Why cross domain?
Due to the homology policy restrictions of the browser. The same origin policy is a kind of convention. It is the core and basic security function of the browser. If the same origin policy is missing, the normal functions of the browser may be affected. It can be said that the Web is built on the basis of homologous strategy, and the browser is only an implementation of homologous strategy. The same origin policy prevents javascript scripts in one domain from interacting with the content of another domain. The so-called homology (that is, in the same domain) means that two pages have the same protocol, host and port number.
What is cross domain?
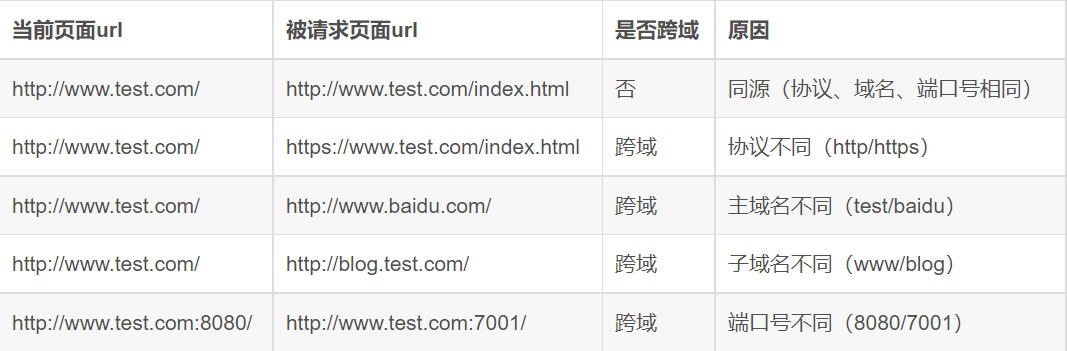
When any of the protocol, domain name and port of a request url is different from the current page url, it is cross domain.
The situation is shown in the figure below:
give an example
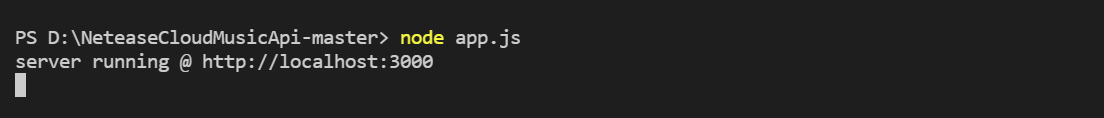
I start a service locally, and the server listens on port 3000
When we directly call the service in the vue project, the interface will report an error
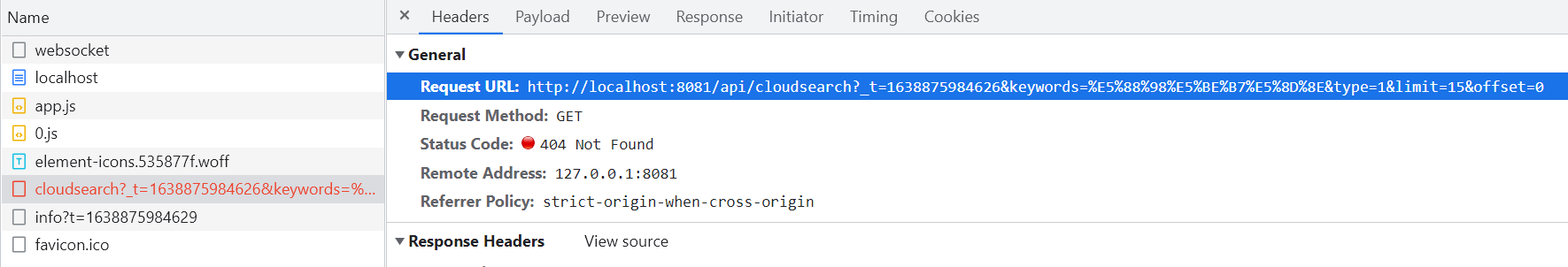
This is because the port we sent the request is 8081, which is inconsistent with the port of the server, resulting in cross domain problems.
Solution
The proxy server is set according to the fact that there is no cross domain between servers.
