3.4 binary search tree
The function of binary search tree
one ️⃣ Provides the ability to find elements that take logn time
two ️⃣ Provides the ability to insert and delete elements taking logn time
For 10000 data
■ using a linear table to find elements requires an average of 5000 comparisons
■ using binary search tree to find elements only needs 14 times on average
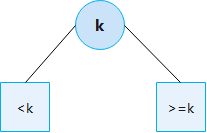
Definition: if the value of any node of the binary search tree is k, the value of any node in the left subtree of the node is less than K; The value of any node in the right subtree of the node is greater than or equal to K.
Interface and node definition
For BST, its interface is defined as follows
public interface BSTADT <K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
public void insert(K key, V value);//Insert Knot
public V remove(K key);//Delete nodes according to the key value
public boolean update(BinNode<K, V> rt, K key, V value);//Update node value
public V search(K key);//Search the value of the node corresponding to the key
public int getHeight(BinNode<K, V> rt);//Gain tree height
public boolean isEmpty();//Judge whether it is empty
public void clear();//Empty tree
}
The nodes of the tree are defined as follows
public class BinNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
private K key;
private V value;
private BinNode<K, V> left;
private BinNode<K, V> right;
public BinNode(K key, V value){
left = right = null;
this.key=key;
this.value=value;
}
public BinNode() {
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return left == null && right == null;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(K key) {
this.key = key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
public BinNode<K, V> getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(BinNode<K, V> left) {
this.left = left;
}
public BinNode<K, V> getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(BinNode<K, V> right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
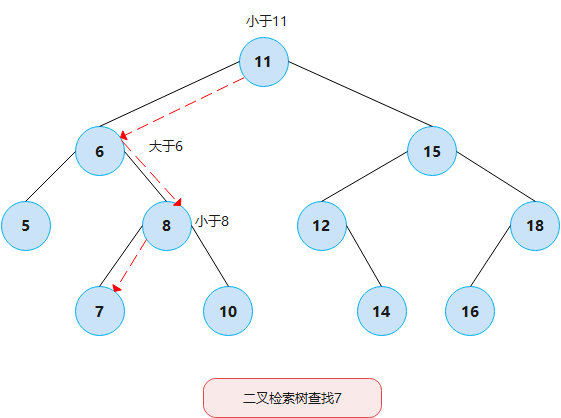
Find an element
Algorithm for finding an element in binary search tree
one ️⃣ Set the current node to point to the root node
two ️⃣ Repeat the following steps;
■ if the current node is empty, exit and no element to match is found
■ if the keyword of the element contained in the current node is greater than the keyword of the element to be searched, set the current node to point to its left child node
■ if the keyword of the element contained in the current node is less than the keyword of the element to be searched, set the current node to point to its right child node
■ otherwise, the matching element is found and exits
public V search(K key) {
return search(root, key);
}
private V search(BinNode<K, V> rt, K key) {
try {
if (key == null)
throw new Exception("key is null");
if (rt == null)
return null;
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) < 0)
return search(rt.getLeft(), key);//If it is less than the current key value, search the left subtree
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) > 0)
return search(rt.getRight(), key);//If it is greater than the current key value, search the right subtree
return rt.getValue();//Value found
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
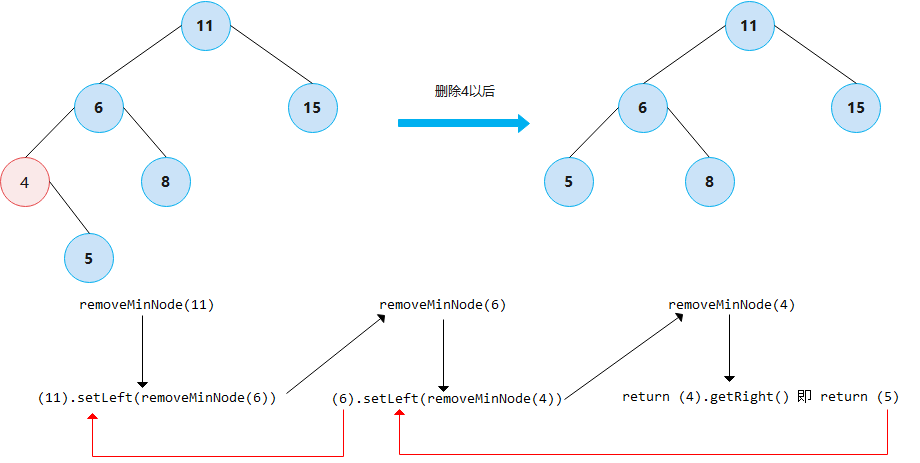
Find and delete the smallest element
Finding the smallest element is relatively simple. You only need to recursively find it to the left until the left child node is empty
The idea of deleting the smallest element is as follows
private K getMinNode(BinNode<K, V> rt) {
if (rt.getLeft() == null)
return rt.getKey();
else
return getMinNode(rt.getLeft());
}
//Returns the updated root node
private BinNode<K, V> removeMinNode(BinNode<K, V> rt) {
if (rt.getLeft() == null) {
return rt.getRight();
}//The right node of the last node. If it is empty, it returns NULL; otherwise, it returns the node
