1. Introduction to JDBC
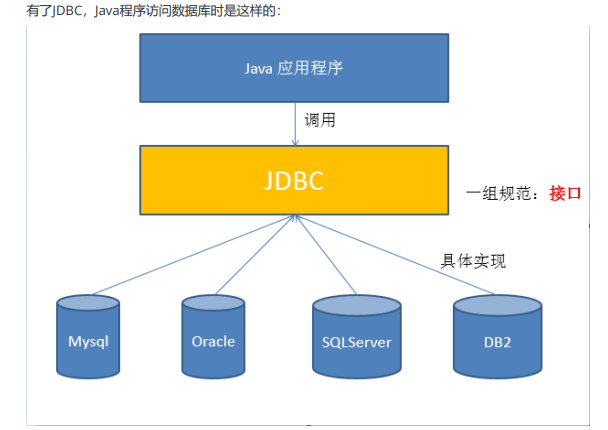
1. What is JDBC?

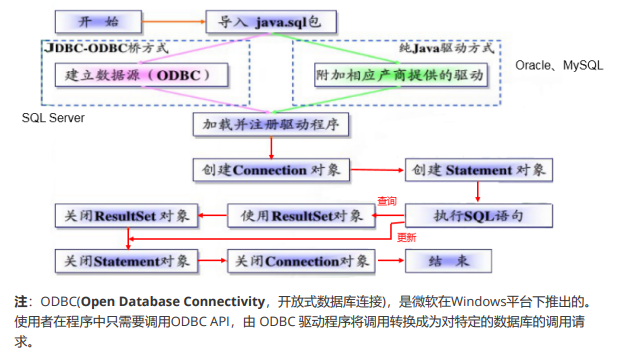
2.JDBC writing steps
2. How to Get Database Connections
Preparations:
1. Create a new lib folder under the project
2. Import the jar package into the lib directory
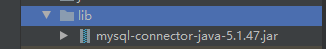
3. Add the imported jar package to the project through Add as library
4. Create related packages and test classes
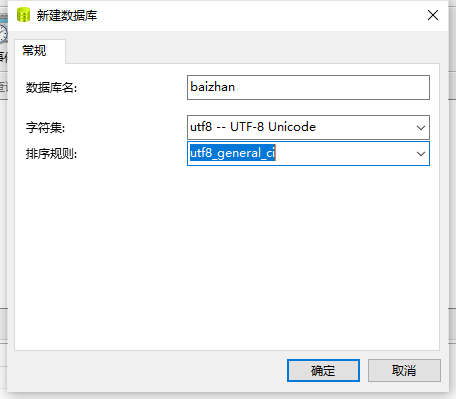
5. Create a new database in the database
6. Important points of knowledge:


1. Get Database Connection Method One
//Get JDBC connection method one
public class jdbc_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//Load Driver
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
//Define url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/baizhan?useSSL=false";
//Set account password through Properties
Properties info = new Properties();
info.setProperty("user","root");
info.setProperty("password","mysql");
//Connect through Connection
Connection conn = driver.connect(url,info);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
2. Get Database Connection Method 2
Getting driver objects by reflection
This method does not have a third-party API to facilitate code migration and compatibility
//Get Database Connection Method Two
public class jdbc_Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, SQLException {
/*
* Getting driver objects by reflection
* */
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/baizhan?useSSL=false";
Properties info = new Properties();
info.setProperty("user","root");
info.setProperty("password","mysql");
Connection conn = driver.connect(url,info);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
3. Getting Database Connection Method 3
Get connections through Driver Manager instead of Drive
//Get Database Connection Method Three
public class jdbc_Test3 {
//Replace Driver with DriverManager
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, SQLException {
//Getting driver from reflection has good code portability
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
//Register driver with DriverManager
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/baizhan?useSSL=false";
String user = "root";
String password = "mysql";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
4. Get Database Connection Method 4
//Get Database Connection Method Four
public class jdbc_Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//When com. Mysql. Jdbc. When Driver is loaded into a memory virtual machine, a static block in the Driver class automatically registers Driver with DriverManager
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/baizhan?useSSL=false";
