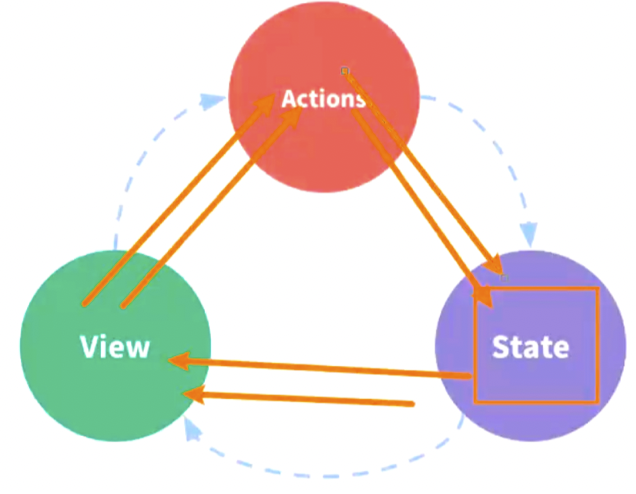
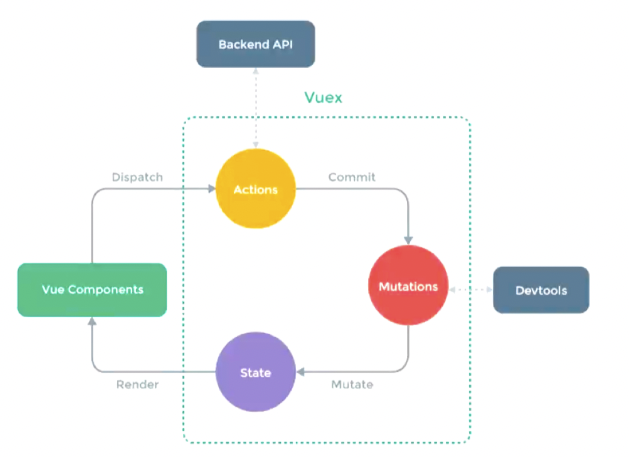
Vuex is suitable for complex state management
Install the specified version in Vue3
npm install vuex@next
Basic use process of Vuex
Simple version
- Create a folder at the same level as components store / index js
import {createStore} from 'vuex'
const store = createStore({
state(){
return{
count:0
}
},
mutations:{
increment(state){
state.count++
},
decrement(state){
state.count--
}
},
})
export default store
- main. Import store from JS entry file
import {createApp} from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
createApp(App).use(store).mount('#app')
- Home.vue
<template>
<h2>{{$store.state.counter}}</h2>
<button @click='increment'>+1</button>
<button @click='decrement'>-1</button>
</template>
<script>
import {mapMutatons} from "vuex"
export default{
setup(){
const storeMutations = mapMutations(['increment','decrement'])
return {
...storeMutations
}
}
}
</script>
Component get status
mapState helper function
Home.vue
<template>
<h2> Home(computed):{{sCounter}}</h2>
<h2>{{counter}}</h2>
<h2> {{height}} </h2>
</template>
Options API implementation
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
1 or 2 or 3 or 4
</script>
- Alias by calculating attributes in the component
computed:{
sCounter(){
return this.$store.state.counter
}
}
- Get the state attribute in all vuex to the component mapping calculation attribute through mapState function
computed:mapState()
- mapState array is written in such a way that the calculation properties of the component itself are reserved ➕ Other attributes in vuex
By calculating the attributes mapped from the attributes, you can directly use {{counter}} in the template without adding $store state
computed:{
homeKey(){
return 'home private key'
},
...mapState(["counter","age","height"])
}
- The mapState object is written in such a way that the attributes in the state can be aliased in the component (in the form of function return value)
computed:{
...mapState({
sCounter:state => state.counter
})
}
Composition API implementation
<script>
import {computed} from 'vue'
import {mapState,useState} from 'vuex'
// The return value of mapState is an object, in which there are functions one by one. After the function is called, the corresponding attribute value in state is obtained
export default{
setup(){
const store = useState()
//1. Map directly with computed
const sCounter = computed(()=>store.state.counter)
//2 mapstate pass in array
const storeStateFns = mapState(["counter","height","age"])
const storeState = {}
// ergodic
Object.keys(stroeStateFns).forEach(fnKey=>{
// Because there is no this in setup, you must pass in {$store:state} and manually point the state of vuex to the calling function
const fn = storeStateFns[fnKey].bind({$store:state})
storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn) // Convert to calculated attribute
})
return {
sCounter,
...storeState
}
}
}
</script>
Extract the section traversing the state attribute into hooks / usestate js
import {computed} from 'vue'
import {mapState,useState} from 'vuex'
export function useState(mapper){
const store = useState()
const storeStateFn = mapState(mapper)
const storeState = {}
Object.keys(storeStateFn).forEach(fnKey => {
const fn = storeStateFn[fnKey].bind({$store:State})
storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn)
})
return storeState
}
Usestate is used in the component JS function
<script>
import useState from '../hooks/useState'
export default{
setup(){
const storeState = useState(["counter","age","height"])
return {...storeState}
}
}
</script>
Basic use of getters
The attributes of vuex are not directly used in the component, and getters is used when it needs to be changed
store / index.js
import {createStore} from 'vuex'
const store = createStore({
state(){
return{
counter:0,
books:[
{
name:"Principle of computer composition",
count:50,
price:22
},
{
name:"Development practice of single chip microcomputer",
count:20,
price:18
},
]
}
},
mutations:{
increment(state){
state.counter++
},
decrement(state){
state.counter--
}
},
getters:{
//Sum
totalPrice(state,getters){
return state.books.reduce((pre,cur)=>{
return pre+cur.count*cur.price
},0)
},
nameInfo(state){
return `name:${state.name}`
}
}
})
Use in components
<h2>Total value{{totalPrice}}</h2>
<script>
import {mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default{
computed:{
nameInfo(){ return this.$store.getters.nameInfo},
computed:{...mapGetters},
computed:{
...mapGetters(["nameInfo","ageInfo","heightInfo"])
},
computed:{
...mapGetters({
sNameInfo:"nameInfo"
})
}
}
}
</script>
Composition API usage
import {computed} from 'vue'
import {mapGetters,useStore} from 'vuex'
export default{
setup(){
const store = useStore()
const sNameInfo = computed(()=>store.getters.nameInfo)
const storeGettersFns = mapGetters(["nameInfo","ageInfo"])
const sotreGettrs = {}
Object.keys(storeGettersFns).forEach(fnKey = >{
const fn = storeGettersFns[fnKey].bind({$store:store})
storeGetters[fnKey] = computed(fn)
})
return{
sNameInfo,
...sotreGettrs
}
}
}
It is very similar to useState, except mapState and mapGetters are different, so the common part is extracted
hooks/index.js
import {useState} from './useState'
import {useGetters} from './useGetters'
export {useState,useGetters}
hooks/useMapper.js
import {computed} from 'vue'
import {useStore} from 'vuex'
export function useMappr(mapper,mapFn){
const store = useStore()
const storeStateFn = mapFn(mapper)
const storeState = {}
Object.keys(storeStateFn).forEach(fnKey => {
const fn = sotreStateFn[fnKey].bind({$store:store})
storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn)
})
return storeState
}
hooks/useGetters.js
import {mapGetter} from 'vuex'
import {useMapper} from './useMapper'
export function useGetters (moduleName,mapper){
let mapperFn = mapGetters
return useMapper(mapper,mapperFn)
}
hooks/useState.js
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
import {useMapper} from './useMapper'
export function useState (moduleName,mapper){
let mapperFn = mapState
return useMapper(mapper,mapperFn)
}
Use in components
import {useGetters,useState} from '../hooks/index'
setup(){
const storeGetters = useGetters(["nameInfo","ageInfo","heightInfo"])
const storeState = useState(["counter","name","age","height"])
return {
...storeGetters,
...storeState
}
}
Basic use of Mutations
The only way to change the state in Vuex's store is to submit changes
Options API usage
1.
this.$store.commit("mutations Inside method name",{Passed parameter object})
2
this.$store.commit({
type:"mutations Inside method name",
age:12,
...Transfer parameters
})
Generally, when the same variable name is used in multiple places, it can be encapsulated as a constant file
store / mutations-type.js
export const INCREMENT_N = "increment_n"
store / index.js
import {INCREMENT_N} from "./mutations-type'
mutations:{
[INCREMENT_N](state,payload){
state.counter += payload.n
}
}
Use in components
mapMutations returns an object. There is a function in the object, and the method binding is also a function. There is no need to convert
<button @click='increment_n({n:10)'>+10</button>
<script>
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'
import {INCREMENT_N} from '../store/mutations-type'
export default{
setup(){
const storeMutations = mapMutations(['increment','decrement',INCREMENT_N])
return {
...storeMutations
}
}
}
</script>
Actions
Asynchronous operations are put here, such as network requests
The difference between actions and changes:
- actions submits changes instead of directly changing the state
- actions can contain any asynchronous operation
actions usage
In component
methods:{
this.$store.dispatch("actions The name inside",{Parameters passed,Can not pass})
}
store / index.js
import {createStore} from 'vuex'
const store = createStore({
state(){
return{
banners:[]
}
},
mutations:{
increment(state,payload){
state.counter++
}
},
actions:{
incrementAction(context,payload){
//Asynchronous operation
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit("increment")
},1000)
}
}
})
- What's in the context?
| name | meaning | usage |
|---|---|---|
| commit | Call the method in mutations | Commit ("") is equivalent to context commit() |
| dispatch | Call other methods in actions | dispatch() |
| getters | Get a property in getters | Getters () is equivalent to context getters() |
| state | Get the value in state |
- context deconstruction
actions:{
decrementAction({commit,dispatch,state}){
commit("decrement")
}
}
Another way to use the methods in actions in components
methods:{
decrement(){
this.$store.dispatch({
type:"decrementAction"
})
}
}
Auxiliary function mapActions of actions
Used in components
<script>
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default{
methods:{
...mapActions(["decrementAction","incrementAction"]),
...mapActions({
add:"incrementAction",
sub:"decrementAction"
})
},
setup(){
const actions = mapActions(["decrementAction","incrementAction"])
return{
...actions
}
}
}
</script>