Network type
Point to point: only two nodes can exist in a network segment MA Multiple access--In the same network segment, the number of nodes is not limited. Normally, there is a layer-2 address, otherwise unicast cannot be performed BMA -- broadcast multi-access NBMA -- Non broadcast multiple access
The network type is distinguished based on the technology selected in the data link layer: some virtual technologies
Ethernet BMA Frame relay MGRE((virtual) NBMA PPP/HDLC PPPOE,GRE(fictitious) Point to point
Two layer packaging technology
1, Ethernet
Ethernet is a shared typical BMA network type
Frequency division: the effect of increasing bandwidth when non-interference frequencies are used to transmit the same data on the same medium.
Frequency division is the core of Ethernet technology. Frequency division technology is the media access control function of Ethernet. In terms of logical link control, BMA's working broadcast is selected - MAC address is used as unicast address, there is conflict - CSMA/CD (wired).
CSMA/CA (wireless); The switch has completely solved the conflict problem in the wired environment. In the wireless aspect, it can only use the multi frequency scheme to further solve the conflict problem, but the effect is poor and the cost is high.
There are flooding and broadcasting mechanisms.
BMA broadcast multiple access - the number of nodes in a network segment is not limited, and there are broadcast and flooding mechanisms at the same time; Layer 2 unicast address must exist to realize layer 2 unicast communication.
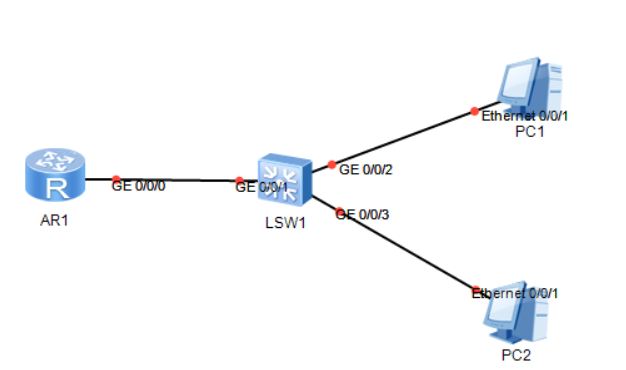
The figure above shows a typical BMA network
2, HDLC – advanced link control protocol
Standard point-to-point network type. HDLC of each manufacturer is a private protocol. It is the default two-layer string technology on Cisco equipment; Only complete the conversion between information and signal.
[r7-Serial4/0/0]link-protocol hdlc Modify the encapsulation of serial link
3, PPP – point to point protocol
The standard point-to-point network type is public technology, which can be used by all manufacturers
Default two-layer string technology on non Cisco devices
Based on HDLC, some upgrades have been made: dial-up Internet access
1. The direct connection can communicate normally in different network segments. PPP will interact with the ip addresses of devices at both ends of the link to generate a direct connection route
2. Authentication -- PAP CHAP
3. Establish virtual link and assign ip address
PAP Pass user name and password in clear text [RTA]aaa Primary authenticator - server [RTA-aaa]local-user huawei password cipher huawei123 [RTA-aaa]local-user huawei service-type ppp [RTA]interface Serial 1/0/0 Interface for connecting clients [RTA-Serial1/0/0]link-protocol ppp [RTA-Serial1/0/0]ppp authentication-mode pap [RTA-Serial1/0/0]ip address 10.1.1.1 30 [RTB]interface Serial 1/0/0 Certified party [RTB-Serial1/0/0]link-protocol ppp [RTB-Serial1/0/0]ppp pap local-user huawei password cipher huawei123 [RTB-Serial1/0/0]ip address 10.1.1.2 30 CHAP ciphertext -- Challenge challenge authentication Primary certifier [RTA]aaa [RTA-aaa]local-user huawei password cipher huawei123 [RTA-aaa]local-user huawei service-type ppp [RTA]interface Serial 1/0/0 [RTA-Serial1/0/0]link-protocol ppp [RTA-Serial1/0/0]ppp authentication-mode chap Certified party [RTB]interface Serial 1/0/0 [RTB-Serial1/0/0]link-protocol ppp [RTB-Serial1/0/0]ppp chap user huawei [RTB-Serial1/0/0]ppp chap password cipher huawei123
4, GRE General routing encapsulation
Virtual technology is also a point-to-point network type
Simple VPN technology, a point-to-point network type
Function: reduce the cost of network construction and build a virtual dedicated line.
[r1]interface Tunnel 0/0/0 Create tunnel interface [r1-Tunnel0/0/0]ip address 192.168.3.1 24 [r1-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre definition**encapsulation**mode GRE newly added IPV4 Source and target in header ip address [r1-Tunnel0/0/0]source 12.1.1.1 [r1-Tunnel0/0/0]destination 23.1.1.2
5, MGRE
MGRE – multipoint GRE belongs to NBMA network type
If multiple LANs use common GRE for interworking, the number of tunnel s increases exponentially and is difficult to manage.
Common GRE is point-to-point network type; If multiple nodes are connected using normal GRE, a large number of network segments and routing information will be configured, and all nodes are fixed IP addresses.
MGRE - multipoint GRE - multiple nodes are built into a network segment; Structure is the center to site structure; The site can realize that the ip address is not fixed based on NHRP.
NHRP - non fixed IP address branch site of next hop path discovery protocol, and actively register with the central site of fixed IP; The center generates a MAP.
Mapping - correspondence between tunnel port IP and public IP address.
If branch to branch, map will be downloaded at the central site to achieve direct communication.
Central site configuration interface Tunnel0/0/0 establish tunnel mouth ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 Configuration interface ip address tunnel-protocol gre p2mp First modify the interface mode to multipoint GRE source 15.1.1.1 Redefining public sources IP address nhrp entry multicast dynamic Local become NHRP Center, and pseudo broadcasting can be carried out at the same time nhrp network-id 100 The default is No. 0, and all nodes in the network segment tunnel The interface must be the same domain
Pseudo broadcast - when the target IP address is multicast or broadcast address, unicast the traffic based on each user; The outer header is unicast header, and the inner header is multicast or broadcast header; If this function is not enabled, the dynamic routing protocol based on multicast and broadcast will not work normally;
[r1]dis nhrp peer all View branch site registration results
Branch site: interface Tunnel0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 tunnel-protocol gre p2mp source GigabitEthernet0/0/2 Hypothetical branch site ip The address is not fixed nhrp network-id 100 nhrp entry 10.1.1.1 15.1.1.1 register The branch needs to register with the central site
If the public ip addresses corresponding to all tunnel s are fixed ip addresses, each router can become a central site and both can be registered manually; A fully connected mesh topology can be formed, and - rip, a protocol with horizontal segmentation mechanism, can converge normally.
When the topology is center to site (hub and spoke, star) - not all nodes are fixed public ip, and all tunnel devices cannot register with each other; The normal convergence of the whole network can only be realized by turning off horizontal segmentation.
[r1-Tunnel0/0/0]undo rip split-horizon
Note: to close the tunnel inlet, do not close it on the physical interface