String user = "root";
String password = "mysql";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
5. Get Database Connection Method 5 (Recommended)
Separate profile from program
Advantage:
1. Separate data from code and decouple
2. Avoid program repackaging if you want to modify a configuration file that can be modified directly
//Get Database Connection Method 5 (Recommended)
public class jdbc_Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//Read Configuration File in
InputStream is = jdbc_Test5.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
//read in data
properties.load(is);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
Class.forName(driverClass);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
3. Basic operation of JDBC
int execute(String sql); // Perform insert, update, delete operations
ResultSet executeQuery(String sql); // Perform query operation
1. Operating and accessing databases through Statement

Use of Statement

//Operating and accessing databases through Statement
public class Statement_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//Get Database Connection
InputStream is = jdbc_Test5.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
Class.forName(driverClass);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//Get the statement object
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
//Stitching sql
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter an account:");
String username = sc.next();
System.out.println("Please input a password:");
String userpassword = sc.next();
String sql = "insert into user(username,userpassword) values('" + username + "','" + userpassword + "')";
//Execute sql
statement.execute(sql);
//close resource
conn.close();
statement.close();
}
}
2. select through ResultSet
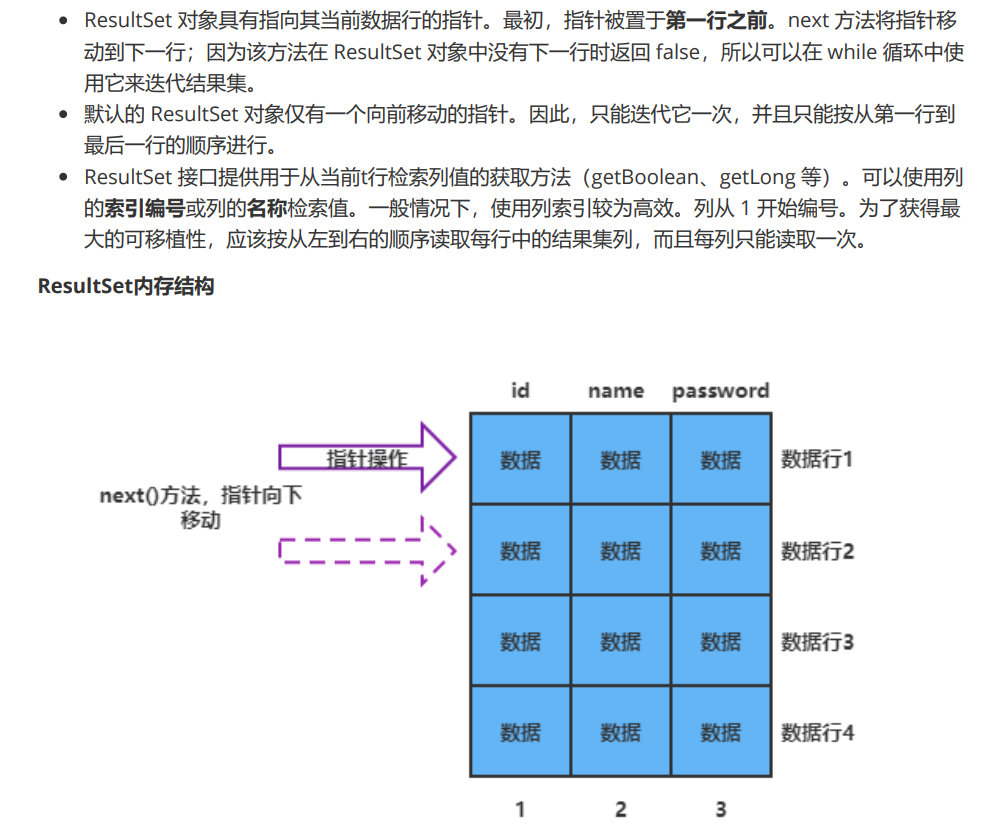
//Execute select through ResultSet
public class Statement_Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//Get Database Connection
InputStream is = jdbc_Test5.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
Class.forName(driverClass);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//Get the statement object
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from user";
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString("username")+" "+rs.getString("userpassword"));
}
conn.close();
statement.close();
rs.close();
}
}

3.PreparedStatement Add Operation
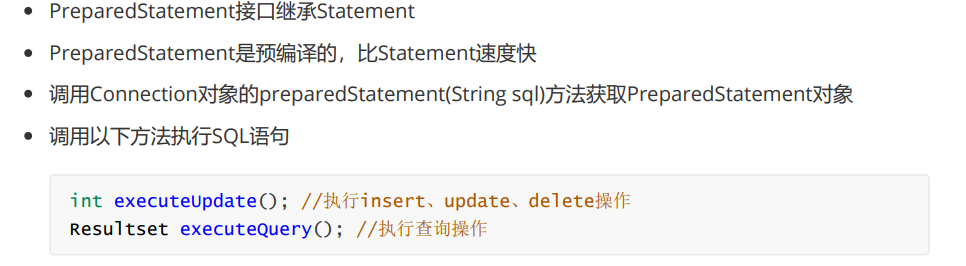
//PreparedStatement Add Operation
public class Statement_Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//Get Database Connection
InputStream is = jdbc_Test5.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
