/*
*Copyright (c)2017, School of computer and control engineering, Yantai University
*All rights reservrd.
*Author: Li Xinhao
*Completion time: November 26, 2017
*Version number: v1.0
*Problem Description: topological sorting algorithm verification
The following figure is an example:
1, Based on graph.h, the header file of graph database
Add the function void TopSort(ALGraph *G); declare
The code is as follows:
#ifndef GRAPH_H_INCLUDED #define GRAPH_H_INCLUDED #define MAXV 100 / / maximum number of vertices #Define inf 32767 / / inf means ∞ typedef int InfoType; //The following defines the type of adjacency matrix typedef struct { int no; //Vertex number InfoType info; //Other information of vertex, where the weight of weighted graph is stored } VertexType; //Vertex Type typedef struct //Definition of Graphs { int edges[MAXV][MAXV]; //adjacency matrix int n,e; //Number of vertices, arcs VertexType vexs[MAXV]; //Store vertex information } MGraph; //Adjacency matrix types of Graphs //The following defines the adjacency table type typedef struct ANode //Node structure type of arc { int adjvex; //End position of the arc struct ANode *nextarc; //Pointer to the next arc InfoType info; //The relevant information of the arc is used to store the weight } ArcNode; typedef int Vertex; typedef struct Vnode //Types of adjacent header nodes { Vertex data; //Vertex information int count; //Store vertex access, only used in topological sorting ArcNode *firstarc; //Point to the first arc } VNode; typedef VNode AdjList[MAXV]; //AdjList is an adjacency table type typedef struct { AdjList adjlist; //Adjacency list int n,e; //Vertex number n and edge number e in the graph } ALGraph; //Adjacency table types of Graphs //Function: construct a graph stored by adjacency matrix from a 2D array reflecting the adjacency relationship of vertices in the graph //Parameter: Arr - array name. Since the formal parameter is a two-dimensional array, the number of elements in each row must be given. Here, the parameter Arr is declared as a one-dimensional array name (pointer to int) // The order of n - matrix // g - adjacency matrix data structure to be constructed void ArrayToMat(int *Arr, int n, MGraph &g); //Constructing adjacency matrix of graph with common array void ArrayToList(int *Arr, int n, ALGraph *&); //Constructing adjacency table of graph with common array void MatToList(MGraph g,ALGraph *&G);//Transforming adjacency matrix G into adjacency table G void ListToMat(ALGraph *G,MGraph &g);//Transforming adjacency table g into adjacency matrix G void DispMat(MGraph g);//Output adjacency matrix g void DispAdj(ALGraph *G);//Output adjacency table G void TopSort(ALGraph *G); #endif // GRAPH_H_INCLUDED
2, Define these functions in the source file graph.cpp file:
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> #include "graph.h" //Function: construct a graph stored by adjacency matrix from a 2D array reflecting the adjacency relationship of vertices in the graph //Parameter: Arr - array name. Since the formal parameter is a two-dimensional array, the number of elements in each row must be given. Here, the parameter Arr is declared as a one-dimensional array name (pointer to int) // The order of n - matrix // g - adjacency matrix data structure to be constructed void ArrayToMat(int *Arr, int n, MGraph &g) { int i,j,count=0; //Count is used to count the number of sides, that is, the number of non-zero elements in the matrix g.n=n; for (i=0; i<g.n; i++) for (j=0; j<g.n; j++) { g.edges[i][j]=Arr[i*n+j]; //The Arr is regarded as a two-dimensional array of n × n, and the Arr[i*n+j] is the Arr[i][j] if(g.edges[i][j]!=0 && g.edges[i][j]!=INF) count++; } g.e=count; } void ArrayToList(int *Arr, int n, ALGraph *&G) { int i,j,count=0; //Count is used to count the number of sides, that is, the number of non-zero elements in the matrix ArcNode *p; G=(ALGraph *)malloc(sizeof(ALGraph)); G->n=n; for (i=0; i<n; i++) //Set the initial value of the pointer field of all header nodes in the adjacency table G->adjlist[i].firstarc=NULL; for (i=0; i<n; i++) //Check every element in adjacency matrix for (j=n-1; j>=0; j--) if (Arr[i*n+j]!=0) //There is an edge. Consider Arr as a two-dimensional array of n × n. Arr[i*n+j] is Arr[i][j] { p=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); //Create a node * p p->adjvex=j; p->info=Arr[i*n+j]; p->nextarc=G->adjlist[i].firstarc; //Insert * p by head insertion G->adjlist[i].firstarc=p; } G->e=count; } void MatToList(MGraph g, ALGraph *&G) //Transforming adjacency matrix G into adjacency table G { int i,j; ArcNode *p; G=(ALGraph *)malloc(sizeof(ALGraph)); for (i=0; i<g.n; i++) //Set the initial value of the pointer field of all header nodes in the adjacency table G->adjlist[i].firstarc=NULL; for (i=0; i<g.n; i++) //Check every element in adjacency matrix for (j=g.n-1; j>=0; j--) if (g.edges[i][j]!=0) //There is an edge { p=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); //Create a node * p p->adjvex=j; p->info=g.edges[i][j]; p->nextarc=G->adjlist[i].firstarc; //Insert * p by head insertion G->adjlist[i].firstarc=p; } G->n=g.n; G->e=g.e; } void ListToMat(ALGraph *G,MGraph &g) //Transforming adjacency table g into adjacency matrix G { int i,j; ArcNode *p; g.n=G->n; //According to the first floor students "report" change. g.n is not assigned, the following initialization does not work g.e=G->e; for (i=0; i<g.n; i++) //Initialize adjacency matrix first for (j=0; j<g.n; j++) g.edges[i][j]=0; for (i=0; i<G->n; i++) //Assign values to adjacency matrix according to adjacency table { p=G->adjlist[i].firstarc; while (p!=NULL) { g.edges[i][p->adjvex]=p->info; p=p->nextarc; } } } void DispMat(MGraph g) //Output adjacency matrix g { int i,j; for (i=0; i<g.n; i++) { for (j=0; j<g.n; j++) if (g.edges[i][j]==INF) printf("%3s","∞"); else printf("%3d",g.edges[i][j]); printf("\n"); } } void DispAdj(ALGraph *G) //Output adjacency table G { int i; ArcNode *p; for (i=0; i<G->n; i++) { p=G->adjlist[i].firstarc; printf("%3d: ",i); while (p!=NULL) { printf("-->%d/%d ",p->adjvex,p->info); p=p->nextarc; } printf("\n"); } } void TopSort(ALGraph *G) { int i,j; int St[MAXV],top=-1; //The pointer of stack St is top ArcNode *p; for (i=0; i<G->n; i++) //Entry setting initial value 0 G->adjlist[i].count=0; for (i=0; i<G->n; i++) //Find the degree of entry of all vertices { p=G->adjlist[i].firstarc; while (p!=NULL) { G->adjlist[p->adjvex].count++; p=p->nextarc; } } for (i=0; i<G->n; i++) if (G->adjlist[i].count==0) //Enter the vertex stack of 0 { top++; St[top]=i; } while (top>-1) //Stack is not a space-time loop { i=St[top]; top--; //Stack out printf("%d ",i); //Output vertex p=G->adjlist[i].firstarc; //Find the first adjacent vertex while (p!=NULL) { j=p->adjvex; G->adjlist[j].count--; if (G->adjlist[j].count==0)//Stack adjacent vertices with degree 0 { top++; St[top]=j; } p=p->nextarc; //Find next adjacent vertex } } }
3, Complete the test in the source file main.cpp
The code is as follows:
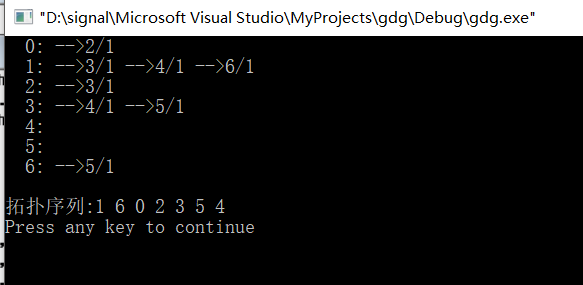
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> #include "graph.h" int main() { ALGraph *G; int A[7][7]= { {0,0,1,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,1,1,0,1}, {0,0,0,1,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,1,1,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,1,0} }; ArrayToList(A[0], 7, G); DispAdj(G); printf("\n"); printf("Topological sequence:"); TopSort(G); printf("\n"); return 0; }
4, The screenshot of the test results is as follows: