1. Preface
In fact, for me, the knowledge of the school is certainly not enough for finding a job after graduation, so I can only constantly expand myself and learn some new knowledge, and the technology changes very quickly. So I vue do a simple study.
2. Template and its simple syntax
1. Brief introduction to elements
<body>
<div id="hellovue">
<p>{{label}}</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#hellovue',
data:{
label:'hello vue!'
},
methods:{
},
})
</script>
</body>
- This double bracket is enclosed by text interpolation, which is used for data binding. Use vue's data to declare the data we need. In the above example, I changed the content of < p > to "hello vue".
In short: {}} is used to output object properties and function return values
- el can be used to specify the id of DOM, so that we can modify the known DOM, add some functions to some data
- method is a function. You can use return to return a value. It contains the whole logic of the page and some trigger events.
2. Introduction to template syntax
- v-html is used to output HTML code to update the tags
<body>
<div id="hellovue">
<p>{{label1}}</p>
<p v-html="label2"></p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#hellovue',
data:{
label1:"Modify text only",
label2:'<h1>Here is the tag language (title)</h1>'
},
})
</script>
</body>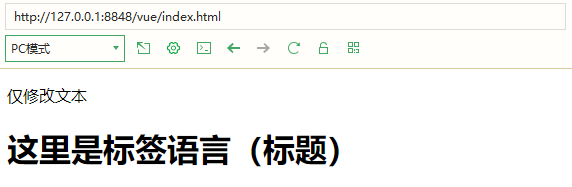
2.v-text replaces the content of the element with the statement
Note: different from the interpolation expression here, it will replace the entire element content. For example, the content I replaced is hello
<p>{{label}} vue</p>
The result is: hello vue
<p v-text='label'>vue</p>
The result is: hello
<body>
<div id="hellovue">
<p v-text="label2">123456</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#hellovue',
data:{
label2:'I'm not 123456'
},
})
</script>
</body>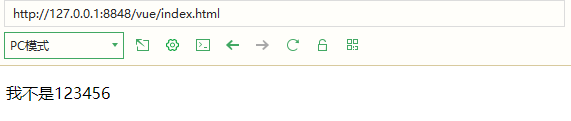
3.v-cloak can solve the problem of page flickering using interpolation expression
<div v-cloak>{{ok}}</div>
<style type="tetxt/css">
[v-cloak]{
display:none;
}
</style}4.v-model implements two-way binding of data, which will change the elements of the other party at the same time
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<input v-model="message">
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hello vue!'
}
})
</script>
</body>
Note: when you enter content in the text box, the bound message content also changes
5.v-once refers to the instruction. The elements, components and all nodes that use the instruction will be treated as static content and skipped. (can be used to optimize update performance)
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-once>Render data once:{{text}}</p>
<p>Data that can be changed:{{text}}</p>
<p ><input type="text" v-model = "text"></p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
text:"Current content "
},
methods:{
},
})
</script>
</body>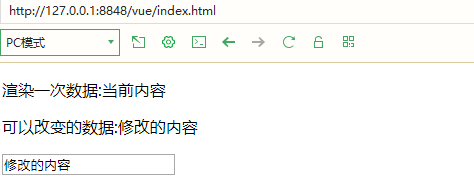
6.v-on can be used to bind events or pass parameters
<body>
<div id="onclick">
<p>{{message}}</p>
<input type="button" value="Click event" v-on:click="alert">
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#onclick',
data:{
message:'ok'
},
methods:{
alert:function() {
this.message='chagetext'
}
},
})
</script>
</body> 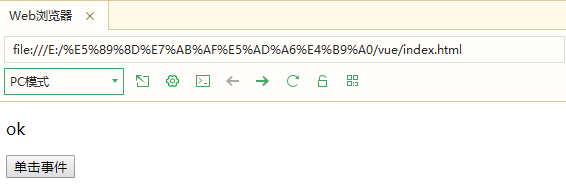
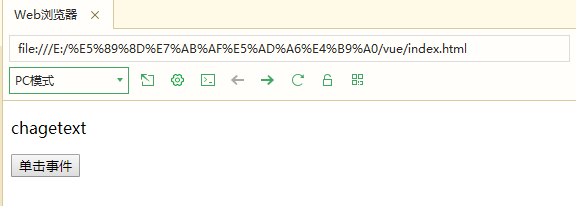
Note; v-on can be abbreviated as @ click
7.v-if Whether to insert the p element depends on the value (true or false) of the expression V-IF (I used bool here)
<body>
<div id="exchange">
<input type="button" value="display/Do not display" @click="exchange">
<p v-if="bool">Display successful</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#exchange',
data:{
bool:false
},
methods:{
exchange:function(){
this.bool=!this.bool;
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
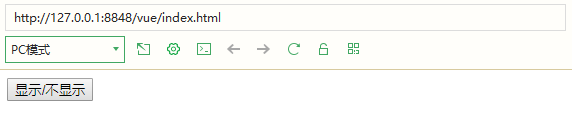
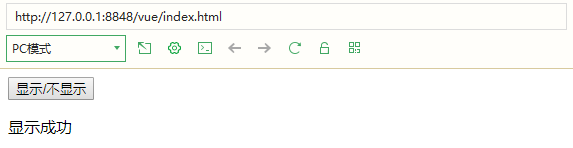
8. If the effect of v-show is the same as that of v-if, no code demonstration will be carried out
Difference: v-if deleting and adding DOM elements
v-show just changes the true and false display style of DOM elements
Obviously, for the above differences, the rendering cost of v-if switching is higher, and the initial rendering cost of v-show is higher
9.v-bind is used to change the attribute name of an element
v-bind can be abbreviated as': '
For example: v-bind:src='url 'can be rewritten as: src='url'
<body>
<div id="app">
<pre><a v-bind:href="url">use Baidu Search </a></pre>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
url: 'http://www.baidu.com'
}
})
</script>
</body>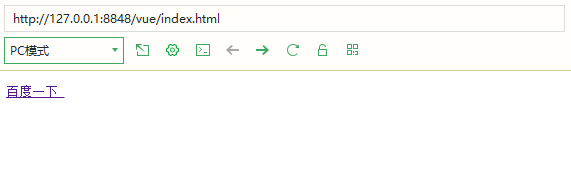
3. Summary
The above is my introduction to vue2.0
Refer to the following blogs and materials: vue beginner's Guide (easy to understand)_ liuzhaoh's blog - CSDN blog_ vue novice introduction