rt.setLeft(removeMinNode(rt.getLeft()));//Continuous recursive update
//It ensures the standardization of binary search tree
return rt;
}
Insert an element
Find the inserted leaf node or branch node first
The inserted location should be the empty child node of the parent node of the location
public void insert(K key, V value) {
try {
if (key == null) {
throw new Exception("Key is null, insert fault!");
}
if (value == null) {
throw new Exception("Value is null, insert fault!.");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
root = insertHelp(root, key, value);
}
private BinNode<K, V> insertHelp(BinNode<K, V> rt, K key, V value) {
if (rt == null) {
return new BinNode<K, V>(key, value);
}
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) < 0) {
rt.setLeft(insertHelp(rt.getLeft(), key, value));
}//It is similar to deleting nodes
else if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) > 0) {
rt.setRight(insertHelp(rt.getRight(), key, value));
}//It is similar to deleting nodes
else {
rt.setValue(value);
}
return rt;
}
Balance
Balance factor: the height difference between the left and right subtrees
As long as the absolute value of the balance factor is less than or equal to 1, it means that the tree is balanced
For binary search tree, if the sequence of given elements is good, the balance is very poor
The destruction of the balance factor can be solved by rotation (which will be discussed in detail later)
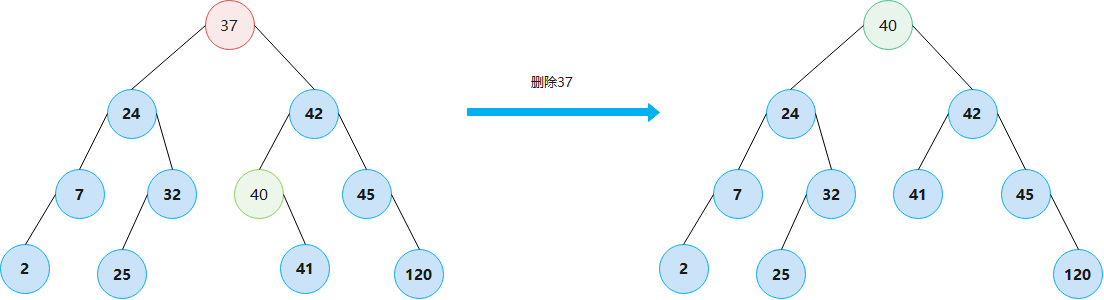
Delete an element
If the deleted node has two nodes, it is special, and the structure of binary search tree should not be damaged
Using substitution, the deletion with two child nodes is replaced by the deletion with one child node
Replace the smallest node in the right subtree with the node to be deleted
/**
*
* @param key keyword
* @return Delete value of node
*/
public V remove(K key) {
removeValue = null;
try {
if (key == null)
throw new Exception("Key is null, remove failure");
root = removeHelp(root, key);
return removeValue;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
private BinNode<K, V> removeHelp(BinNode<K, V> rt, K key) {
if (rt == null)
return null;
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) < 0) {
rt.setLeft(removeHelp(rt.getLeft(), key));
} else if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) > 0) {
rt.setRight(removeHelp(rt.getRight(), key));
} else {
if (rt.getLeft() == null) {
removeValue = rt.getValue();
rt = rt.getRight();
//If the left child node is empty, the right child node is directly taken as the current root node
} else if (rt.getRight() == null) {
removeValue = rt.getValue();
rt = rt.getLeft();
//If the right child node is empty, the left child node is directly taken as the current root node
} else {
//The node to be deleted has two child nodes
rt.setKey((K) getMinNode(rt.getRight()).getKey());
rt.setValue((V) getMinNode(rt.getRight()).getValue());
//Update the key and value of the current node to the value of the smallest node in the right subtree
rt.setRight(removeMinNode(rt.getRight()));
//Update the right child node of the current node
}
}
return rt;
}
Each time cost
Search cost
The operation cost of balanced binary search tree is O(logn)
The worst cost of unbalanced binary search tree is O(n)
The costs of inserting and deleting are similar to those of searching
The cost of traveling around a binary search tree is O(n)
Only when a binary search tree is balanced can it really play its role
source code
/**
* @author yjq
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021/11/20 22:51
*/
public class BinarySearchTree<K extends Comparable<K>, V> implements BSTADT<K, V> {
private BinNode<K, V> root;
private V removeValue;
public BinarySearchTree() {
root = null;
}
public BinNode<K, V> getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void insert(K key, V value) {
