Log frame
Common log frames
JUL, JCL, Jboss-logging, logback, log4j, log4j2, slf4j...
- Log facade (abstract layer of log): JCL (Jakarta common logging), slf4j (Simple Logging Facade for Java), JBoss logging
- Log implementation: log4j, Jul (Java. Util. Logging), log4j2, logback
Select a facade (abstract layer) at the top and an implementation at the bottom;
Log facade: SLF4J; Log implementation: Logback;
Spring boot: the bottom layer is the spring framework, which uses JCL by default;
SLF4J and logback are selected for Spring boot;
SLF4J use
In future development, the call of logging methods should not directly call the log implementation class, but call the methods in the log abstraction layer; Import slf4j jars and logback implementation jars into the system.
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}
Log diagram:
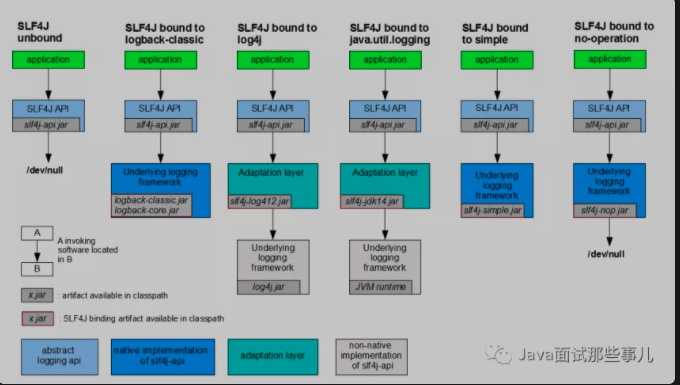
Each log implementation framework has its own configuration file. After using slf4j, the configuration file is still made into the log implementation framework's own configuration file;
remaining problems
Spring boot(slf4j+logback): Spring(commons-logging),Hibernate(jboss-logging),MyBatis...
Unified logging, even if other frameworks use slf4j for output together with me?
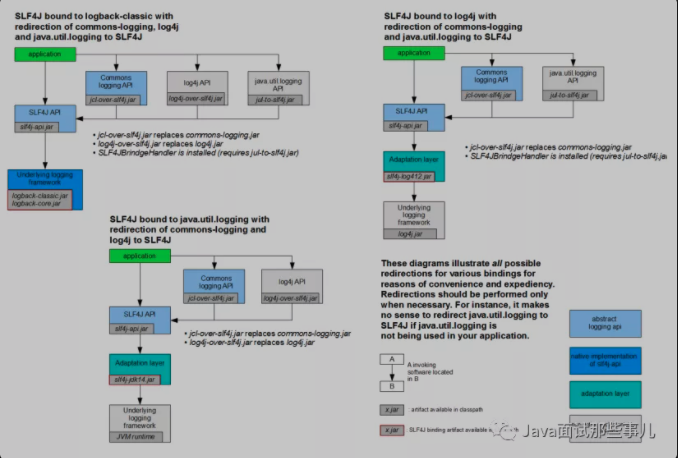 How to unify all logs in the system to slf4j:
How to unify all logs in the system to slf4j:
- Exclude other log frames in the system first;
- Replace the original log framework with a tundish;
- We import slf4j other implementations;
SpringBoot log relationships
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter</artifactId> </dependency>
SpringBoot uses it for logging:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐logging</artifactId> </dependency>
Underlying dependencies
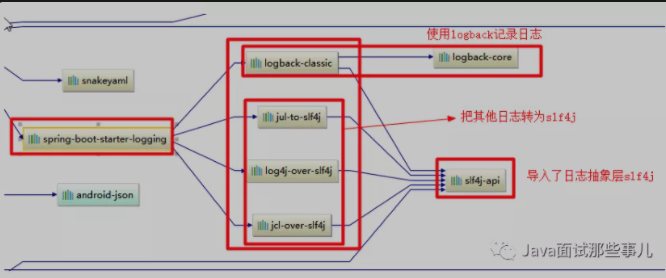 Summary:
Summary:
- The bottom layer of SpringBoot also uses slf4j+logback for logging;
- SpringBoot also replaces other logs with slf4j;
- Tundish replacement?