Class.forName(driverClass);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//Create PreparedStatement object
String sql = "insert into user(username,userpassword) values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//Fill placeholders
ps.setString(1,"admin6");
ps.setString(2,"123456");
//Perform Add
ps.executeUpdate();
//close resource
ps.close();
conn.close();
}
}
4. Encapsulate Get Connection and Release Connection Code into JDBCUtils
To unify the management and use of Connection resources, create a JDBCUtils tool class to unify the connection and release of databases
Management.
//Encapsulate Get Connection and Release Connection Code into JDBCUtils
public class JDBCUtils {
//Get Connections
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
InputStream is = jdbc_Test5.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
Class.forName(driverClass);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
return conn;
}
//Close Resource Operation
public static void close(Connection conn,Statement statement) throws SQLException {
if (conn != null){
conn.close();
}
if (statement != null){
statement.close();
}
}
}
5. Modify data through PreparedStatement
//Modify data through PreparedStatement
public class PreparedStatement_Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//Get the connection and create the PreparedStatement object
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "update user set username = ? where id = ?";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//Fill placeholders
ps.setObject(1,"admintest");
ps.setInt(2,1);
//Perform modifications
ps.executeUpdate();
//close resource
JDBCUtils.close(conn,ps);
}
}
6.PreparedStatement General Addition and Deletion Method
//PreparedStatement General Addition and Deletion Method
public class Statement_Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String sql = "delete from user where id = ? or id = ?";
update(sql,1,2);
}
public static void update(String sql,Object...args) throws Exception {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i<args.length; i++){
ps.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
ps.executeUpdate();
JDBCUtils.close(conn,ps);
}
}
7.PreparedStatement General Query Method
//General Query Method for PreparedStatement
public class PreparedStatement_Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String sql = "select * from user where id < ?";
query(sql,6);
}
public static void query(String sql,Object...args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0;i<args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
//Get ResultSet Metadata
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