try {
if (key == null) {
throw new Exception("Key is null, insert fault!");
}
if (value == null) {
throw new Exception("Value is null, insert fault!.");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
root = insertHelp(root, key, value);
}
private BinNode<K, V> insertHelp(BinNode<K, V> rt, K key, V value) {
if (rt == null) {
return new BinNode<K, V>(key, value);
}
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) < 0) {
rt.setLeft(insertHelp(rt.getLeft(), key, value));
}//It is similar to deleting nodes
else if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) > 0) {
rt.setRight(insertHelp(rt.getRight(), key, value));
}
else {
rt.setValue(value);
}//Update if the key value is the same
return rt;
}
/**
*
* @param key keyword
* @return Value of deleted node
*/
public V remove(K key) {
removeValue = null;
try {
if (key == null)
throw new Exception("Key is null, remove failure");
root = removeHelp(root, key);
return removeValue;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
private BinNode<K, V> removeHelp(BinNode<K, V> rt, K key) {
if (rt == null)
return null;
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) < 0) {
rt.setLeft(removeHelp(rt.getLeft(), key));
} else if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) > 0) {
rt.setRight(removeHelp(rt.getRight(), key));
} else {
if (rt.getLeft() == null) {
removeValue = rt.getValue();
rt = rt.getRight();
//If the left child node is empty, the right child node is directly taken as the current root node
} else if (rt.getRight() == null) {
removeValue = rt.getValue();
rt = rt.getLeft();
//If the right child node is empty, the left child node is directly taken as the current root node
} else {
//The node to be deleted has two child nodes
rt.setKey((K) getMinNode(rt.getRight()).getKey());
rt.setValue((V) getMinNode(rt.getRight()).getValue());
//Update the key and value of the current node to the value of the smallest node in the right subtree
rt.setRight(removeMinNode(rt.getRight()));
//Update the right child node of the current node
}
}
return rt;
}
private BinNode getMinNode(BinNode<K, V> rt) {
if (rt.getLeft() == null)
return rt;
else
return getMinNode(rt.getLeft());
}
//Returns the updated root node
private BinNode<K, V> removeMinNode(BinNode<K, V> rt) {
if (rt.getLeft() == null) {
return rt.getRight();
}
rt.setLeft(removeMinNode(rt.getLeft()));
//It ensures the standardization of binary search tree
return rt;
}
public V search(K key) {
return search(root, key);
}
private V search(BinNode<K, V> rt, K key) {
try {
if (key == null)
throw new Exception("key is null");
if (rt == null)
return null;
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) < 0)
return search(rt.getLeft(), key);//If it is less than the current key value, search the left subtree
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) > 0)
return search(rt.getRight(), key);//If it is greater than the current key value, search the right subtree
return rt.getValue();//Value found
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public boolean update(K key, V value) {
return update(root, key, value);
}
public boolean update(BinNode<K, V> rt, K key, V value) {
try {
if (key == null)
throw new Exception("Key is null, update failure.");
if (value == null)
throw new Exception("value is null, update failure");
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) == 0) {
rt.setValue(value);
return true;
}
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) < 0)
return update(rt.getLeft(), key, value);
if (key.compareTo(rt.getKey()) > 0)
return update(rt.getRight(), key, value);
return false;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null;
}
public void clear() {
root = null;
}
public int getHeight(BinNode<K, V> rt) {
int height = 0;
if (rt == null)
return 0;
else
height++;
height += Math.max(getHeight(rt.getLeft()), getHeight(rt.getRight()));
return height;
}
}