Simulate BGP group attribute policy configuration instance using eNSP
Problem elicitation
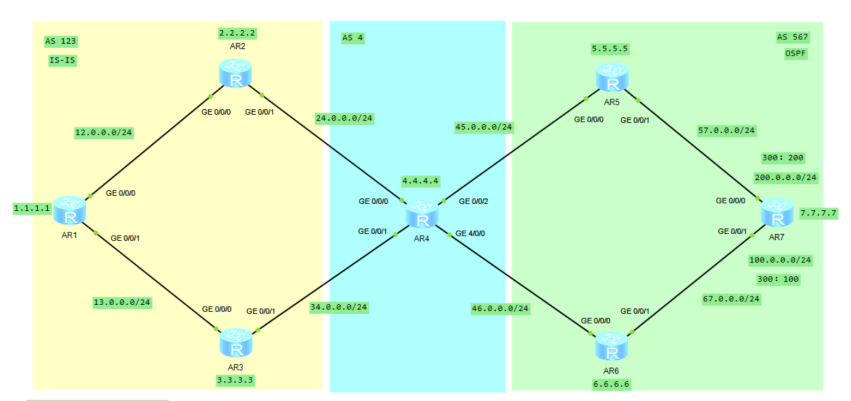
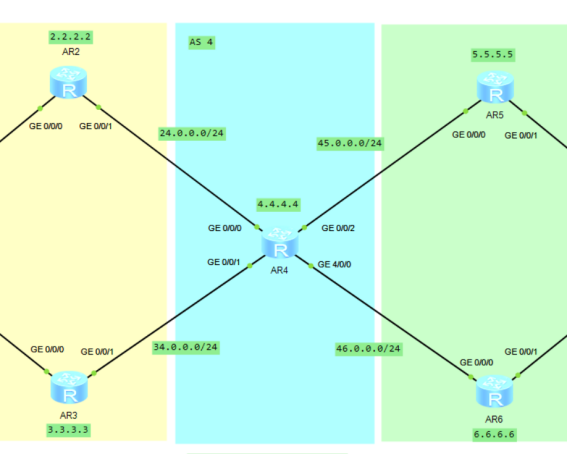
As shown in the figure
There are two user network segments in AS 300
When users in AS 100 access these two network segments
It is hoped to realize traffic sharing on R2 and R3
When AS 200 accesses these two network segments
It is hoped that traffic sharing can be realized on RTE and RTF
Please implement the above requirements in as many ways as possible
Topology Preview
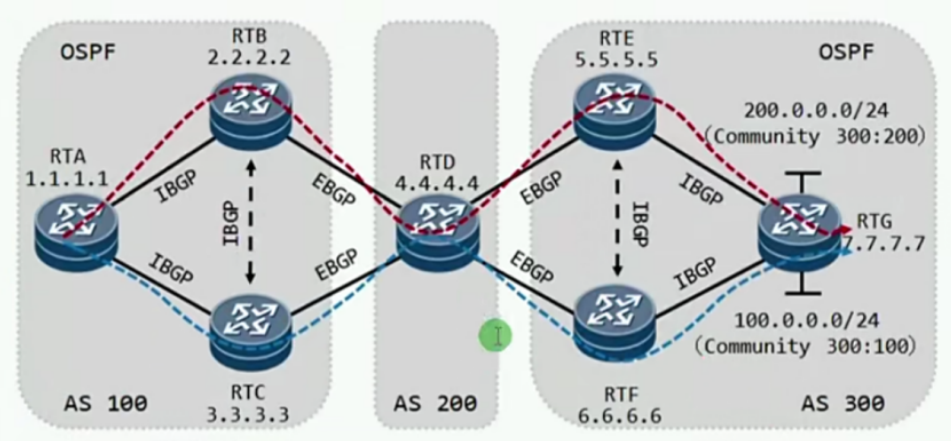
According to the title
Build AS 123, AS 4, AS 567
AS 123 area configuration IS-IS
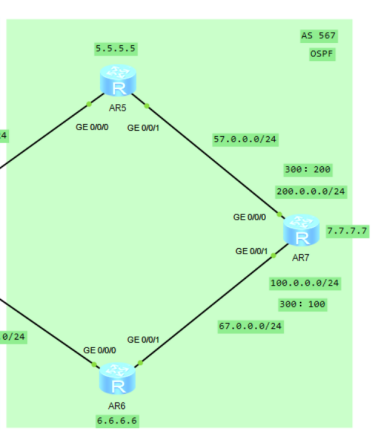
OSPF configuration in AS 567 area
(if you haven't learned IS-IS, it doesn't matter. Here you need two link state routing protocols to transfer routing)
Link state routing protocol & distance vector routing protocol
Here is a knowledge point
Have a better understanding of routing protocols
Routing protocols are divided into IGP and EGP
IGP: Interior Gateway Protocol
It includes distance vector routing protocol and link state routing protocol
Link State Routing Protocol
Including OSPF, IS-IS and other protocols
Each router will receive the link status information of all other routers in the routing domain
Each router can create its own network topology and independently calculate the shortest path to each network
Dijkstra algorithm based on SPF shortest path first
Triggered update
Higher resource requirements
Occupy more bandwidth (because of flooding LSA)
Therefore, the size of the routing domain should be controlled to reduce the flooding range
Reduce network load and improve network performance
Distance vector routing protocol
Including rip, EIGRP and other protocols
Do not know the complete topology of the routing domain
Basic cycle update
EIGRP is a Cisco private protocol, which is much better than RIP and belongs to triggered update
External gateway protocol
The most important is BGP protocol
Routing protocol used between AS
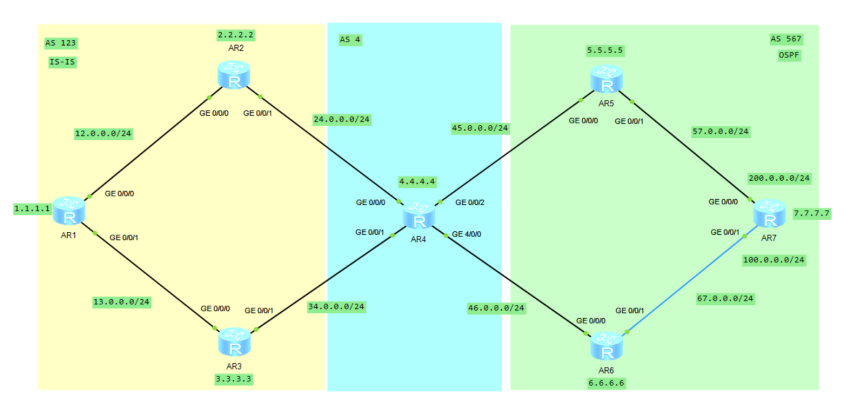
1, Basic configuration
1. Basic configuration of as 123 area and configuration of IS-IS (yellow)
