Lesson: Functions
target
- Function function
- To use a function
- Parameter action of function
- Function return value
- Documentation for functions
- Function nesting
1, Function function
Demand: users withdraw money from ATM:
- After entering the password, the 'Select function' interface is displayed
- After querying the balance, the select function interface is displayed
- After withdrawing 2000 yuan, the 'Select function' interface will be displayed
⭕ Features: how to display the "select function" interface, which needs to be repeatedly output to the user?
Function is to integrate a piece of code block with independent functions into a whole and name it, and call the name where necessary to complete the corresponding requirements,
⭕ In the process of function development, code duplication can be realized more efficiently.
2, To use a function
2.1 defining functions
def function name (parameter):
Code 1
Code 2
......
2.2 calling functions
Function name (parameter)
⭐ be careful:
1. Parameters are optional for different requirements,
2. In python, functions must be defined before use.
2.3 quick experience
Demand: reproduce ATM withdrawal function.
1. Build the overall framework (reproduction requirements)
print('The password is correct and the login is successful')
#The 'Select function' interface is displayed
print('Balance query completed')
#The 'Select function' interface is displayed
print('Took 2000 yuan')
# The 'Select function' interface is displayed2. Determine the content of the 'Select function' interface
print('Check the balance')
print('deposit')
print('withdraw money')3. Package 'selection function'---
⭐ Note: we must first define functions and then call functions.
encapsulation ATM Machine function options----Define function
def select_func():
print('-----Please select a function------')
print('Check the balance')
print('deposit')
print('withdraw money')
print('-----Please select a function------')4. Call function
Call the function where the 'Select function' function needs to be displayed.
print('Password login succeeded')
# Display 'Select function' interface ----- call function
select_func()
print('Your balance is 99999')
# Display 'Select function' interface ----- call function
select_func()
print('Successfully took 100 yuan')
# Display 'Select function' interface ----- call function
select_func()Print results:

3, Parameter action of function
Thinking: the requirements are as follows: how to write a program when a function completes the addition of two 1 and 2?
#Define function
def add_num():
result1 = 1 +2
print(result)
# Call function
add_num1()Think: add above_ Num1 function can only add data 1 and 2. If you want this function to be more flexible, you can calculate the sum of any two numbers specified by the user. How to write the program?
Analysis: if the user needs to specify a specific number when calling the function, the number specified by the user needs to be received when defining the function. The number specified when calling the function and the number received when defining the function are the parameters of the function.
#The definition function also defines parameters a and b for receiving user data. A and b are formal parameters
def add_num2(a,b):
result2 = a + b
print(result2)
# Real data 10 and 20 are passed in when calling the function, and the real data is the argument
add_num2(10,30)4, Function return value
For example, when we go shopping in the supermarket, such as buying cigarettes, will the salesperson return us the product of cigarettes after giving the money? In the function, if you need to return the result to the user, you need to use the return value of the function.
def buy():
return 'smoke'
# Use variables to save function return values
goods = buy()
print(goods)return function:
1. Responsible for function return value
2. Push out the current function: all the codes under return (inside the function body) will not be executed
4.1 application
Requirements: make a calculator, calculate the sum of any two numbers, and save the results.
def sum_num(a,b):
return a + b
# Save the return value of the function with the result variable
result = sum_num(1,2)
print(result)5, Documentation for functions
Thinking: after defining a function, how can a programmer write a program that can quickly prompt the function?
Answer: Notes
Think: if there is a lot of code, do we need to find the location of this function in a lot of code to see the comments? What if you want to view the function more conveniently?
Answer: function description document
● the function description document is also called the function description document.
5.1 syntax
● documentation defining functions
def function name (parameter):
'' description document location '' '
Code
........
● check the description document of the function
help (function name)
5.2 quick experience
def sum_num1(a,b):
'''Summation function'''
return a + b
help(sum_num1)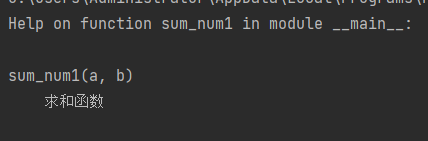
5.2.1 advanced writing method
# Advanced use of function documentation
def sum_num2(a,b):
"""
Summation function sum_num2
:param a: Parameter 1
:param b: Parameter 2
:return: Return value
"""
return a + b
help(sum_num2)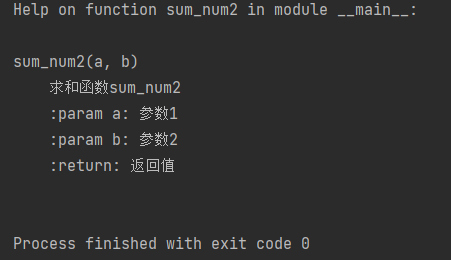
Vi. nesting of functions
The so-called function nested call means that another function is called in one function.
● examples
def testB():
print('Here is TestB Code of------')
print('BBBBB')
print('B1B1B1B1''')
def testA():
print('Here is TestA Code of------')
#Call function
testB()
print('AAAAAA')
print('A1A1A1A1A1')
testA()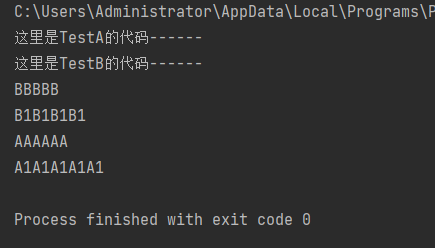
7.1 printing graphics
1. Print a horizontal line
#Requirement: print a horizontal line
def print_line():
print('-' * 20)
print_line()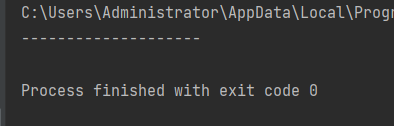
2. Print multiple horizontal lines
def print_line():
print('-' * 20)
def print_lines(num):
i = 0
while i < num:
print_line()
i += 1
print_lines(5) 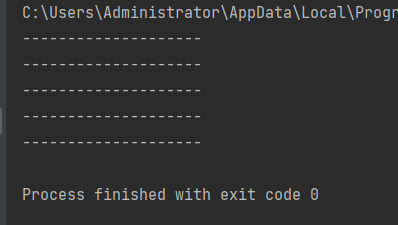
7.2 function calculation
1. Sum three numbers
def sum_num(a,b,c):
return a + b + c
reslt = sum_num(1,2,3)
print(reslt) # 62. Average the three numbers
def sum_num2(a,b,c):
sumResult = sum_num(a,b,c)
return sumResult / 3
sumResultline = sum_num2(1,2,3)
print(sumResultline) # 2.0VIII summary
- Function: encapsulate code and reuse code efficiently
- Function usage steps
● define functions
def function name ():
Code 1
Code 2
.......
● call function
Function name ()
- Function parameters: real data can be passed in during function call to increase the flexibility of function use
- Formal parameter: parameter written during function definition (non real data)
- Argument: parameter written during function call (real data)
- Return value of function
- Function: returns the result to be calculated after function call
- Writing method
return expression
- Documentation for functions
- Function: save function explanation information
- Writing method
def function name ():
"" "function description document" ""
- Nested function call: a function is nested inside another function