How to redirect
Common redirection methods include 301 redirect, 302 redirect and meta fresh.
301 redirect
301 stands for permanently moved. 301 redirection is the best way to change the address of a web page and be friendly to the search engine. It is recommended to use 301 for address transfer as long as it is not temporarily moved.
302 redirect
302 stands for temporary moved. In previous years, many Black Hat SEO s have widely used this technology to cheat. At present, major search engines have strengthened their crackdown, such as Google's punishment on the king of domain names (Business) and BMW's German website. Even if the website is not spam objectively, it is easy for search engines to misjudge it as spam and be punished.
meta fresh
This was popular before 2000, but it is rare now. Specifically, it redirects to a new web page after a specific time through the meta instruction in the web page. If the delay time is too short (within about 5 seconds), it will be judged as spam.
ServletContext object
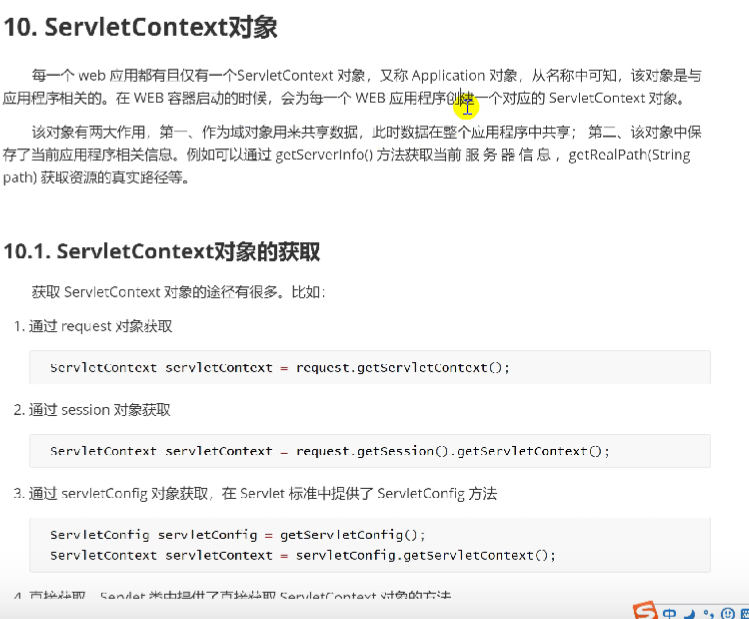
Each web application has only one ServletContext object
getServerInfo method gets the information of the current server
getRealPath(String path) gets the real path of the resource
/*
* Get ServletContext object
* */
@WebServlet("/s01")
public class Context01 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Get through request pair
ServletContext servletContext = req.getServletContext();
//Obtained through sessIon object
ServletContext sservletContext = req.getSession().getServletContext();
//Get from ServletConfig object
ServletContext servletContext3 = getServletConfig().getServletContext();
//Direct acquisition
ServletContext servletContext4 = getServletContext();
//common method
//Get the version information of the current server
String serverInfo = req.getServletContext().getServerInfo();
System.out.println("Get the version information of the current server:"+serverInfo);
//Gets the real path of the current project
String realPath = req.getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
System.out.println(""+realPath);
}
}
The domain object of ServletContext and the three domain objects of Servlet

The data in the ServletContext is not manually removed and will always be saved

The request domain object is used the most
Implementation of Servlet file upload foreground
File upload
Front page
The request method of the form is post