Type the following command in R1:
sys sys R1 int g0/0/0 ip add 12.0.0.1 24 int g0/0/1 ip add 13.0.0.1 24 int lo 1 ip add 1.1.1.1 32 q isis 1 network-entity 49.0001.0000.0000.0001.00 is-level level-2 int g0/0/0 isis enable 1 int g0/0/1 isis enable 1 int lo 1 isis enable 1
Type the following command in R2:
sys sys R2 int g0/0/0 ip add 12.0.0.2 24 int g0/0/1 ip add 24.0.0.2 24 int lo 2 ip add 2.2.2.2 32 q isis 1 network-entity 49.0002.0000.0000.0002.00 is-level level-2 int g0/0/0 isis enable 1 int g0/0/1 isis enable 1 int lo 2 isis enable 1
Type the following command in R3:
sys sys R3 int g0/0/0 ip add 13.0.0.3 24 int g0/0/1 ip add 34.0.0.3 24 int lo 3 ip add 3.3.3.3 32 q isis 1 network-entity 49.0003.0000.0000.0003.00 is-level level-2 int g0/0/0 isis enable 1 int g0/0/1 isis enable 1 int lo 3 isis enable 1
2. Basic configuration of as 4 area (blue)
Type the following command in R4:
sys sys R4 int g0/0/0 ip add 24.0.0.4 24 int g0/0/1 ip add 34.0.0.4 24 int g0/0/2 ip add 45.0.0.4 24 int g4/0/0 ip add 46.0.0.4 24 int lo 4 ip add 4.4.4.4 32
3. Basic configuration of as 567 area and OSPF configuration (green)
Type the following command in R5:
sys sys R5 int g0/0/0 ip add 45.0.0.5 24 int g0/0/1 ip add 57.0.0.5 24 int lo 5 ip add 5.5.5.5 32 q ospf 1 router-id 5.5.5.5 area 0 net 57.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 net 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
Type the following command in R6:
sys sys R6 int g0/0/0 ip add 46.0.0.6 24 int g0/0/1 ip add 67.0.0.6 24 int lo 6 ip add 6.6.6.6 32 q ospf 1 router-id 6.6.6.6 area 0 net 67.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 net 6.6.6.6 0.0.0.0
Type the following command in R7:
sys sys R7 int g0/0/0 ip add 57.0.0.7 24 int g0/0/1 ip add 67.0.0.7 24 int lo 7 ip add 7.7.7.7 32 int lo 100 ip add 100.0.0.1 24 int lo 200 ip add 200.0.0.1 24 q ospf 1 router-id 7.7.7.7 area 0 net 57.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 net 67.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 net 7.7.7.7 0.0.0.0
2, Configuration of IBGP in AS 123 area
Type the following command in R1:
