1. Overview
This article mainly shares the code implementation of NettyRoutingFilter.
NettyRoutingFilter, Netty Routing Gateway Filter.It uses a Netty-based HttpClient to request back-end Http services based on http:// or https:// Prefix (Scheme) filtering.
NettyWriteResponseFilter, a gateway filter used in pairs with NettyRoutingFilter.It writes back the response of the NettyRoutingFilter request back-end Http service to the client.
The general process is as follows:
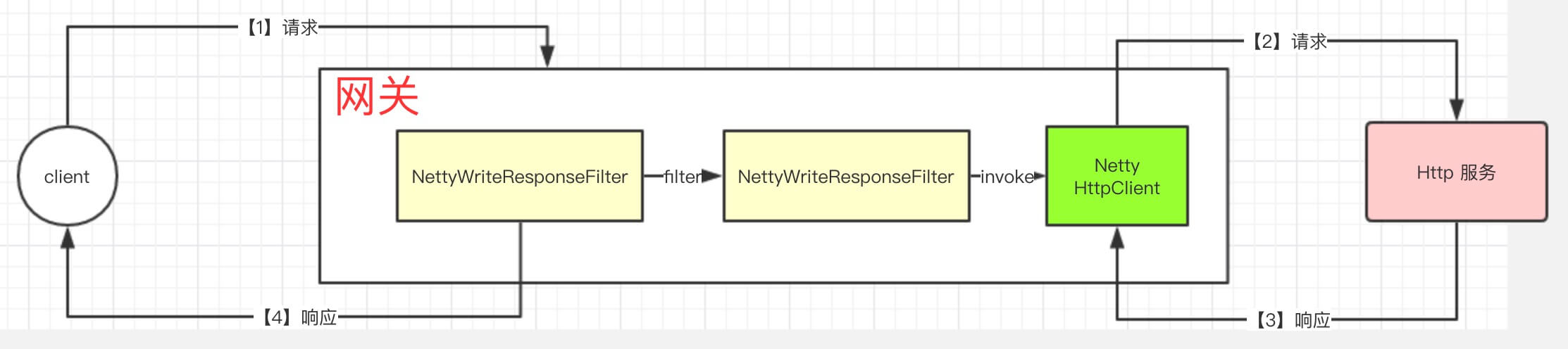
In addition, Spring Cloud Gateway implements WebClientHttpRoutingFilter / WebClientWriteResponseFilter, which is functionally the same as NettyRoutingFilter / NettyWriteResponseFilter, except that it is based onOrg.springframework.cloud.Gateway.filter.WebClientImplemented HttpClient requests back-end Http services.In Spring-Cloud-Gateway Source Parsing - WebClientHttpRoutingFilter for Filter (4.8) And we'll look at it in more detail.
2. NettyRoutingFilter
Org.springframework.cloud.Gateway.filter.NettyRoutingFilterNetty Routing Gateway Filter.
Construction method, code as follows:
public class NettyRoutingFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
private final HttpClient httpClient;
public NettyRoutingFilter(HttpClient httpClient) {
this.httpClient = httpClient;
}
}- HttpClient property, HttpClient based on Netty implementation.Through this property, the backend Http service is requested.
#getOrder() method with the following code:
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}- Return order is Integer.MAX_VALUE.In "Spring-Cloud-Gateway Source Parsing - An Overview of Gateway Filters for Filters (4.1)" "3. GlobalFilter" , we list the order of all GlobalFilter s.
#filter(ServerWebExchange, GatewayFilterChain) method with the following code:
1: @Override
2: public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
3: // Get requestUrl
4: URI requestUrl = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR);
5:
6: // Determine if you can handle it
7: String scheme = requestUrl.getScheme();
8: if (isAlreadyRouted(exchange) || (!scheme.equals("http") && !scheme.equals("https"))) {
9: return chain.filter(exchange);
10: }
11:
12: // Set Routed
13: setAlreadyRouted(exchange);
14:
15: ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
16:
17: // Request Method
18: final HttpMethod method = HttpMethod.valueOf(request.getMethod().toString());
19:
20: // Get url
21: final String url = requestUrl.toString();
22:
23: // Request Header
24: final DefaultHttpHeaders httpHeaders = new DefaultHttpHeaders();
25: request.getHeaders().forEach(httpHeaders::set);
26:
27: // request
28: return this.httpClient.request(method, url, req -> {
29: final HttpClientRequest proxyRequest = req.options(NettyPipeline.SendOptions::flushOnEach)
30: .failOnClientError(false) // //Whether the request failed and an exception was thrown
31: .headers(httpHeaders);
32:
33: // Request Form
34: if (MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED.includes(request.getHeaders().getContentType())) {
35: return exchange.getFormData()
36: .flatMap(map -> proxyRequest.sendForm(form -> {
37: for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry: map.entrySet()) {
38: for (String value : entry.getValue()) {
39: form.attr(entry.getKey(), value);
40: }
41: }
42: }).then())
43: .then(chain.filter(exchange));
44: }
45:
46: // Request Body
47: return proxyRequest.sendHeaders() //I shouldn't need this
48: .send(request.getBody()
49: .map(DataBuffer::asByteBuffer) // Flux<DataBuffer> => ByteBuffer
50: .map(Unpooled::wrappedBuffer)); // ByteBuffer => Flux<DataBuffer>
51: }).doOnNext(res -> {
52: ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
53: // Response Header
54: // put headers and status so filters can modify the response
55: HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
56: res.responseHeaders().forEach(entry -> headers.add(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
57: response.getHeaders().putAll(headers);
58:
59: // Response Status
60: response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.valueOf(res.status().code()));
61:
62: // Set Response to CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR
63: // Defer committing the response until all route filters have run
64: // Put client response as ServerWebExchange attribute and write response later NettyWriteResponseFilter
65: exchange.getAttributes().put(CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR, res);
66: }).then(chain.filter(exchange));
67: }- Line 4: Get requestUrl.
