- Create from yaml file
-
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: cm-appvars data: apploglevel: info appdatadir: /var/data
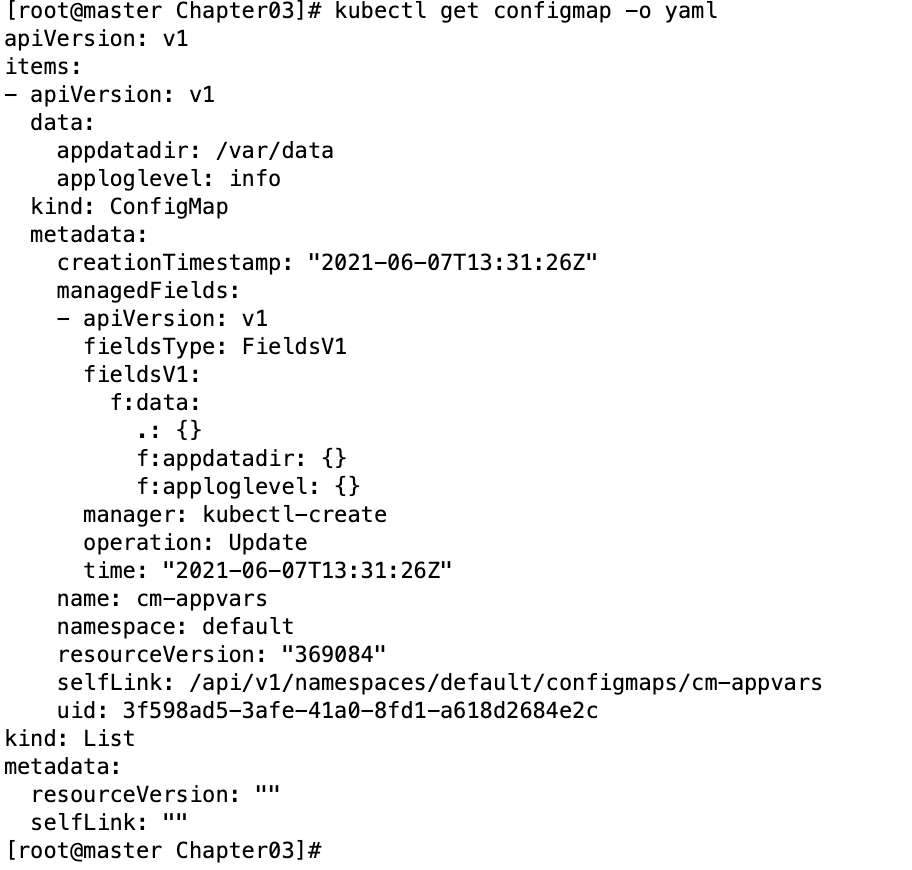
-
Define the two configuration files server.xml and logging.properties as ConfigMap:
-
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: cm-appconfigfiles data: key-serverxml: | <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN"> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener" /> <GlobalNamingResources> <Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container" type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase" description="User database that can be updated and saved" factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory" pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" /> </GlobalNamingResources> <Service name="Catalina"> <Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" connectionTimeout="20000" redirectPort="8443" /> <Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" /> <Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost"> <Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm"> <Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm" resourceName="UserDatabase"/> </Realm> <Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps" unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"> <Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs" prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt" pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" /> </Host> </Engine> </Service> </Server> key-loggingproperties: "handlers = 1catalina.org.apache.juli.FileHandler, 2localhost.org.apache.juli.FileHandler, 3manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler, 4host-manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler, java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler\r\n\r\n.handlers = 1catalina.org.apache.juli.FileHandler, java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler\r\n\r\n1catalina.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.level = FINE\r\n1catalina.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.directory = ${catalina.base}/logs\r\n1catalina.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.prefix = catalina.\r\n\r\n2localhost.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.level = FINE\r\n2localhost.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.directory = ${catalina.base}/logs\r\n2localhost.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.prefix = localhost.\r\n\r\n3manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.level = FINE\r\n3manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.directory = ${catalina.base}/logs\r\n3manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.prefix = manager.\r\n\r\n4host-manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.level = FINE\r\n4host-manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.directory = ${catalina.base}/logs\r\n4host-manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler.prefix = host-manager.\r\n\r\njava.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.level = FINE\r\njava.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.formatter = java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter\r\n\r\n\r\norg.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.[Catalina].[localhost].level = INFO\r\norg.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.[Catalina].[localhost].handlers = 2localhost.org.apache.juli.FileHandler\r\n\r\norg.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.[Catalina].[localhost].[/manager].level = INFO\r\norg.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.[Catalina].[localhost].[/manager].handlers = 3manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler\r\n\r\norg.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.[Catalina].[localhost].[/host-manager].level = INFO\r\norg.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.[Catalina].[localhost].[/host-manager].handlers = 4host-manager.org.apache.juli.FileHandler\r\n\r\n"
- Create from the command line
You can directly create a ConfigMap through kubectl create configmap, or you can specify the content using the parameters -- from file or -- from literal, and you can specify multiple parameters in one line of command.
