This article has been included in a Zhuang's personal website: https://jonssonyan.com , welcome to comment and forward.
Hi, I'm Zhuang, an interesting programmer. Today, I'd like to share with you about SQL optimization.
MYSQL performance optimization can make MYSQL run faster and save resources by reasonably arranging resources and adjusting system parameters. MYSQL performance optimization includes query speed optimization, update speed optimization, MYSQL server optimization and so on. Here, the following optimizations are introduced. Including server hardware optimization, system configuration optimization, database structure optimization, SQL and index optimization.
common problem
- block
- Slow query
We can start from the following aspects
- Server hardware optimization
- System configuration optimization
- Database structure optimization
- SQL and index optimization
Usually optimize 3 and 4
Slow query log
show variables like 'slow_query_log'; # Enable slow query log set global slow_query_log=on; # Query the storage location of slow query log files show variables like 'slow_query_log_file'; # Set the storage location of slow query log files set global slow_query_log_file= '/home/mysql/sql_log/mysql-slow.log' # Set whether to record SQL without index to slow query log set global log_queries_not_using_indexes=on; # Set whether to record SQL with query events exceeding 0 seconds into the slow query log, and set 0.01 seconds for general production set global long_query_time=0;
Practical operation
Slow query log is not enabled by default
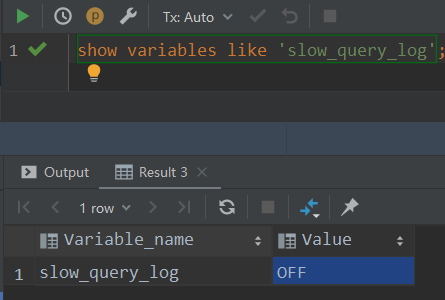
Slow query log storage location
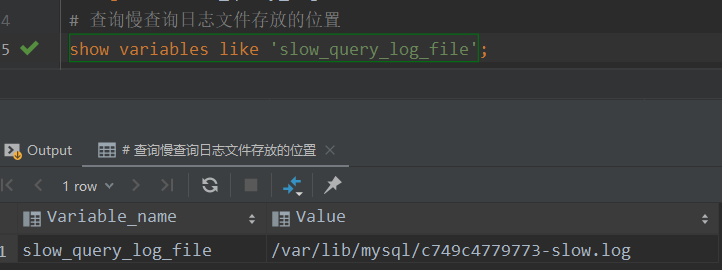
Query log. Here I am the Docker container, deploy mysql, and map it to the / data/mysql directory on the server
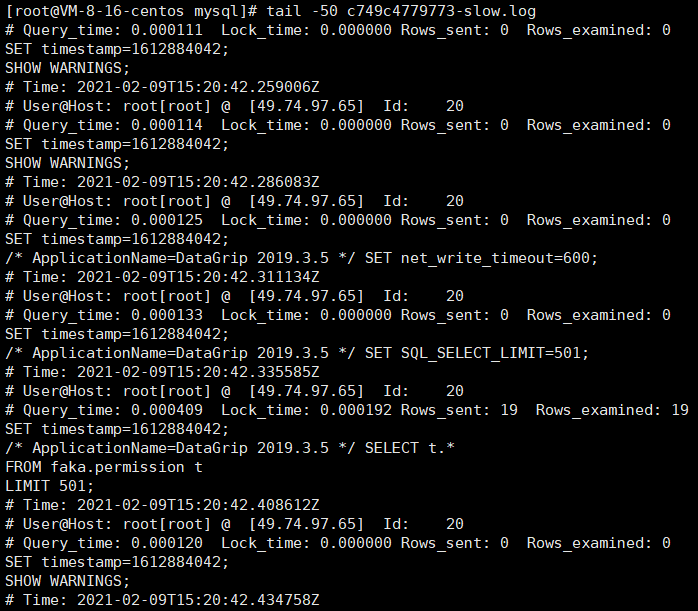
Log format

Line 1: host information of executing SQL
Line 2: SQL execution information
Line 3: SQL execution event
Line 4: SQL content
Slow query log analysis tool
mysqldumpslow (official tool)
Parameter interpretation
-s yes order Order of al Average lock time ar Average return record time at Average query time (default) c count l Lock time r return recording t Query time -t yes top n It means to return the previous data -g A regular matching pattern can be written in the back, which is case insensitive
Basic use
# Get up to 10 SQL statements that return recordsets. mysqldumpslow -s r -t 10 /database/mysql/mysql06_slow.log # Get the top 10 SQL queries accessed mysqldumpslow -s c -t 10 /database/mysql/mysql06_slow.log # Get the first 10 query statements with left connection in chronological order. mysqldumpslow -s t -t 10 -g "left join" /database/mysql/mysql06_slow.log # In addition, it is recommended to use these commands in combination with | and more, otherwise screen swiping may occur. mysqldumpslow -s r -t 20 /mysqldata/mysql/mysql06-slow.log | more
pt-query-digest
express setup
wget https://www.percona.com/downloads/percona-toolkit/2.2.16/RPM/percona-toolkit-2.2.16-1.noarch.rpm && yum localinstall -y percona-toolkit-2.2.16-1.noarch.rpm
Parameter interpretation
pt-query-digest [OPTIONS] [FILES] [DSN] --create-review-table When used--review When the parameter outputs the analysis results to the table, it will be automatically created if there is no table. --create-history-table When used--history When the parameter outputs the analysis results to the table, it will be automatically created if there is no table. --filter The input slow query is matched and filtered according to the specified string, and then analyzed --limit Limit the percentage or quantity of output results. The default value is 20,The slowest 20 statements will be output. If it is 