1. Preface
What is the difference between websocket and socket.io?
websocket
- A technology for two-way real-time communication between client and server
- While mainstream browsers already support it, there may be incompatibilities when using it
- Suitable for client and node-based server use
socket.io
- Encapsulate WebSocket, AJAX, and other communication methods into a unified communication interface
- When using, do not worry about compatibility issues, the bottom layer will automatically choose the best way to communicate
- Suitable for both client and server data communication
The description of socket.io on w3cschool is as follows:

This article will implement
- Integrated netty-socket IO based on springboot2.1.8.RELEASE: socket.io server implemented by imitating node.js
- Integrated socket.io-client:socket.io client
- Implement communication between server and client
2. Java integrated socket.io server
1. Import required dependencies into pom.xml
Warm Tip: In order to facilitate the future needs of the client socket.io-client dependency together directly introduced oh~
<!-- netty-socketio: Imitate`node.js`Realized socket.io Server --> <dependency> <groupId>com.corundumstudio.socketio</groupId> <artifactId>netty-socketio</artifactId> <version>1.7.7</version> </dependency> <!-- socket.io Client --> <dependency> <groupId>io.socket</groupId> <artifactId>socket.io-client</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency>
2. Configure socket.io server in application.yml
# netty-socketio configuration socketio: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 8888 # Set the maximum length of processing data per frame to prevent others from using large data to attack the server maxFramePayloadLength: 1048576 # Set maximum content length for http interaction maxHttpContentLength: 1048576 # Size of socket connections (e.g., listening on only one port box thread group is 1) bossCount: 1 workCount: 100 allowCustomRequests: true # Protocol upgrade timeout (milliseconds), default 10 seconds.HTTP handshake upgrade to ws protocol timeout upgradeTimeout: 1000000 # Ping message timeout (milliseconds), default 60 seconds, within which a timeout event is sent if no heartbeat message is received pingTimeout: 6000000 # Ping message interval (milliseconds), default 25 seconds.Client sends a heartbeat message interval to server pingInterval: 25000
3. socket.io Service-side Configuration Class
@Configuration public class SocketIOConfig { @Value("${socketio.host}") private String host; @Value("${socketio.port}") private Integer port; @Value("${socketio.bossCount}") private int bossCount; @Value("${socketio.workCount}") private int workCount; @Value("${socketio.allowCustomRequests}") private boolean allowCustomRequests; @Value("${socketio.upgradeTimeout}") private int upgradeTimeout; @Value("${socketio.pingTimeout}") private int pingTimeout; @Value("${socketio.pingInterval}") private int pingInterval; @Bean public SocketIOServer socketIOServer() { SocketConfig socketConfig = new SocketConfig(); socketConfig.setTcpNoDelay(true); socketConfig.setSoLinger(0); com.corundumstudio.socketio.Configuration config = new com.corundumstudio.socketio.Configuration(); config.setSocketConfig(socketConfig); config.setHostname(host); config.setPort(port); config.setBossThreads(bossCount); config.setWorkerThreads(workCount); config.setAllowCustomRequests(allowCustomRequests); config.setUpgradeTimeout(upgradeTimeout); config.setPingTimeout(pingTimeout); config.setPingInterval(pingInterval); return new SocketIOServer(config); } }
4. socket.io Server-side Service Layer
Service Class