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public abstract class LogFactory {
static String UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION_IN_JCL_OVER_SLF4J =
"http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#unsupported_operation_in_jcl_over_slf4j";
static LogFactory logFactory = new SLF4JLogFactory();
- What if we want to reference other frameworks? Be sure to remove the default log dependency of this framework?
The Spring framework uses commons logging;
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring‐core</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>commons‐logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons‐logging</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
SpringBoot can automatically adapt all logs, and the bottom layer uses slf4j+logback to record logs. When introducing other frameworks, you only need to exclude the logging framework that this framework depends on;
Use of logs
- Default configuration
SpringBoot helps us configure the log by default;
//Recorder
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
//System.out.println();
//Log level;
//From low to high trace < debug < info < warn < error
//You can adjust the log level of the output; The log will only take effect at this level and at a later high level
logger.trace("This is trace journal...");
logger.debug("This is debug journal...");
//By default, SpringBoot uses the info level for us. If no level is specified, use the level specified by SpringBoot by default; root
level
logger.info("This is info journal...");
logger.warn("This is warn journal...");
logger.error("This is error journal...");
}
Log output format:
- %d represents date and time
- %Thread represents the thread name
- %- 5level: the level displays 5 characters from the left
- %logger{50} indicates that the maximum length of the logger name is 50 characters, otherwise it is divided according to the period
- %msg: log messages
- %n is a newline character
- %d{yyyy‐MM‐dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %‐5level %logger{50}-%msg%n
Spring Boot modifies the default configuration of the log
logging.level.com.atguigu=trace
#logging.path=
# Do not specify a path to generate springboot.log logs under the current project
# You can specify a complete path;
#logging.file=G:/springboot.log
# Create the spring folder and the log folder in the root path of the current disk; Use spring.log as the default file
logging.path=/spring/log
# Format of log output in console
logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd} [%thread] %‐5level %logger{50} ‐ %msg%n
# Specifies the format of log output in the file
logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd} === [%thread] === %‐5level === %logger{50} ==== %msg%n
 2. Specify configuration
2. Specify configuration
Put the configuration file of each log framework on the classpath; SpringBoot will not use its default configuration.
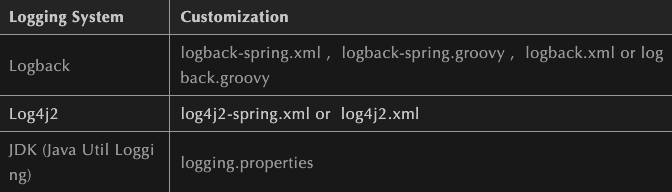 logback.xml: directly recognized by the log framework;
logback.xml: directly recognized by the log framework;
logback-spring.xml: the log framework does not directly load the log configuration items. The log configuration is parsed by SpringBoot. You can use the advanced Profile function of SpringBoot.
<springProfile name="staging">
<!‐‐ configuration to be enabled when the "staging" profile is active ‐‐>
You can specify that a certain configuration only takes effect in a certain environment
</springProfile>
<appender name="stdout" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!‐‐
Log output format:
%d Represents the date and time,
%thread Represents the thread name,
%‐5level: The level is displayed 5 characters wide from the left
%logger{50} express logger The maximum length of the name is 50 characters, otherwise it is divided according to the period.
%msg: Log messages,
%n Is a newline character
‐‐>
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<springProfile name="dev">
<pattern>%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ‐‐‐‐> [%thread] ‐‐‐> %‐5level
%logger{50} ‐ %msg%n</pattern>
</springProfile>
<springProfile name="!dev">
<pattern>%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ==== [%thread] ==== %‐5level
%logger{50} ‐ %msg%n</pattern>
</springProfile>
</layout>
</appender>
If logback.xml is used as the log configuration file and the profile function is also used, the following errors will occur:
no applicable action for [springProfile]
Switch log frame:
Relevant switching can be carried out according to the log adaptation diagram of slf4j;
slf4j+log4j:
dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>logback‐classic</artifactId>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>log4j‐over‐slf4j</artifactId>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j‐log4j12</artifactId>
</dependency>
Switch to log4j2
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐logging</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐log4j2</artifactId>
</dependency>