Check the root directory of the Vue project. If there is a vue.config.js file (usually imported by yourself), open it and find devServer {} and add the following code:
devServer: {
// If it is set to 0.0.0.0, all addresses can be accessed
host: '0.0.0.0',
port: 8080,
https: false,
hotOnly: false,
// Cross domain problem solving agent (key part)
proxy: {
'/api': {
target: 'http://localhost:3000 ', / / attention! This is the real interface provided by the backend
changeOrigin: true, // Allow cross domain
pathRewrite: {
// If there is no api in the interface, set it to null directly, '^ / api': '',
// If there is an api in the interface, it must be written as {'^ / api':'/api'}
'^/api': ''
}
}
}
}Core part

If there is no vue.config.js file, find the index.js file in the config folder in the project
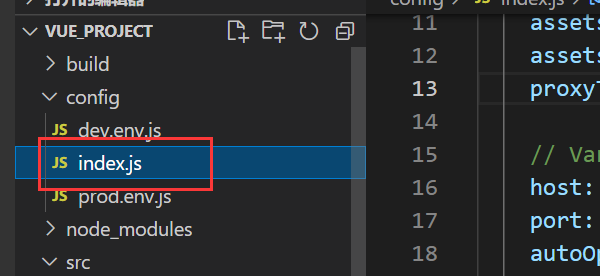
Find proxyTable {} and add the same code as above
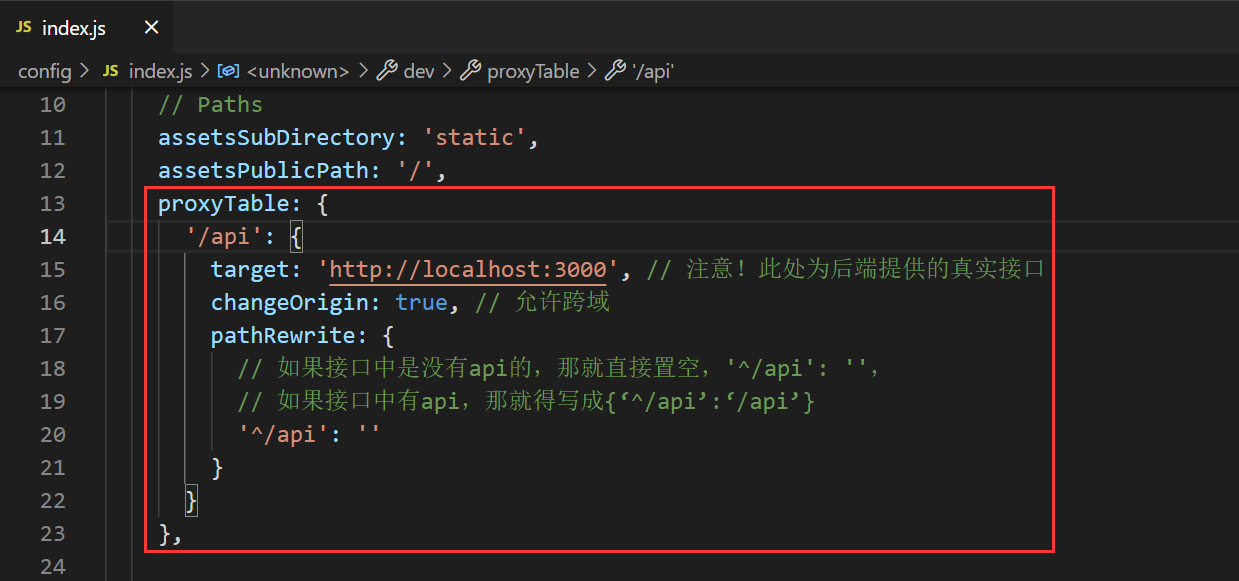
The vue project is stopped and restarted
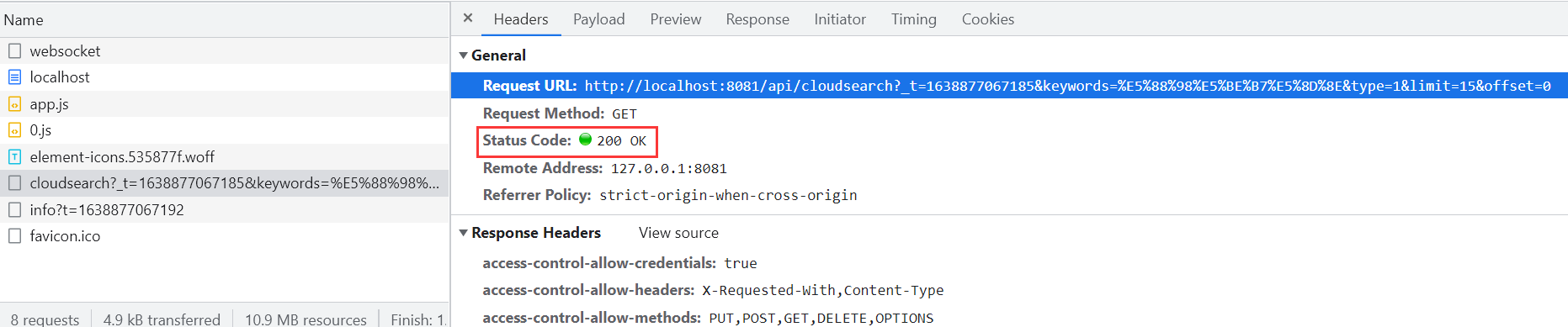
The cross domain problem was resolved and the request was successful. If the project is packaged and launched, you can use Nginx to set up a proxy server.
vue.config.js standard configuration
// vue.config.js
const path = require('path');
const IS_PROD = ['production', 'prod'].includes(process.env.NODE_ENV);
const resolve = (dir) => path.join(__dirname, dir);
module.exports = {
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '/site/vue-demo/' : '/', // Public path
indexPath: 'index.html' , // Relative to the package path index.html
outputDir: process.env.outputDir || 'dist', // 'dist ', the directory of the production environment build file
assetsDir: 'static', // Static resource (js, css, img, fonts) directory relative to outputDir
lintOnSave: false, // Whether to use eslint loader to save lint code every time in the development environment