sys sys R1 bgp 123 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 2.2.2.2 as 123 peer 2.2.2.2 con lo 1 peer 2.2.2.2 next-hop-local peer 3.3.3.3 as 123 peer 3.3.3.3 con lo 1 peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local net 1.1.1.1 32
Type the following command in R2:
sys sys R2 bgp 123 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 1.1.1.1 as 123 peer 1.1.1.1 con lo 2 peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local peer 3.3.3.3 as 123 peer 3.3.3.3 con lo 2 peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local net 2.2.2.2 32
Type the following command in R3:
sys sys R3 bgp 123 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 1.1.1.1 as 123 peer 1.1.1.1 con lo 3 peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local peer 2.2.2.2 as 123 peer 2.2.2.2 con lo 3 peer 2.2.2.2 next-hop-local net 3.3.3.3 32
3, Configuration of EBGP
Type the following command in R2:
sys sys R2 bgp 123 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 24.0.0.4 as 4
Type the following command in R3:
sys sys R3 bgp 123 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 34.0.0.4 as 4
Type the following command in R4:
sys sys R4 bgp 4 router-id 4.4.4.4 peer 24.0.0.2 as 123 peer 34.0.0.3 as 123 peer 45.0.0.5 as 567 peer 46.0.0.6 as 567 net 4.4.4.4 32
Type the following command in R5:
sys sys R5 bgp 567 router-id 5.5.5.5 peer 45.0.0.4 as 4
Type the following command in R6:
sys sys R6 bgp 567 router-id 6.6.6.6 peer 46.0.0.4 as 4
4, Configuration of IBGP in AS 567 area
Type the following command in R5:
sys sys R5 bgp 567 router-id 5.5.5.5 peer 6.6.6.6 as 567 peer 6.6.6.6 con lo 5 peer 6.6.6.6 next-hop-local peer 7.7.7.7 as 567 peer 7.7.7.7 con lo 5 peer 7.7.7.7 next-hop-local
Type the following command in R6:
sys sys R6 bgp 567 router-id 6.6.6.6 peer 5.5.5.5 as 567 peer 5.5.5.5 con lo 6 peer 5.5.5.5 next-hop-local peer 7.7.7.7 as 567 peer 7.7.7.7 con lo 6 peer 7.7.7.7 next-hop-local
Type the following command in R7:
sys sys R7 bgp 567 router-id 7.7.7.7 peer 5.5.5.5 as 567 peer 5.5.5.5 con lo 7 peer 5.5.5.5 next-hop-local peer 6.6.6.6 as 567 peer 6.6.6.6 con lo 7 peer 6.6.6.6 next-hop-local net 100.0.0.0 24 net 200.0.0.0 24
5, Testing
Type the following command in R1 R4 R7:
dis bgp routing-table