public interface ISocketIOService { /** * Start Services */ void start(); /** * Out of Service */ void stop(); /** * Push information to specified client * * @param userId: Client Unique Identification * @param msgContent: Message Content */ void pushMessageToUser(String userId, String msgContent); }
Service implementation class:
@Slf4j @Service(value = "socketIOService") public class SocketIOServiceImpl implements ISocketIOService { /** * Store connected clients */ private static Map<String, SocketIOClient> clientMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); /** * Custom Event`push_data_event` for service side to client communication */ private static final String PUSH_DATA_EVENT = "push_data_event"; @Autowired private SocketIOServer socketIOServer; /** * Spring IoC After the container is created, start after loading the SocketIOServiceImpl Bean */ @PostConstruct private void autoStartup() { start(); } /** * Spring IoC Container closes before destroying SocketIOServiceImpl Bean to avoid restarting project service port occupancy */ @PreDestroy private void autoStop() { stop(); } @Override public void start() { // Listen for client connections socketIOServer.addConnectListener(client -> { log.debug("************ Client: " + getIpByClient(client) + " Connected ************"); // Custom Events `connected` -> communicate with clients (built-in events such as Socket.EVENT_CONNECT can also be used) client.sendEvent("connected", "You're connected successfully..."); String userId = getParamsByClient(client); if (userId != null) { clientMap.put(userId, client); } }); // Listening Client Disconnect socketIOServer.addDisconnectListener(client -> { String clientIp = getIpByClient(client); log.debug(clientIp + " *********************** " + "Client disconnected"); String userId = getParamsByClient(client); if (userId != null) { clientMap.remove(userId); client.disconnect(); } }); // Custom Event`client_info_event` ->Listen for client messages socketIOServer.addEventListener(PUSH_DATA_EVENT, String.class, (client, data, ackSender) -> { // When a client pushes a `client_info_event` event, onData accepts data, which is json data of type string here and can be Byte[], other types of object String clientIp = getIpByClient(client); log.debug(clientIp + " ************ Client:" + data); }); // Start Services socketIOServer.start(); // Broadcast: The default is to broadcast to all socket connections, but not to the sender himself, who needs to be sent separately if he intends to receive the message himself. new Thread(() -> { int i = 0; while (true) { try { // Send broadcast message every 3 seconds Thread.sleep(3000); socketIOServer.getBroadcastOperations().sendEvent("myBroadcast", "Broadcast message " + DateUtil.now()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); } @Override public void stop() { if (socketIOServer != null) { socketIOServer.stop(); socketIOServer = null; } } @Override public void pushMessageToUser(String userId, String msgContent) { SocketIOClient client = clientMap.get(userId); if (client != null) { client.sendEvent(PUSH_DATA_EVENT, msgContent); } } /** * Get the userId parameter in the client url (modified here to suit individual needs and client side) * * @param client: Client * @return: java.lang.String */ private String getParamsByClient(SocketIOClient client) { // Get the client url parameter (where userId is the unique identity) Map<String, List<String>> params = client.getHandshakeData().getUrlParams(); List<String> userIdList = params.get("userId"); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(userIdList)) { return userIdList.get(0); } return null; } /** * Get the connected client ip address * * @param client: Client * @return: java.lang.String */ private String getIpByClient(SocketIOClient client) { String sa = client.getRemoteAddress().toString(); String clientIp = sa.substring(1, sa.indexOf(":")); return clientIp; } }
3. Java Development socket.io Client
- socket.emit: Send data to server events
- socket.on: listen for server-side events
@Slf4j public class SocketIOClientLaunch { public static void main(String[] args) { // Server socket.io Connection Communication Address String url = "http://127.0.0.1:8888"; try { IO.Options options = new IO.Options(); options.transports = new String[]{"websocket"}; options.reconnectionAttempts = 2; // Time interval for failed reconnection options.reconnectionDelay = 1000; // Connection timeout (ms) options.timeout = 500; // userId: Unique identity passed to the server-side store final Socket socket = IO.socket(url + "?userId=1", options); socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT, args1 -> socket.send("hello...")); // Custom Event`Connected` ->Receive Server Successful Connection Message socket.on("connected", objects -> log.debug("Server:" + objects[0].toString())); // Custom Event`push_data_event` ->Receive Service-side Messages socket.on("push_data_event", objects -> log.debug("Server:" + objects[0].toString())); // Custom Event`myBroadcast` ->Receive Service-side Broadcast Messages socket.on("myBroadcast", objects -> log.debug("Server:" + objects[0].toString())); socket.connect(); while (true) { Thread.sleep(3000); // Custom Event`push_data_event` ->Send a message to the server socket.emit("push_data_event", "send data " + DateUtil.now()); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4. Running tests
When the client comes online, a message is sent to the server every 3 seconds through the custom event push_data_event, as follows
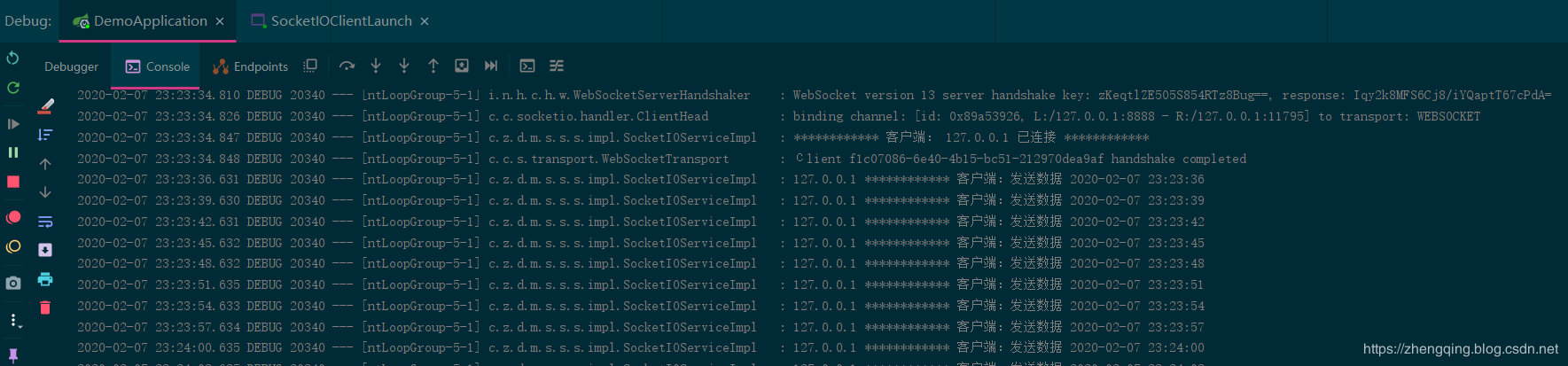
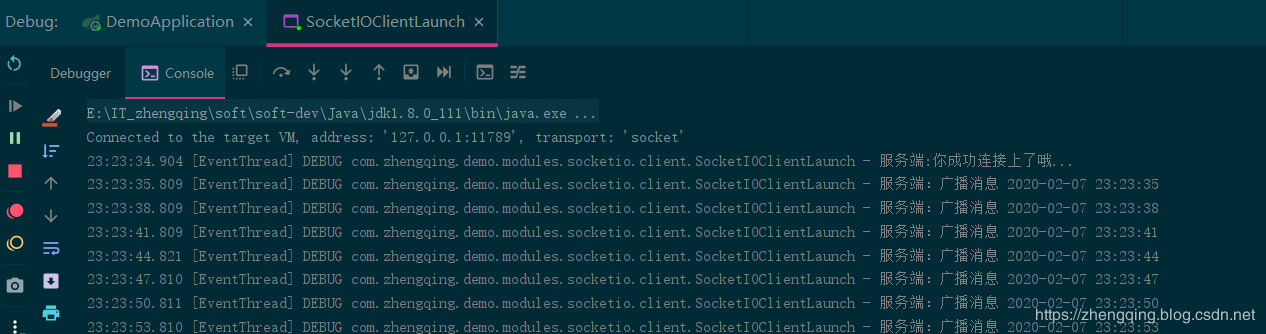
A broadcast message (custom event myBroadcast) running in the server is returned to the client every 3 seconds
Broadcast events: broadcast message data to all socket connections
socketIOServer.getBroadcastOperations().sendEvent("myBroadcast", "Broadcast message " + DateUtil.now());
The logs are as follows:
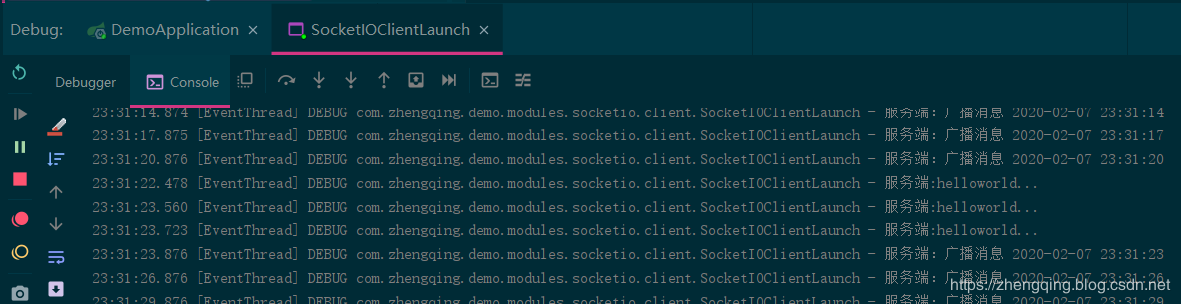
Write active messaging from the server to the client interface
@RestController @RequestMapping("/api/socket.io") @Api(tags = "SocketIO test-Interface") public class SocketIOController { @Autowired private ISocketIOService socketIOService; @PostMapping(value = "/pushMessageToUser", produces = Constants.CONTENT_TYPE) @ApiOperation(value = "Push information to specified client", httpMethod = "POST", response = ApiResult.class) public ApiResult pushMessageToUser(@RequestParam String userId, @RequestParam String msgContent) { socketIOService.pushMessageToUser(userId, msgContent); return ApiResult.ok(); } }
Call interface test to send helloworld...
V. Summary
socket.io Communications, Server:
1.socketIOServer.addConnectListener: Listen for client connections 2. socketIOServer.addDisconnectListener: Listen for client disconnection 3. socketIOServer.addEventListener: listens for messages transmitted by clients 4. client.sendEvent("Custom Event Name", "Message Content"): The service side sends messages to the specified clien client 5. socketIOServer.getBroadcastOperations().sendEvent("Custom Event Name", "Message Content"): The server sends broadcast messages to all clients
socket.io Communication, Client:
- IO.socket(url): Establishes a connection to the specified socket.io server
- socket.emit: Send data to server events
- socket.on: listen for server-side events