50%Then the total response time will be sorted from large to small, and the total output will reach 50%Position cut-off. --host mysql server address --user mysql user name --password mysql User password --history Save the analysis results to the table. The analysis results are more detailed and can be used next time--history If the same statement exists and the time interval of the query is different from that in the history table, it will be recorded in the data table. You can query the same statement CHECKSUM To compare the historical changes of a certain type of query. --review Save the analysis results to the table. This analysis only parameterizes the query criteria. One type of query is one record, which is relatively simple. When used next time--review If the same statement analysis exists, it will not be recorded in the data table. --output Output type of analysis result. The value can be report(Standard analysis report),slowlog(Mysql slow log),json,json-anon,General use report,For easy reading. --since When does the analysis start? The value is a string, which can be a specified value yyyy-mm-dd [hh:mm:ss]"The time point in format can also be a simple time value: s(second),h(hour),m(minute),d(day),Such as 12 h It means that the statistics began 12 hours ago. --until Deadline, with - since Can analyze slow queries over a period of time.
Basic use
# output to a file pt-query-digest slow-log > slow_log.report # Output to database -- create review table means that the slow query log is output to a table pt-query-digest slow.log -review h=127.0.0.1,D=test,p=root,P=3306,u=root.t=query_review --create-reviewtable --review-history t= hostname_slow
SQL optimization
SQL features that need to be optimized
- SQL with many queries and long time for each query
- SQL with large IO (the more rows scanned in SQL, the larger IO)
- SQL that missed the index
Use explain to query the execution plan of SQL
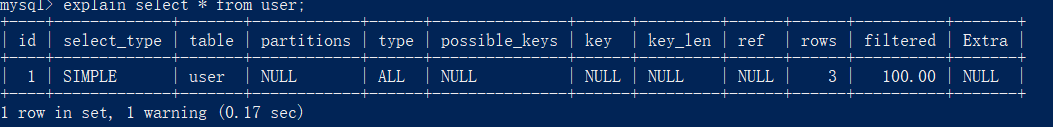
interpretative statement
table About which table when displaying this row of data type This is an important column that shows what type of connection is used. The connection type from best to worst is const,eq_reg,ref,range,index,ALL. const Common in primary keys/Unique index lookup, eq_reg It is common to find the range of primary keys, ref Common in connection query,range Common in index range lookup, index Common in index scanning, ALL Common in table scanning possible_keys Displays the indexes that may be applied to this table. If empty, there is no possible index. key The index actually used. If yes NULL,No index is used. key_len Index length used. The shorter the length, the better without losing accuracy ref The column that displays the index is used, if available, as a constant rows MySQL The number of rows considered necessary to check to return the requested data
SQL optimization
- Properly index the frequently queried fields
- Avoid sub queries and optimize them to join queries. Pay attention to whether there is a one to many relationship and data duplication may occur
How to select a reasonable column to establish an index
- Columns appearing in where, group by, order by and on clauses
- The smaller the index field, the better
- Columns with large dispersion are placed in front of the joint index
For example:
select * from payment where staff_id = 2 and customer_id = 584;
Due to customer_ ID is more discrete, so index(customer_id,staff_id) should be used
How to judge the discreteness of columns
select count(distinct customer_id),count(distinct staff_id) from payment
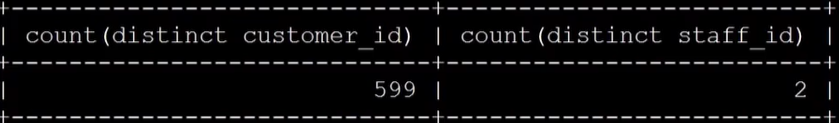
The higher the unique value of the column, the greater the degree of dispersion and the higher the selectivity.