View BGP routing table
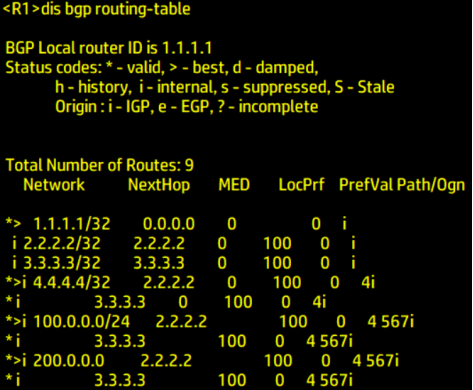
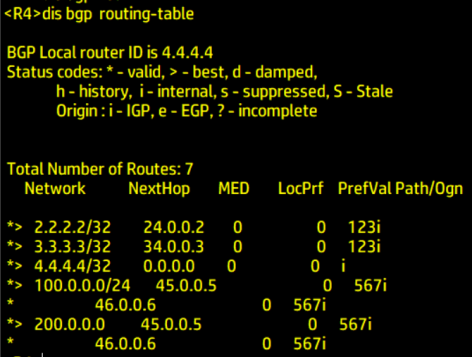
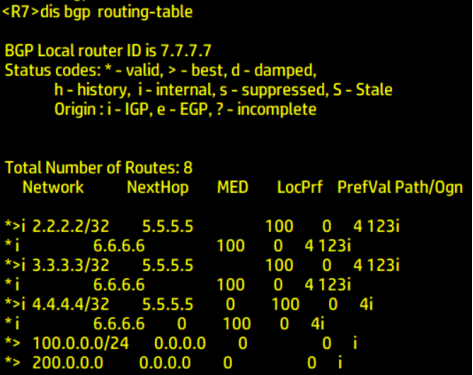
It can be seen from the above
100.0. 0.0/24 and 200.0 0.0/24 network segments arrive at R1 from R7 through R5 R2
Next, we configure the policy
2, BGP group attribute filtering
1 knowledge review
The Community attribute is an optional transition attribute
Identifying BGP routes with the same characteristics makes the application of routing strategy more flexible
Reducing the difficulty of maintenance and management is similar to tagging some routes
1.1 recognized group attributes
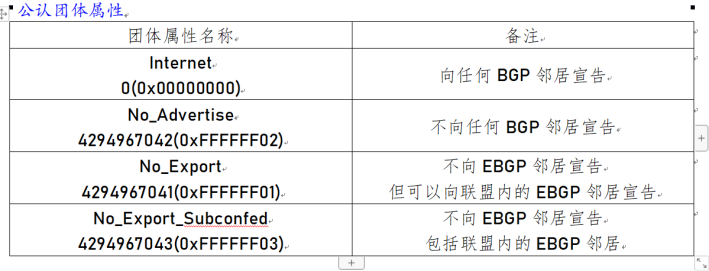
1.2 private group attributes

1.3 basic command
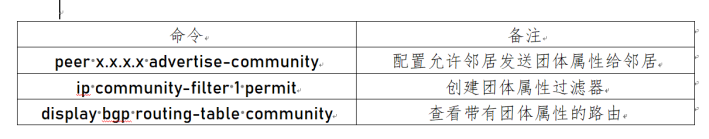
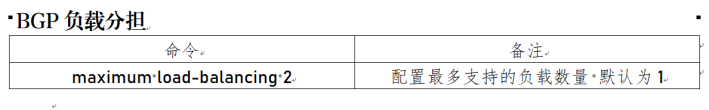
2. Policy configuration
2.1 label 100 200 network segments with private group attribute
Type the following command in R7:
sys sys R7 ip ip-pre 100 permit 100.0.0.1 24 route-policy admin permit node 10 if-match interface lo 100 if-match ip-pre 100 apply community 300:100 ip ip-pre 200 permit 200.0.0.1 24 route-policy admin permit node 20 if-match ip-pre 200 if-match interface lo 200 apply community 300:200 route-policy admin permit node 30 bgp 567 peer 5.5.5.5 route-policy admin export peer 6.6.6.6 route-policy admin export bgp 567 peer 5.5.5.5 advertise-community peer 6.6.6.6 advertise-community
Verify labeling
Type the following command in R7:
dis bgp routing-table community
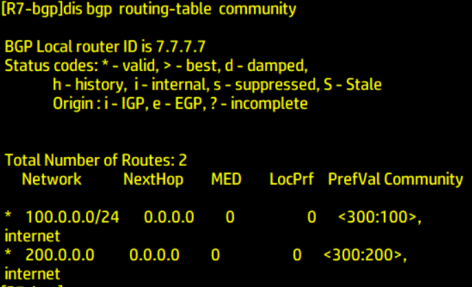
2.2 declare group attributes to IBGP and EBGP
Type the following command in R6
sys sys R6 bgp 567 peer 46.0.0.4 advertise-community
Type the following command in R5
sys sys R5 bgp 567 peer 45.0.0.4 advertise-community
Type the following command in R4
sys sys R4 bgp 4 peer 24.0.0.2 advertise-community peer 34.0.0.3 advertise-community
Type the following command in R3
sys sys R3 bgp 123 peer 1.1.1.1 advertise-community
Type the following command in R2
sys sys R2 bgp 123 peer 1.1.1.1 advertise-community
Check whether there is a group attribute tag in R1
Type the following command in R1
dis bgp routing-table community
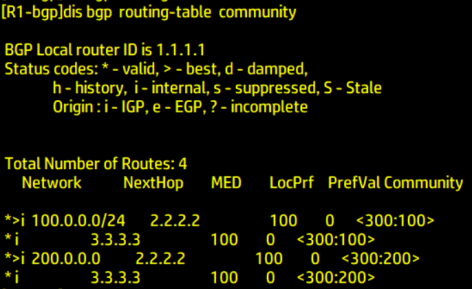
R1: Roger!
