1. Create Vue under the root path config. JS file
2.vue.config.js file needs to be configured
module.exports = {
publicPath:'./' ,
productionSourceMap: false,
devServer: {
open: false, // Auto launch browser
host: '0.0.0.0', // localhost
port: 6060, // Port number
hotOnly: false, // Hot renewal
overlay: {
// Displays a full screen overlay in the browser when a compiler error or warning occurs
warnings: false,
errors: true
},
proxy: { //Proxy forwarding
//Configure cross domain
'/api': {
target: 'https://www.test.com ', / / domain name of the interface
// ws: true, / / whether to enable websockets
changOrigin: true, // Open the agent and create a virtual server locally
pathRewrite: {
'^/api': '/'
}
}
}
}
}
3. Modify the configuration of static resources (in vue.config.js)
publicPath:'./' // Static resource path (default /, white screen after packaging)
4. Remove the production environment sourceMap (in vue.config.js)
Problem: after the vue project is packaged, some map files will be automatically generated in the js folder, which takes up a considerable part of the space
The sourceMap resource mapping file stores the code location before and after packaging, which is convenient for development and use. This takes up a considerable part of space.
The function of the map file is: after the project is packaged, the code is compressed and encrypted. If an error is reported during operation, the output error information cannot accurately know where the code reports an error. With a map, you can accurately output which line and column has an error like unencrypted code.
sourceMap is not required in the production environment. The following configurations can be removed
module.exports = {
//Remove the productionSourceMap from the production environment
productionSourceMap: false,
}
After removing the comparison before and after sourceMap, a large volume is reduced.
Front: dist size is 7M
Rear: dist size 3M
4. Remove the console Log printing and comments
Download plug-ins
cnpm install uglifyjs-webpack-plugin --save-dev
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production';
configureWebpack: config => {
const plugins = [];
if (isProduction) {
plugins.push(
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
output: {
comments: false, // Remove comments
},
warnings: false,
compress: {
drop_console: true,
drop_debugger: false,
pure_funcs: ['console.log']//Remove console
}
}
})
)
}
},
Conclusion: the volume of dist decreased little after repackaging. Because congsole Log () and comments do not take up too much volume (that is, 10-30kb)
5. Use CDN to accelerate optimization
cdn optimization refers to the introduction of third-party libraries (vue, vue router, axios) into the project through cdn, so that the vendor JS will significantly reduce and greatly improve the loading speed of the home page of the project. The following are the specific operations:

const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production';
// externals exclusion
const externals = {
vue: 'Vue',
'vue-router': 'VueRouter',
vuex: 'Vuex',
vant: 'vant',
axios: 'axios'
}
// The CDN outer chain will be inserted into the index HTML
const cdn = {
// development environment
dev: {
css: [],
js: []
},
// production environment
build: {
css: ['https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vant@2.12/lib/index.css'],
js: [
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.11/dist/vue.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue-router@3.1.5/dist/vue-router.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios@0.19.2/dist/axios.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vuex@3.1.2/dist/vuex.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vant@2.12/lib/vant.min.js'
]
}
}
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: config => {
// Modify configuration for production environment
if (isProduction) {
// externals
config.externals = externals
}
},
chainWebpack: config => {
/**
* Add the CDN parameter to the htmlWebpackPlugin configuration
*/
config.plugin('html').tap(args => {
if (isProduction) {
args[0].cdn = cdn.build
} else {
args[0].cdn = cdn.dev
}
return args
})
}
}
In public / index Add in HTML
<!-- use CDN of CSS file -->
<% for (var i in
htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn&&htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.css) { %>
<link href="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.css[i] %>" rel="preload" as="style" />
<link href="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.css[i] %>" rel="stylesheet" />
<% } %>
<!-- use CDN Accelerated JS File, configuration in vue.config.js lower -->
<% for (var i in
htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn&&htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.js) { %>
<script src="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.js[i] %>"></script>
<% } %>
Conclusion: cdn introduction is configured, and the volume of 1.1M is less than 660kb. The effect is obvious.
5. Compress the resource file (not used temporarily)
6. Picture compression
Image webpack loader needs to be downloaded
cnpm install image-webpack-loader --save-dev
module.exports = {
// Change here according to your actual situation
publicPath,
assetsDir: 'assets',
lintOnSave: true,
// image compression is defined in chainWebpack
chainWebpack: config => {
config.module
.rule('images')
.use('image-webpack-loader')
.loader('image-webpack-loader')
.options({
bypassOnDebug: true
})
.end()}
}
This plug-in is easy to fail to download, resulting in an error
1. If image webpack loader is installed, uninstall it first
//The npm installed by cnpm is removed cnpm uninstall image-webpack-loader //If yarn is installed, remove yarn yarn remove image-webpack-loader
2. Using cnpm means installing cnpm and then setting the global registry to the image of Ali. Domestic Ali is faster
npm install cnpm -g --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
3. Install the image webpack loader using cnpm and you will find that it will be installed soon. [manual]
cnpm install --save-dev image-webpack-loader
7. Public code extraction
// Common code extraction
configureWebpack: config => {
//....
//Optimize Item Configuration
config.optimization = {
splitChunks: { // Split code block
cacheGroups: {
vendor: {//Third party library withdrawal
chunks: 'all',
test: /node_modules/,
name: 'vendor',
minChunks: 1,//The minimum number of times this code block should be referenced before splitting
maxInitialRequests: 5,
minSize: 0,//Greater than 0 bytes
priority: 100//weight
},
common: { //Common module extraction
chunks: 'all',
test: /[\\/]src[\\/]js[\\/]/,
name: 'common',
minChunks: 2,The minimum number of times this code block should be referenced before splitting
maxInitialRequests: 5,
minSize: 0,//Greater than 0 bytes
priority: 60
},
styles: { //Style extraction
name: 'styles',
test: /\.(sa|sc|c)ss$/,
chunks: 'all',
enforce: true
},
runtimeChunk: {
name: 'manifest'
}
}
}
}
}
8. Installing Nginx under Windows
Installation steps
1. Download Nginx
Download address: http://nginx.org/en/download.html (Nginx official website)

General download stable version
2. After downloading, unzip it to the specified directory, and you can see the following directory

3. Switch the console (CMD) to the Nginx directory, enter start nginx, and then enter localhost on the browser page. The following interface indicates that the installation is successful. The default listening port number is 80.