1. Prepare the form
2. Set the submission type of the form
3.enctype sets the form type to file upload form
4. Set the address of document submission
5. Prepare form elements
- Normal form item type = "text"“
- File item type = "file"
6. Set the name attribute value of the form element, otherwise the background cannot accept data
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>File upload</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" action="uploadServlet">
full name:<input type="text" name="uname"><br>
file:<input type="file" name="myfile"><br>
<button>Submit</button>
<!-- type Default to submit-->
</form>
</body>
</html>
Background implementation
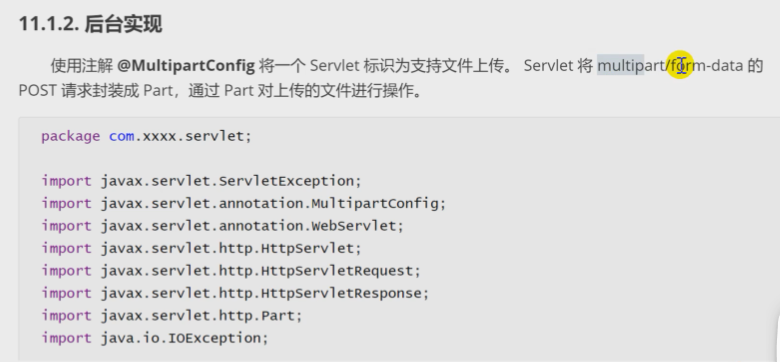
Servlet encapsulates the POST request of multipart / form data into parts
Operate the uploaded file through Part
Part object
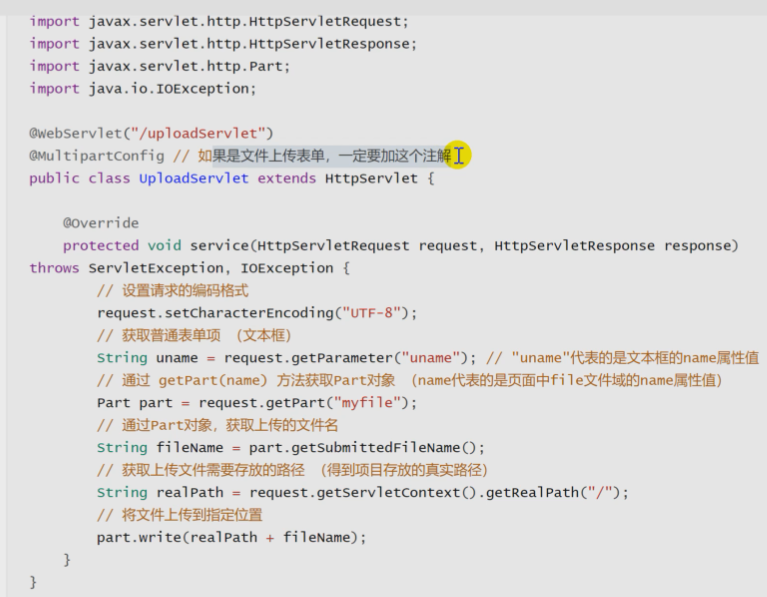
@MultipartConfig supports file upload
package com.xxx.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.MultipartConfig;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.Part;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/uploadServlet")
@MultipartConfig
public class UploadServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("File upload");
//Set the coding of the submission
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
//Get common form items and parameters
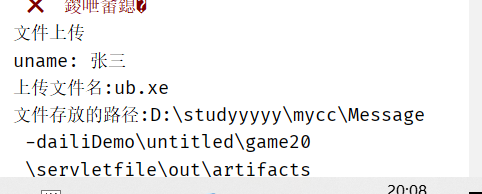
String uname=req.getParameter("uname"); //The name attribute value of the form element in the form
System.out.println("uname: "+uname);
//Get the part object Servlet and encapsulate the POST request of multipart / form data into a part object
Part part = req.getPart("myfile");//name attribute value of file field in the form
//Get the uploaded file name through the Part object
String fileName = part.getSubmittedFileName();
System.out.println("Upload file name:"+fileName);
//Get the file storage path
String filePath=req.getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
System.out.println("File storage path:"+filePath);
//Upload files to the specified path
part.write(filePath+"/"+fileName);
}
}
Get the uploaded file name part.getSubmittedFileName()
File upload part.write()
File download hyperlink Download
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>File download</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
Hyperlink download, when using hyperlink a Label, encounter recognizable display
If you can't recognize it, download it
-->
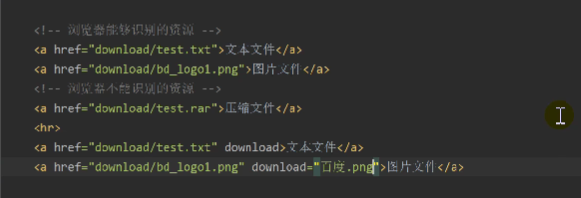
<!--Resources recognized by the browser-->
<a href="download/hello.txt" download>text file</a>'
<a href="download/test.jpg" download>Picture file</a>
<!--Resources not recognized by the browser-->
<a href="download/hello.zip">Compressed file</a>
</body>
</html>
File download background code download
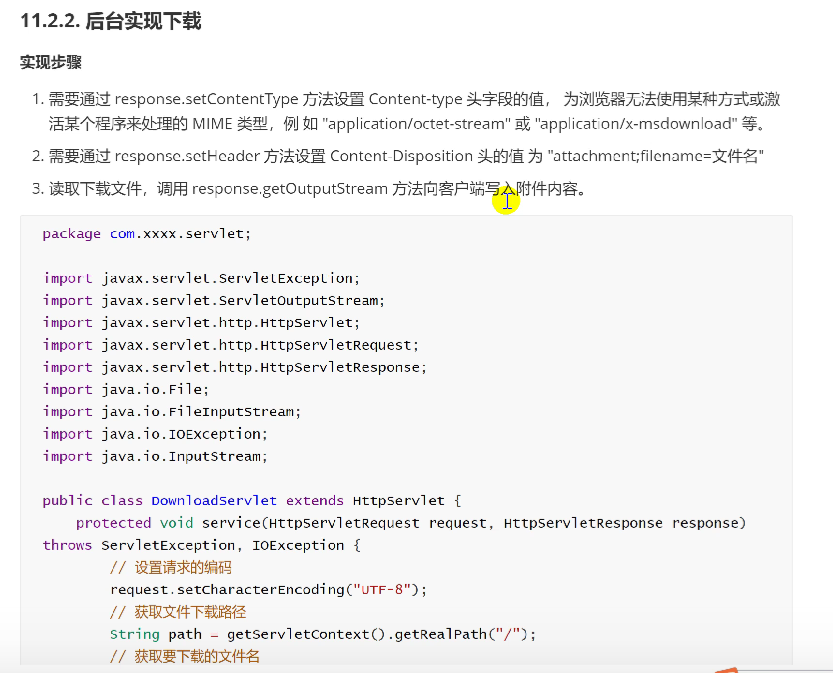

- Set the value of the content type header field through the response.setContentType method, so that the browser cannot use a certain method or activate a program to process MiMe types,
Application / octet stream or application/x-msdownload, etc - You need to set the value of the content disposition header to "attachment;filename = filename" through the response.setHeader method
- Read the download file and call the response.getOutputStream method to write the attachment content to the client

package com.xxx.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
@WebServlet("/downloadServlet")
public class DownloadServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("File download");
//Set the encoding format of the request
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
//Set the encoding format of the response
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
//Get the parameter to get the file name to download
String fileName=req.getParameter("fileName");
if(fileName == null||"".equals(fileName.trim())){
//trim removes spaces before and after
resp.getWriter().write("Please enter the file name to download");
resp.getWriter().print("Happy everyday");
resp.getWriter().close();
return;
}
//Get the path where the picture is stored
String path = req.getServletContext().getRealPath("/download/");
//Get the file object through the path
File file = new File(path+fileName);
//Determine whether the file object exists
if(file.exists()&&file.isFile()){
//Set response type
resp.setContentType("application/x-msdownload");
//Set response header
resp.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename="+fileName);
//Get file input stream
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
//Get byte output stream
ServletOutputStream out= resp.getOutputStream();
//Define byte array
byte[] bytes= new byte[1024];
//Define length
int len=0;
//Cyclic output
while((len=in.read(bytes))!=-1){
//output
out.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//close resource
out.close();
in.close();
}else{
resp.getWriter().write("The file does not exist. Please try again");
resp.getWriter().close();
}
}
}