2.3 configure group attribute filter
bring
R5-R2 for 200 network segment
100 network segment R6-R3
2.3. Routing of 1 R4
Type the following command in R4
sys sys R4 ip community-filter 100 permit 300:100 route-policy admin100 permit node 10 if-match community-filter 100 apply local-preference 101 bgp 4 peer 46.0.0.6 route-policy admin100 import route-policy admin100 permit node 20
View the BGP routing table
Type the following command in R4
dis bgp routing-table
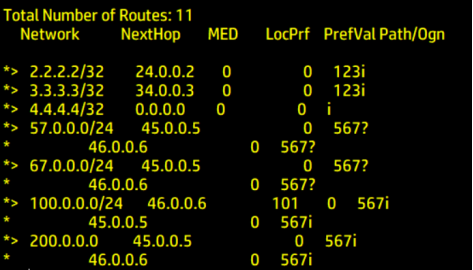
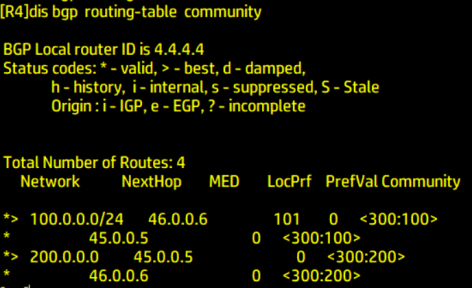
100 network segment according to the configured
apply local-preference 101
Select R6 with higher local priority. The higher the local priority, the higher the priority
2.3. 2 routing of R1
Type the following command in R3
sys sys R3 ip ip-prefix admin100 permit 100.0.0.1 24 route-policy 100 permit node 10 if-match ip-prefix admin100 apply cost 10 route-policy 100 permit node 20 bgp 123 peer 1.1.1.1 route-policy 100 export
Type the following command in R2
sys sys R2 ip ip-prefix admin100 permit 100.0.0.1 24 route-policy 100 permit node 10 if-match ip-prefix admin100 apply cost 20 route-policy 100 permit node 20 bgp 123 peer 1.1.1.1 route-policy 100 export
View the BGP routing table
Type the following command in R1
dis bgp routing-table
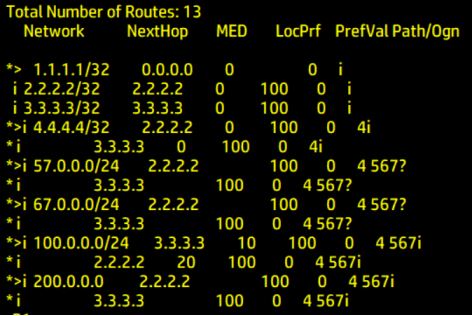
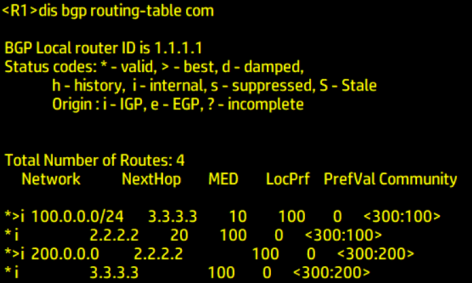
Here, the MED is modified by modifying the Cost value Cost
For 100 network segments
Change the cost value of R3 to 10
Change the cost value of R2 to 20
apply cost 10/20
The smaller the MED, the better
Configuring the replica topology
More routing methods are available for update... To be continued