-
Lines 7 to 10: To determine whether ForwardRoutingFilter can process the request, two conditions need to be met:
- http:// or https:// Prefix (Scheme).
-
Call the ServerWebExchangeUtils#isAlreadyRouted(ServerWebExchange) method to determine that the request is not being processed by another Routing gateway at this time.The code is as follows:
public static boolean isAlreadyRouted(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return exchange.getAttributeOrDefault(GATEWAY_ALREADY_ROUTED_ATTR, false);
}- Line 13: Set that the request has been processed.The code is as follows:
public static void setAlreadyRouted(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ALREADY_ROUTED_ATTR, true);
}-
Line 18: Create the Netty Request Method object.request#getMethod() did not returnIo.netty.handler.Codec.http.HttpMethodTherefore, a conversion is required.
- Line 21: Get the url.
- Lines 24 to 25: Create a Netty Request Header object (io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultHttpHeaders), set the requested Header to it.
- - Lines 28 to 50: Call the HttpClient#request(HttpMethod, String, Function) method to request the back-end Http service.
-
Lines 29 to 31: Create a Netty Request object (reactor.ipc.netty.http.client.HttpClientRequest).
- Line 29: TODO [3024]NettyPipeline.SendOptions::flushOnEach
-
Line 30: When the setup request fails (the back-end service returns a response code >= 400), no exception is thrown.The code is as follows:
// HttpClientOperations#checkResponseCode(HttpResponse response)
// ...omit unrelated code
if (code >= 400) {
if (clientError) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("{} Received Request Error, stop reading: {}",
channel(),
response.toString());
}
Exception ex = new HttpClientException(uri(), response);
parentContext().fireContextError(ex);
receive().subscribe();
return false;
}
return true;
}-
-
- By setting clientError = false, line 51 calls the Mono#doNext(Consumer) method to unify the returned subscription processingReactor.ipc.netty.Http.client.HttpClientResponseObject.
-
Line 31: Set the Header for the Netty Request object.
-
-
Lines 34 to 44: [TODO 3025] is currently a BUG, fixed in version 2.0.X.See FormIntegrationTests#formUrlencodedWorks() Note description for unit tests.
-
Lines 47 to 50: Request the backend Http service.
- Line 47: Send the request Header.
- Lines 48 to 50: Send the request Body.The middle #map(...) process is Flux <DataBuffer> => ByteBuffer => Flux <DataBuffer>.
-
- Lines 51 to 65: Request backend Http service complete, assign Netty Response to response.
- Lines 53 to 57: CreateOrg.springframework.httpThe.HttpHeaders object, sets the Netty Response Header to it, and then sets it back to the response.
- Line 60: Set the status code of the response.
- Line 65: Set Netty Response to CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR.Subsequent Netty WriteResponseFilter writes the Netty Response back to the client.
- - Line 66: Submit the filter chain to continue filtering.
3. NettyWriteResponseFilter
Org.springframework.cloud.Gateway.filter.NettyWriteResponseFilterNetty Writeback Response Gateway Filter.
#getOrder() method with the following code:
public static final int WRITE_RESPONSE_FILTER_ORDER = -1;
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return WRITE_RESPONSE_FILTER_ORDER;
}- The return order is -1.In "Spring-Cloud-Gateway Source Parsing - An Overview of Gateway Filters for Filters (4.1)" "3. GlobalFilter" , we list the order of all GlobalFilter s.
#filter(ServerWebExchange, GatewayFilterChain) method with the following code:
1: @Override
2: public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
3: // NOTICE: nothing in "pre" filter stage as CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR is not added
4: // until the WebHandler is run
5: return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.defer(() -> {
6: // Get Response
7: HttpClientResponse clientResponse = exchange.getAttribute(CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR);
8: // HttpClientResponse clientResponse = getAttribute(exchange, CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR, HttpClientResponse.class);
9: if (clientResponse == null) {
10: return Mono.empty();
11: }
12: log.trace("NettyWriteResponseFilter start");
13: ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
14:
15: // Write the Netty Response back to the client.
16: NettyDataBufferFactory factory = (NettyDataBufferFactory) response.bufferFactory();
17: //TODO: what if it's not netty
18: final Flux<NettyDataBuffer> body = clientResponse.receive()
19: .retain() // ByteBufFlux => ByteBufFlux
20: .map(factory::wrap); // ByteBufFlux => Flux<NettyDataBuffer>
21: return response.writeWith(body);
22: }));
23: }- Line 5: Call the #then(Mono) method to implement After Filter logic.
- Lines 7 to 11: from CLIENT_RESPONSE_In ATTR, get Netty Response.
- Lines 15 to 21: Write the Netty Response back to the client.BecauseOrg.springframework.http.Server.reactive#writeWith(Publisher<? Extends DataBuffer>) The required parameter type is Publisher<? Extends DataBuffer>, so the conversion process for Lines 18 to 20 is ByteBufFlux => Flux<NettyDataBuffer>.
- Line 19: TODO [3024] ByteBufFlux#retain()