runtimeCompiler: true, // Use Vue build with runtime Compiler
productionSourceMap: !IS_PROD, // source map of production environment
parallel: require("os").cpus().length > 1, // Whether to use thread loader for Babel or TypeScript. This option is automatically enabled when the CPU of the system has more than one kernel and only works on production builds.
pwa: {}, // Pass options to the PWA plug-in.
chainWebpack: config => {
config.resolve.symlinks(true); // Fix hot update failure
// If you use multi page packaging, use vue inspect --plugins to check whether the html is in the result array
config.plugin("html").tap(args => {
// Fix Lazy loading routes Error
args[0].chunksSortMode = "none";
return args;
});
config.resolve.alias // add alias
.set('@', resolve('src'))
.set('@assets', resolve('src/assets'))
.set('@components', resolve('src/components'))
.set('@views', resolve('src/views'))
.set('@store', resolve('src/store'));
},
css: {
extract: IS_PROD,
requireModuleExtension: false,// Remove the. module from the file name
loaderOptions: {
// Pass Less.js related options to less loader
less: {
// `globalVars ` defines global objects and can be added to global variables
globalVars: {
primary: '#333'
}
}
}
},
devServer: {
overlay: { // Let the browser overlay display both warnings and errors
warnings: true,
errors: true
},
host: "localhost",
port: 8080, // Port number
https: false, // https:{type:Boolean}
open: false, //Configure auto start browser
hotOnly: true, // Hot renewal
// proxy: 'http://localhost:8080 '/ / configure cross domain processing. There is only one agent
proxy: { //Configure multiple cross domains
"/api": {
target: "http://172.10.10.12:3000",
changeOrigin: true,
// ws: true,//websocket support
secure: false,
pathRewrite: {
"^/api": ""
}
},
"/api2": {
target: "http://172.10.12.13:8089",
changeOrigin: true,
//ws: true,//websocket support
secure: false,
pathRewrite: {
"^/api2": "/"
}
},
}
}
}