Index maintenance and optimization
Duplicate and redundant indexes. Duplicate indexes refer to the indexes of the same type established by the same column in the same order. For example, the indexes on the following primary key and ID columns are duplicate indexes
create table test(id int not null primart key),name vachar(10) not null,title varchar(50) not null,unique(id) ) engine=innodb
Use the PT duplicate key Checker tool to check duplicate and redundant indexes
pt-duplicate-key-checker -uroot -p'' -h 127.0.0.1
Database and table structure optimization
Select the appropriate data type
- Use the smallest data type that can store your data
- Using simple data type, int is simpler than varchar in MySQL processing
- Use not null to define fields whenever possible
- Try to use less text type. When it is necessary, it is best to consider sub table
for example
Use bigint to store IP address and INET_ ATON(),INET__ The two functions of ntoa() are converted
insert into sessions(ipaddress) values (INET_ATON('127.0.0.1'));
select INET__NTOA('127.0.0.1') from sessions;
Paradigm and anti paradigm
Paradigm
-
The first paradigm emphasizes atomicity and requires that attributes have atomicity and cannot be decomposed
-
The second paradigm emphasizes the primary key, which requires the record to have a unique identification, that is, the uniqueness of the entity, and there is no partial dependency at the level
-
The third paradigm, which emphasizes foreign keys, requires that any field cannot be derived from other fields, and requires that the field has no redundancy, that is, there is no dependency transfer
Anti paradigm
In order to consider the query efficiency, the tables that originally conform to the third normal form are appropriately added with redundancy, so as to optimize the query efficiency. Anti normal form is an operation that changes time with controls.
Optimization of database structure
Vertical split of table
Splitting the original table with many columns into multiple tables solves the problem of table width. Generally, vertical splitting can be carried out according to the following principles:
- Store the uncommon fields in a separate table
- Large fields exist independently in a table
- Put together fields that are often used together
Horizontal split of table
In order to solve the problem of large amount of data in a single table, the structure of each horizontal split table is completely consistent
System configuration optimization
The database is based on the operating system. At present, most MySQL is installed on Linux, so some parameter configurations of the operating system will also affect the performance of MySQL. The common system configurations are listed below
Network configuration
Modify / etc / sysctl Coonf file
# Increase the number of queues supported by tcp net.ip4.tcp_max_syn_backlog=65535 # Reduce resource recycling when disconnected net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets=8000 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse=1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle=1 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout=10
Open the limit of the number of files. You can use ulimit -a to view the limits of the directory. You can modify / etc / security / limits Conf file, add the following content to modify the limit of the number of open files
soft nofile 65335 hard nofile 65535
In addition, it is better to close iptables,selinux and other firewall software on MySQL server
MySQL profile
Profile path
Linux: /etc/my.cnf
parameter
innodb_buffer_pool_size: a very important parameter used to configure the buffer pool of InnoDB. If there are only InnoDB tables in the database, the recommended configuration amount is 75% of the total memory
innodb_buffer_pool_instances: MySQL5. The parameter added in 5 can control the number of cache pools. By default, there is only one cache pool
innodb_log_buffer_size: the size of innodb log cache. Since the log is refreshed every second at most, it is generally not too large
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit: a key parameter that has the greatest impact on the IO efficiency of InnoDB. The default value is 1. You can take three values: 0, 1 and 2. It is generally recommended to set it to 2. However, if the data security requirements are high, the default value of 1 is used
innodb_read_io_threads/innodb_write_io_threads: determines the number of InnoDB read / write IO processes. The default is 4
innodb_file_per_table: the key parameter that controls InnoDB. No table uses an independent table space. The default is OFF, that is, all tables will be established in a shared table space
innodb_stats_on_metadata: determines when MySQL will refresh the statistics of InnoDB table
Third party configuration tools
Percon Configuration Wizard
Optimization of server hardware
CPU
Choose the right CPU, a single CPU with faster frequency
- Some MySQL work can only use a single core
- MySQL's support for CPU cores is not as fast as possible. MySQL 5 5. The server used should not exceed 32 cores
disk IO optimization
Introduction to common RAID levels
RAID0: also known as stripe, it is used to connect multiple disks into one hard disk. This level of IO is the best
RAID1: also known as mirroring, it requires at least two disks, each of which stores the same data
RAID5: it is also used to combine multiple (at least 3) hard disks into one logical disk. Parity information will be established during data reading and writing, and parity information and corresponding data will be stored on different hard disks respectively. When a disk data of RAID5 is damaged, the remaining data and corresponding parity information are used to recover the damaged data.
RAID1+0: it is the combination of RAID1 and RAID0, with two levels of advantages and disadvantages at the same time. This level is generally recommended for databases.
Is SNA and NAT suitable for database
- Commonly used for highly available solutions
- Sequential reading and writing efficiency is very high, but random reading and writing is not satisfactory
- The random reading and writing efficiency of database is very high
summary
SQL optimization is a common interview question. It can be said that 80% of the interviews will be asked more or less. At the same time, SQL optimization is also a technology often used in actual production practice. Learning optimization well can enable us to write higher performance programs.
I'm Zhuang, wechat search: Tech cat, pay attention to this interesting programmer. I'll see you next time