListener implementation class to send configuration information
this.fireConfigChange(new ConfigChangeEvent(m_namespace, actualChanges));
Tracer.logEvent("Apollo.Client.ConfigChanges", m_namespace);
}
private Map<String, ConfigChange> updateAndCalcConfigChanges(Properties newConfigProperties,
ConfigSourceType sourceType) {
// Configuration of initial statistical changes
List<ConfigChange> configChanges =
calcPropertyChanges(m_namespace, m_configProperties.get(), newConfigProperties);
ImmutableMap.Builder<String, ConfigChange> actualChanges =
new ImmutableMap.Builder<>();
/** === Double check since DefaultConfig has multiple config sources ==== **/
//1. Set old values for configuration
for (ConfigChange change : configChanges) {
change.setOldValue(this.getProperty(change.getPropertyName(), change.getOldValue()));
}
//2. Update m "configproperties
updateConfig(newConfigProperties, sourceType);
clearConfigCache();
//3. Traverse all new configurations, and finally confirm the type of each configuration (ADDED/MODIFIED/DELETED)
for (ConfigChange change : configChanges) {
change.setNewValue(this.getProperty(change.getPropertyName(), change.getNewValue()));
switch (change.getChangeType()) {
case ADDED:
if (Objects.equals(change.getOldValue(), change.getNewValue())) {
break;
}
if (change.getOldValue() != null) {
change.setChangeType(PropertyChangeType.MODIFIED);
}
actualChanges.put(change.getPropertyName(), change);
break;
case MODIFIED:
if (!Objects.equals(change.getOldValue(), change.getNewValue())) {
actualChanges.put(change.getPropertyName(), change);
}
break;
case DELETED:
if (Objects.equals(change.getOldValue(), change.getNewValue())) {
break;
}
if (change.getNewValue() != null) {
change.setChangeType(PropertyChangeType.MODIFIED);
}
actualChanges.put(change.getPropertyName(), change);
break;
default:
//do nothing
break;
}
}
return actualChanges.build();
}

