Python comments
Block and inline comments
# Block comments are generally used to describe the code below
if a > 10 :
# according to PEP8 Specification, block annotation with a#And a space, unless indenting is required in block comments
a = 10
else:
# A block comment should have the same indentation as the code it is commenting on
a *= 2
# Inline comments are used to comment a line of code
a //=2 # it's hard to imagine what needs to be commented on a line of code, so it's useless most of the time
b **= 2 # Don't comment on such obvious code
c = {word : annotation for word, annotation in dictionary if len(annotation) > 1} # Select words with multiple interpretations
Block comments and inline comments are the simplest and most common comments, and they are also very common in other languages
Documentation Comments
It can be used to annotate modules, functions, classes and methods. It consists of six pairs of single quotation marks or double quotation marks (preferably double quotation marks)
modular
Put between the ID at the beginning of the file and import
module1.py
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- """this is a test module""" import requests from lxml import etree
Actually, it's at the beginning of the document
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
It can also be regarded as a comment, but this comment is not (only) for people to see. It identifies the program and code of the running file
function
The function documentation comments are placed on the next line of def
module1.py
# Multiline function document comments
def max(*args, key=None): # known special case of max
"""
max(iterable, *[, default=obj, key=func]) -> value
max(arg1, arg2, *args, *[, key=func]) -> value
With a single iterable argument, return its biggest item. The
default keyword-only argument specifies an object to return if
the provided iterable is empty.
With two or more arguments, return the largest argument.
"""
pass
# Single line function documentation comments should keep quotation marks on the same line
def foo(a, b):
"""write annotation in one line"""
# Functions with document comments can have no function body
A common function document annotation format is several keywords starting with a colon to describe parameters, return values, exceptions, etc
Format is
[General notes] :<keyword> <name>: <annotation> :<keyword> <name>: <annotation> ... :<keyword> <name>: <annotation>
from operator import lt
def foo_max(lhs, rhs):
"""
return bigger item, if equals return left one
:param lhs: left hand side item
:param rhs: right hand side item
:return: bigger item or left item
"""
return rhs if lt(lhs, rhs) else lhs
Common keywords are
- param: parameter
- Type: parameter type
- Return: return value
- rtype: return value type
- Exception: except ion type
In addition, there are many other formats, you can read the official code or third-party code to learn
class
Write on the next line of class
module1.py
class Foo:
"""Fooooooooooooooo"""
Get document comments
Can pass__ doc__ Get document comments using magic properties