//Get the number of table columns
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
while (rs.next()){
for (int i =0;i<columnCount;i++){
System.out.print(rs.getObject(i+1)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
rs.close();
JDBCUtils.close(conn,ps);
}
}
8.ORM Programming Ideas
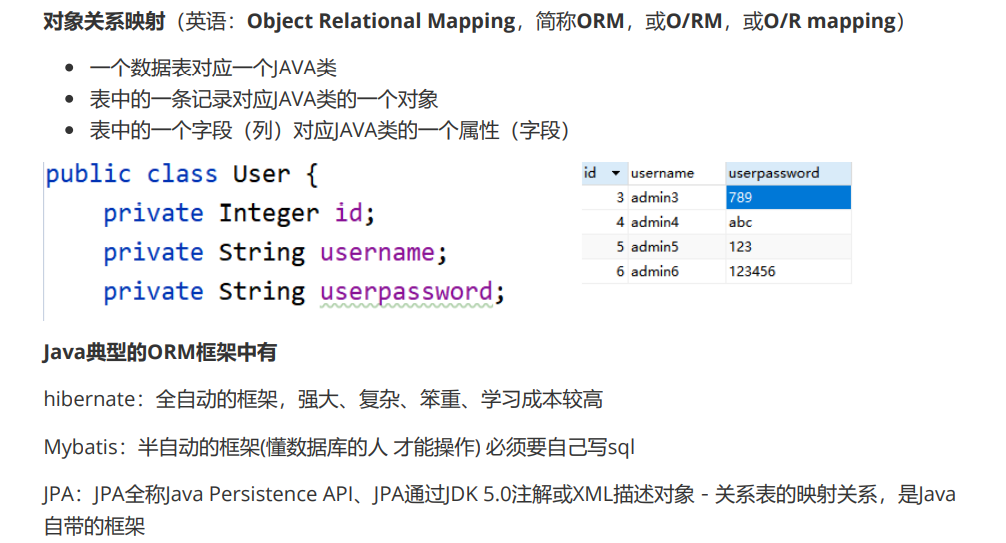
//ORM Programming Ideas
public class PreparedStatement_Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException {
String sql = "select * from user where id < ?";
List<User> users = queryUser(sql,6);
System.out.println();
}
public static List<User> queryUser(String sql,Object...args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
//Get Connection
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//Preprocessing
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//Setting Indefinite Parameters
for (int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i+1,args);
}
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
//Query operation
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
//Acquiring Metadata
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
//Get the number of columns
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
while (rs.next()){
User u = new User();
for (int i=0;i<columnCount;i++){
//Get column values
Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i+1);
//Get Column Name
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
//Getting attributes through reflection
Field field = u.getClass().getDeclaredField(columnName);
//Promote permissions
field.setAccessible(true);
//assignment
field.set(u,columnValue);
}
//Add the assigned user object to the list
users.add(u);
}
rs.close();
JDBCUtils.close(conn,ps);
return users;
}
}
4. JDBC Implements User Login Function
1. Business Introduction
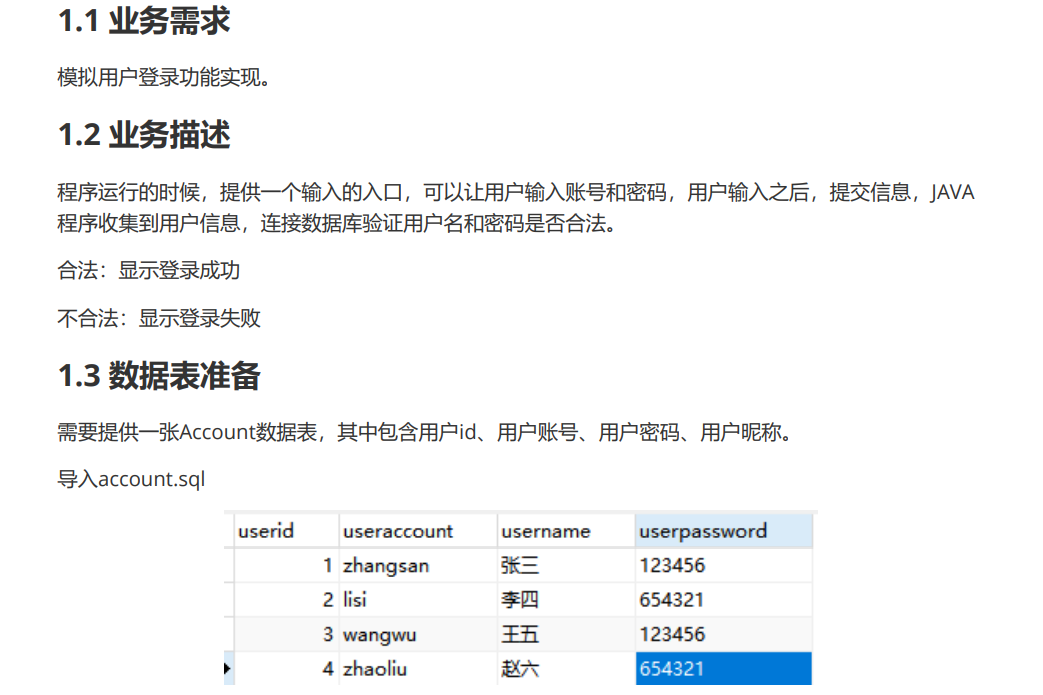
2. Initialization of login interface
//User login function_ Logon interface initialization
public class Login {
public static void main(String[] args) {
initUI();
}
public static Map<String,String> initUI(){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter an account:");
String account = sc.next();
System.out.println("Please input a password:");
String password = sc.next();
Map<String,String> userLoginInfo = new HashMap<>();
userLoginInfo.put("account",account);
userLoginInfo.put("password",password);
return userLoginInfo;
}
}
3. Logon implementation
Account Entity Class
//Account Entity Class
public class Account {
private Integer userid;
private String useraccount;
private String username;
private String userpassword;
public Integer getUserid() {
return userid;
}
public void setUserid(Integer userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
public String getUseraccount() {
return useraccount;
}
public void setUseraccount(String useraccount) {
this.useraccount = useraccount;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getUserpassword() {
return userpassword;
}
public void setUserpassword(String userpassword) {
this.userpassword = userpassword;
}
}
Implementing common queries against account tables
//Implementing common queries against account tables
public static List<Account> queryAccount(String sql,Object...args) throws Exception{
List<Account> accounts = new ArrayList<>();
//Get a connection to the database
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//Precompiled sql statement, returning an instance of PrepareStatement
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//Fill placeholders
for (int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
//implement
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
//Get Result Set Metadata
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
//Get the number of columns in the result set from ResultSetMetaData
int columncount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
while (rs.next()){
Account account = new Account();
for (int i =0;i<columncount;i++){
//Get the value of the column
Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i+1);
//Get the name of the column
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
//Get the field related properties
Field field = account.getClass().getDeclaredField(columnName);
//Promote permissions
field.setAccessible(true);
//assignment
field.set(account,columnValue);
}
accounts.add(account);
}
//Closing of resources
rs.close();
JDBCUtils.close(conn,ps);
return accounts;
}
Logon implementation
//Logon implementation
public static boolean login(Map<String,String> userLoginInfo) throws Exception{
//Define sql
String sql = "select * from account where useraccount = ? and userpassword = ?";
//Get all account objects matching account passwords
List<Account> accounts = queryAccount(sql,userLoginInfo.get("account"),userLoginInfo.get("password"));
//If the set is 0, the account or password does not match and the login fails
if (accounts.size() == 0){
return false;
}
return true;
}
Test login functionality
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map<String,String> userLoginInfo = initUI();
System.out.println(login(userLoginInfo)?"Login Successful":"Logon Failure");
}
4. JDBC Advanced
1. What is SQL injection
SQL injection refers to the use of systems that do not adequately check the data entered by the user and that injection into the user's input data is illegal
SQL statement segments or commands to use the system's SQL engine to accomplish malicious behavior.
For example, when using a Statement implementation:
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
Change the SQL statement to:
String sql = "select * from account where useraccount = '" +userLoginInfo.get("account")+ "' and userpassword = '" + userLoginInfo.get("password") +"'";
When you test:

The account and password entered above, through SQL splicing, the SQL in the execution process is actually:
select * from account where useraccount = 'zhangsan' and userpassword ='baizhan'or'1=1'
Since 1=1 is always true, the correct password will be returned regardless of whether the account password is correct or not.
The root cause of SQL injection:
The information entered by the user contains keywords of the SQL statement, and these keywords participate in the compilation of the SQL statement, which distorts the intent of the SQL statement, thus achieving the purpose of SQL injection.
2. How to Solve SQL Injection
As long as the information provided by the user does not participate in the compilation of the SQL statement, even if the information provided by the user contains the keyword of the SQL statement, however
Not participating in compilation, still not working.
PreparedStatement can parameterize information and still use PreparedStatement for login:
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);

The account and password entered above, precompiled by PreparedStatement, takes baizhan'or'1=1 as a string parameter as a whole
Number is set in SQL, and the SQL during execution is actually:
select * from account where useraccount = 'zhangsan' and userpassword ="baizhan'or'1=1"
3. Bulk Insert Data
Insert data in three different ways and test its time-use.
First create an empty list of items through Navicat:
CREATE TABLE goods(id int PRIMARY key auto_increment,goodsname VARCHAR(25))
Insert 2000 pieces of data into the table in three ways:
Method 1. Insert data in batch by Statement + for loop to calculate execution time:
//1. Calculate execution time by batch inserting data in Statement + for loop
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
//Get Start Time
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<2000;i++){
String sql = "insert into goods(goodsname)values('name_"+i+"')";
statement.execute(sql);
}
//Get End Time
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
JDBCUtils.close(conn,statement);
System.out.println("Total insertion time is:"+(end-start));
Since this method uses statement, the sql string needs to be regenerated each time. The results are as follows:
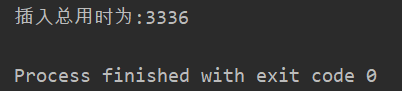
Method 2. Insert data in batch by PreparedStatement + for loop to calculate execution time:
//2. Calculate execution time by batch inserting data through PreparedStatement + for loop
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into goods(goodsname)value(?)";
PreparedStatement psmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<2000;i++){
psmt.setObject(1,"name_"+ i);
psmt.executeUpdate();
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
JDBCUtils.close(conn,psmt);
System.out.println("Total insertion time is:"+(end-start));
}
Method 2 uses PreparedStatement, PreparedStatement is a precompiled mode, and DBServer's compiler compiler
The translated execution code is cached, so the next call will not need to be compiled as long as it is the same precompiled statement, as long as the parameters are
Direct incoming can be executed. The results are as follows:
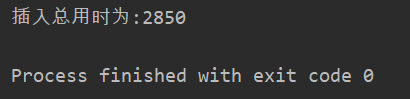
Method 3. Bulk insertion of data through addBatch() and executeBatch() of PreparedStatement
1. addBatch() loads several SQL statements together and transfers them to the database for execution at once, that is, the number of SQLs in batch processing
According to.
2. executeBatch() executes the SQL statements loaded together.
3. clearBatch() Clears the cache
Note: MySql does not support batching by default, but a rewriteBatchStatement parameter has been added since 5.1.13 to allow MySql to support batching. Set this parameter when loading url: rewriteBatchedStatements=true
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/baizhan?useSSL=false&rewriteBatchedStatements=true
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into goods(goodsname)value(?)";
PreparedStatement psmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<=2000;i++){
psmt.setObject(1,"name_"+i);
//Caching sql
psmt.addBatch();
//Execute every 500 caches
if (i%500==0){
//Batch execution of sql
psmt.executeBatch();
//Clear Cache
psmt.clearBatch();
}
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
JDBCUtils.close(conn,psmt);
System.out.println("Total insertion time is: "+(end - start));
}
Result: