User defined and enumerated data types
1. User defined type
The user-defined type keyword is typedef, for example
typedef int unsigned uint; //unit is a custom data type unit a, b; //Declare two variables with a custom data type
Look at an example
module type1_tb;
typedef bit bit_t; //Customize a bit_ Tdata type
bit_t a = 0;
initial
$display("\n\t the value of a is %b",a);
endmodule
module type2_tb;
bit_t b = 1;
initial
$display("\n\t the value of b is %b", b);
endmodule
In this example, we are only in module type1_tb customizes a bit_ Type of T, in module type2_ Using bit directly in TB_ T declare variables and see what happens
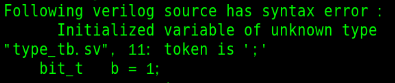
The results show that the variable type is unknown if we put the module type2_tb comment out, will there be this result
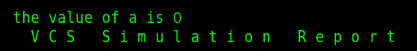
The results were printed successfully
This shows that the custom data type is bit_t is indeed defined successfully, but it only works on module type1_tb, because we are not in module type2_tb redefine
So if you want module type2_tb can also be printed successfully, which can be displayed in module type2_tb make a customization again, like this
module type1_tb;
typedef bit bit_t; //Customize a bit_ Tdata type
bit_t a = 0;
initial
$display("\n\t the value of a is %b",a);
endmodule
module type2_tb;
typedef bit bit_t; //Customize a bit_ Tdata type
bit_t b = 1;
initial
$display("\n\t the value of b is %b", b);
endmodule
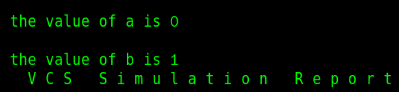
You can also use the previous compilation unit field $unit
package definition;
typedef bit bit_t; //Customize a bit_ Tdata type
endpackage
module type1_tb;
bit_t a = 0;
initial
$display("\n\t the value of a is %b",a);
endmodule
import definition :: *; //Import wildcards into $unit
module type2_tb;
bit_t b = 1;
initial
$display("\n\t the value of b is %b", b);
endmodule
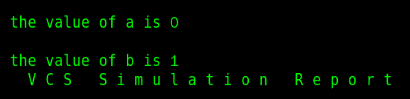
You can see that user-defined types can be defined locally or shared
In order to increase the readability of the source code, it is generally added after the user-defined name_ t. To distinguish
2. Enumerate data types
2.1 basic contents
The format of enumeration data types is:
enum {Tag name 1, Tag name 2, ...} Variable name;
Enumeration can be understood as assigning a value to a tag name or a tag to a value
If the data type is not explicitly given, the value in the enumeration is of type int, and the values are 0, 1, 2
Is this situation very similar to the definition of state by finite state machine, like this:
//State definition parameter S0 = 3'd0; parameter S1 = 3'd1; parameter S2 = 3'd2; parameter S3 = 3'd3; parameter S4 = 3'd4;
It will be much simpler to change it to enumeration
//State definition
enum {S0,S1,S2,S3,S4} state_t;
Tag names in enumerated data types can also be represented by vectors, which can be further simplified
//State definition
enum {S[5]} state_t;
These three state definitions are equivalent
In addition, the values, value types, and value widths of enumeration types can also be defined by themselves
For example, when defining the FSM state, you can use the ont hot code to directly define the value
//State definition
enum bit [2:0] {
S0 = 3'b001,
S1 = 3'b010,
S2 = 3'b100
} state_t;
It should be noted here that if we give a bit width of 3, we can't give a value beyond the bit width range
2.2 assignment of enumeration types
Enumeration types can only be assigned the following values:
- Enumerates a label in the list of types
- Other variables of the same enumeration type (variables declared with the same enumeration type)
- Convert to numeric value of enumeration type variable through cast
Explain this with an enumeration type
/*****Variable declaration*****/
typedef enum {one, two, three}state_t;
state_t state, next_state;
int info;
/*****Assignment*****/
state = one; //Assign values with tags in the enumeration list
next_state = state; //Other variables of the same enumeration type
$cast(next_state, state + 1); //Convert to numeric value of enumeration type variable through cast
It should be noted that the tag in the enumeration list actually represents a value (which will be mentioned below). In this example, the value is of type int, which is the same as the data type of info, so there is the writing method of info = state + 1; but state = info + 1 is not feasible, because the enumeration assignment does not give this form
In addition, state =state + 1; state + +, etc. are not allowed
2.3 enumeration type specific tasks and methods
< enumeration variable names > First: returns the value of the first member in the specified variable list
< enumeration variable names > Last: returns the value of the last member in the specified variable list
< enumeration variable names > Next (): returns the value of the next N member in the specified variable list. If it reaches the end of the list, it will return to the beginning of the list
< enumeration variable names > Prev(): returns the value of the first N member in the specified variable list. If it reaches the beginning of the list, it will return to the end of the list
< enumeration variable names > Num: returns the number of elements in the enumeration list of variables
< enumeration variable names > Name: returns the string representing this value in the enumeration variable
The following is the simulation of these situations
The source code is as follows:
module enum_tb;
enum {s[9]} state_t;
initial begin
state_t = s5;
end
initial begin
$display("\n\t the initial state_t is %0d", state_t);
$display("\n\t <Variable name>.first is %0d", state_t.first);
$display("\n\t <Variable name>.last is %0d", state_t.last);
$display("\n\t <Variable name>.prev(3) is %0d", state_t.prev(3));
$display("\n\t <Variable name>.prev(7) is %0d", state_t.prev(7));
$display("\n\t <Variable name>.next(3) is %0d", state_t.next(3));
$display("\n\t <Variable name>.next(7) is %0d", state_t.next(7));
$display("\n\t <Variable name>.num is %0d", state_t.num);
$display("\n\t <Variable name>.name is %s", state_t.name);
end
endmodule
The operation results are as follows
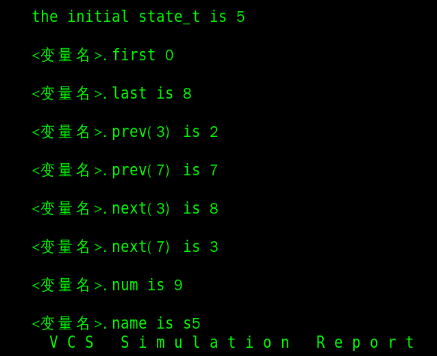
As you can see, state from beginning to end_ T is s5, and these operations will not change the state_t itself
In addition, by < variable name > Prev (7) and < variable name > As you can see from next (7), this method is cyclic
This paper mainly refers to system Verilog hardware design and modeling