# The previously written functions and classes are in module1 Py module import module1 print(module1.__doc__) print(module1.foo_max.__doc__) print(Foo.__doc__)
Third party tools such as type checker, IDE and static checker also have the ability to obtain document comments
The following is the case in PyCharm (module1 is changed to main)
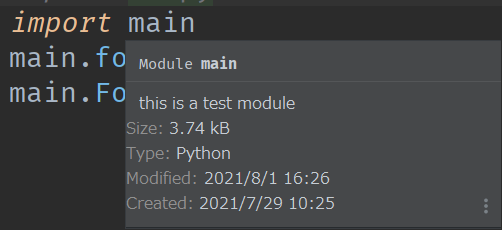
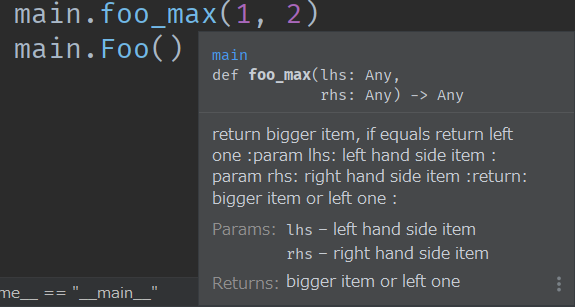
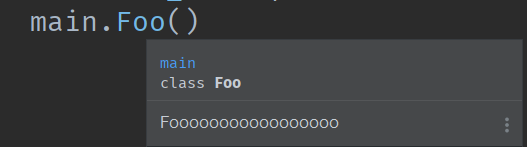
type annotation
Python, as a language of dynamic types (type binding at runtime), does not need to provide types. However, if type annotation is provided, it can be used for third-party tools such as type checker, IDE and static checker
Write type comment
Type comments can be written in code, function parameters, and return values
from typing import List, Tuple
a: list = [1, 2, 3]
# Parameter type and return value type
def foo(a: int = 5) -> int:
# int is the type and 5 is the default (default)
return a
# String comment
def bar(b: "it's b'") -> "return b itself":
return b
# Comments for complex types
def baz(c: List[Tuple, ...]):
return c
In fact, after colon, you can write other things, such as numbers and functions, but the most commonly used are type comments and string comments
You can even call functions
def qux(d: print(4 if 5 > 8 else 7)):
return d
As in normal code, but this writing should not appear in actual use
According to the PEP8 specification, type comments should have the following spaces
# Yes: def munge(input: AnyStr): pass def munge() -> AnyStr: pass # No: def munge(input:AnyStr): pass def munge()->PosInt: pass
Get type comment
Pass__ annotations__ Magic attribute acquisition, which can only be used for functions
print(foo.__annotations__)
print(bar.__annotations__)
print(baz.__annotations__)
# display:
# {'a': <class 'int'>, 'return': <class 'int'>}
# {'b': "it's b'", 'return': 'return b itself'}
# {'c': typing.List[typing.Tuple]}
Using the typing module
The typing module (and collections.abc module) can help us write better type annotations. In fact, the official documents have been written very clearly. Only several commonly used types are provided here
from typing import Any, List, Tuple, Iterator, NoReturn, Literal
# Most common use
def foo(a: Any) -> NoReturn:
raise RuntimeError('no way')
# The demonstration of the combination of types can be extended to other types
# Empty tuple
Tuple[()]
# Single element tuple
Tuple[int]
# Dual element list
List[int, str]
# Variable length homogeneous tuple
Tuple[int, ...]
# More complex
Tuple[Union[Tuple[int, str], List[int, str]], ...]
# Union select one more
def foo(arg: Union[int, str]) -> NoReturn:
pass
# Optional, with default value
def foo(arg: Optional[int] = None) -> NoReturn:
pass
# Literal choose one more
def foo(arg: Literal[1, 2, 3]) -> NoReture:
pass
# Callable callable
# Iterator generator
Similarly, in PyCharm, type annotations can be perceived, and various methods of tuple and list are provided here
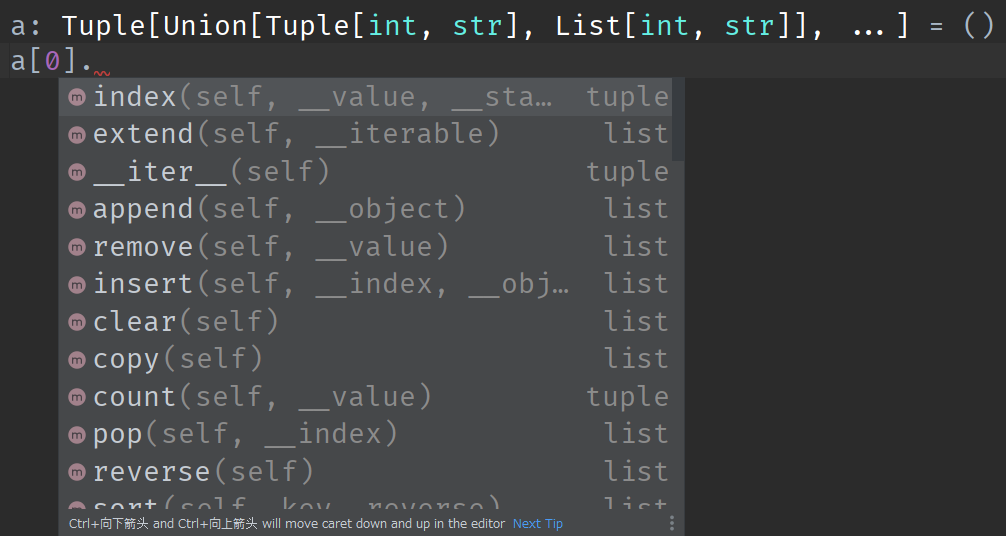
Various other types of notes are also available in official documents