(1) Create from a file with the -- from file parameter. You can specify a key name or create configmaps for multiple keys on one command linekubectl create config NAME --from-file=[key=] source --from-file=[key=] source
2) Create in the directory through the -- from file parameter. The name of each configuration file in the directory is set to key, and the content of the file is set to value,
kubectl create configmap NAME --from-file=config-files-dir
(3) When using -- from literal, it will be created from the text, and the directly specified key#=value # will be created as the ConfigMap content
kubectl create configmap NAME --from-literal=key1=value1 --from-literal=key2=value2
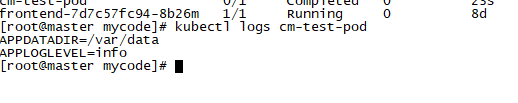
3. Use ConfigMap resource object in Pod Set the contents of "cm appvars" in ConfigMap as the environment variables inside the container in the form of environment variables, and the container startup command displays these two environment variables
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: cm-test-pod spec: containers: - name: cm-test image: busybox command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "env | grep APP" ] env: - name: APPLOGLEVEL #Defines the name of the environment variable valueFrom: configMapKeyRef: name: cm-appvars #Environment variables are taken from cm appvars key: apploglevel #key is the value corresponding to apploglevel - name: APPDATADIR #Define environment variable name valueFrom: configMapKeyRef: name: cm-appvars #Environment variables are taken from cm appvars key: appdatadir #The key is appdatadir restartPolicy: NeverViewing the Pod log, you can see that the ConfigMap value is configured correctly
kubernetes introduces a new field envFrom from version 1.6 to automatically generate the key=value defined in configmap (which can also be used for Secret resource object) into an environment variable in the Pod environment.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: cm-test-pod spec: containers: - name: cm-test image: busybox command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "env" ] envFrom: - configMapRef name: cm-appvars #Automatically generate environment variables according to cm appvars restartPolicy: NeverUsing ConfigMap through volumeMount
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: cm-test-app spec: containers: - name: cm-test-app image: kubeguide/tomcat-app:v1 ports: - containerPort: 8080 volumeMounts: - name: serverxml #The name of the reference volume mountPath: /configfiles #Mount to the directory inside the container volumes: - name: serverxml #Defines the name of the volume configMap: name: cm-appconfigfiles #Use ConfigMap "cm appconfigfiles" items: - key: key-serverxml #Use key = key serverxml path: server.xml #value mount server.xml - key: key-loggingproperties #Use key = key logging properties path: logging.properties #value mount logging.properties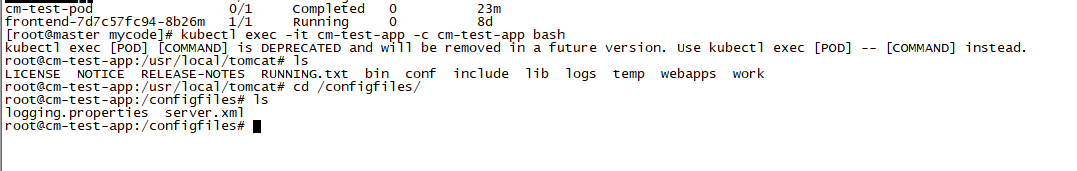
Enter Pod The CM test app container in cm test app can see two mounted files in the / configfile directory.
4. Restrictions on using ConfigMap
ConfigMap must be created before pod before pod can reference it ConfigMap is limited by namespace. Only pods in the same namespace can reference it. ConfigMap cannot be used for static pods. If pod uses evnFrom to define environment variables based on ConfigMap, invalid environment variable names will be ignored and recorded in the event
Kubernetes--Pod management and configuration apiversion: v1kind: configmapmetadata: Name: cm appvarsdata: apploglevel:
Posted by apocryia on Sun, 07 Nov 2021 01:28:18 +0100
1, Configuration management of Pod
The best practice of application deployment is to separate the configuration information required by the application from the program, so that the application can be reused better, and better functions can be realized through different configurations. After the application is packaged into a container image, configuration injection can be carried out when creating a container through environment variables or plug-in files. However, in a large-scale container environment, different configurations of multiple containers will become very complex. K8S provides a unified configuration management scheme - ConfigMap in version 1.2.
1.ConfigMap overview
Typical usage of ConfigMap for containers:
(1) Generate environment variables within the container
(2) Set the container startup command startup parameters (to be set as environment variables)
(3) Mount as volume inside the container
ConfigMap is saved in the K8S system in the form of one or more key: values. It can be used to represent the value of a variable (for example, apploglevel=info) or the content of a complete configuration file (for example, server. XML = <? XML >). ConfigMap can be created through YAML file or kubectl create configmap command line.
2. Create ConfigMap resource object