Access your own projects
hash mode
1. Packing
npm run build
2. Put the generated dist directory into the html directory.
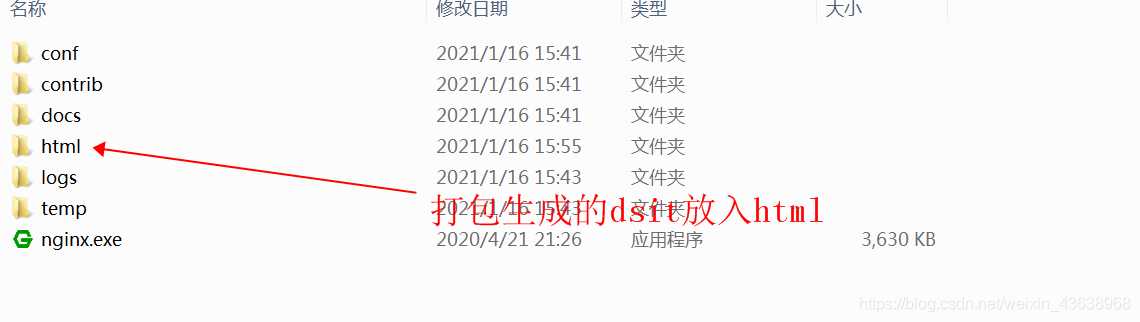
3. Browser access: localhost / dist / index HTML and you can see the page.
9. Complete configuration
const path = require('path');
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin') // Remove comments
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin'); // Turn on compression
const { HashedModuleIdsPlugin } = require('webpack');
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, dir)
}
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production';
// cdn preload usage
const externals = {
'vue': 'Vue',
'vue-router': 'VueRouter',
'vuex': 'Vuex',
'axios': 'axios',
"element-ui": "ELEMENT"
}
const cdn = {
// development environment
dev: {
css: [
'https://unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'
],
js: []
},
// production environment
build: {
css: [
'https://unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'
],
js: [
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.5.17/dist/vue.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue-router@3.0.1/dist/vue-router.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vuex@3.0.1/dist/vuex.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios@0.18.0/dist/axios.min.js',
'https://unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/index.js'
]
}
}
module.exports = {
lintOnSave: false, // Close eslint
productionSourceMap: false,
publicPath: './',
outputDir: process.env.outputDir, // Directory name of the generated file
chainWebpack: config => {
config.resolve.alias
.set('@', resolve('src'))
// Compressed picture
config.module
.rule('images')
.test(/\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/)
.use('image-webpack-loader')
.loader('image-webpack-loader')
.options({ bypassOnDebug: true })
// Webpack will enter chunk vendors for commonChunk by default, so you need to delete the configuration of webpack
config.optimization.delete('splitChunks')
config.plugin('html').tap(args => {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
args[0].cdn = cdn.build
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
args[0].cdn = cdn.dev
}
return args
})
config
.plugin('webpack-bundle-analyzer')
.use(require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin)
},
configureWebpack: config => {
const plugins = [];
if (isProduction) {
plugins.push(
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
output: {
comments: false, // Remove comments
},
warnings: false,
compress: {
drop_console: true,
drop_debugger: false,
pure_funcs: ['console.log']//Remove console
}
}
})
)
// The server should also open gzip accordingly
plugins.push(
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
algorithm: 'gzip',
test: /\.(js|css)$/,// Match file name
threshold: 10000, // Data compression over 10k
deleteOriginalAssets: false, // Do not delete source files
minRatio: 0.8 // Compression ratio
})
)
// It is used to generate a hash according to the relative path of the module as the module id, which is generally used in the production environment
plugins.push(
new HashedModuleIdsPlugin()
)
// Open separation js
config.optimization = {
runtimeChunk: 'single',
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all',
maxInitialRequests: Infinity,
minSize: 1000 * 60,
cacheGroups: {
vendor: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
name(module) {
// Exclude node_modules then replace @ with null, considering the compatibility of the server
const packageName = module.context.match(/[\\/]node_modules[\\/](.*?)([\\/]|$)/)[1]
return `npm.${packageName.replace('@', '')}`
}
}
}
}
};
// Cancel the performance prompt for webpack warning
config.performance = {
hints: 'warning',
//Maximum volume of inlet starting point
maxEntrypointSize: 1000 * 500,
//Maximum volume of generated file
maxAssetSize: 1000 * 1000,
//Only performance tips for js files are given
assetFilter: function (assetFilename) {
return assetFilename.endsWith('.js');
}
}
// Transfer npm packet to CDN during packaging
config.externals = externals;
}
return { plugins }
},
pluginOptions: {
// Configure global less
'style-resources-loader': {
preProcessor: 'less',
patterns: [resolve('./src/style/theme.less')]
}
},
devServer: {
open: false, // Auto launch browser
host: '0.0.0.0', // localhost
port: 6060, // Port number
https: false,
hotOnly: false, // Hot renewal
proxy: {
'^/sso': {
target: process.env.VUE_APP_SSO, // Rewrite path
ws: true, //Open WebSocket
secure: false, // If it is an https interface, this parameter needs to be configured
changeOrigin: true
}
}
}
}