preface
The article is linked to: Detailed analysis of YOLO-V3-SPP
This paper mainly explains the processing of YoloV3-SPP in the verification reasoning stage, which is divided into the following points:
- Preprocessing data
- Processing of validation
- Reasoning NMS processing
- drawbox for visualization of reasoning results
For the calculation of map, the source code of ultralytic version calls the pycoco library function to calculate map. Therefore, the calculation of map is not discussed here. If you are interested, you can go to my friend's blog about map calculation of yoov5: [YOLOV5-5.x source code interpretation] val.py
Source code
Yolo-V3-SPP is the ultralytics version. For more details, please go to github to download
NMS source code
validation.py call
pred = model(imgs)[0] # only get inference result
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres=0.01, iou_thres=0.6, multi_label=False)
predict_test.py call
# The network propagates forward. t is the time difference and pred is the return result
t1 = torch_utils.time_synchronized()
pred = model(img)[0] # only get inference result
t2 = torch_utils.time_synchronized()
print(t2 - t1)
# Non maximum suppression processing
pred = utils.non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres=0.1, iou_thres=0.6, multi_label=True)[0]
Here pred is the return value of model, and the processing of the return value refers to model Py, here are the codes of the key parts:
else: # Information if it is the verification or reasoning stage
# Shpae of io (batch_size, anchor_num, grid_cell, grid_cell, xywh + obj_confidence + classes_num)
io = p.clone() # inference output
# clone returns a copy of the tensor with the same size and data type as the original tensor.
# And copy_ () different, this function is recorded in the calculation diagram. The gradient passed to the clone tensor propagates to the original tensor
# The shape of grid = [batch_size, Na, grid_h, grid_w, wh], which is consistent with the shape after taking the first two xy in the last dimension of io, and add
io[..., :2] = torch.sigmoid(io[..., :2]) + self.grid
# xy calculates the xy coordinates on the feature map, corresponding to sigmoid(tx)+cx of the paper
# anchor_ Shape of wh: [batch_size, na, grid_h, grid_w, wh] is consistent with the shape after wh in the last dimension of io, and multiplication is performed
io[..., 2:4] = torch.exp(io[..., 2:4]) * self.anchor_wh # wh yolo method calculates wh on the feature map
io[..., :4] *= self.stride # xywh conversion mapping back to the original drawing scale
# obj and category predicted by sigmoid
torch.sigmoid_(io[..., 4:])
return io.view(bs, -1, self.no), p # view [1, 3, 13, 13, 85] as [1, 507, 85],3X13X13=507
# Shape of io (batch_size,..., xywh + obj_confidence + classes_num)
# The shape of p is (batch_size,anchor_num,grid_cell,grid_cell,xywh+obj_confidence+classes_num)
NMS source code
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.1, iou_thres=0.6,
multi_label=True, classes=None, agnostic=False, max_num=100):
"""
Performs Non-Maximum Suppression on inference results
param: prediction[batch, num_anchors X (gird_x X gird_y), (xywh+obj_conf+cls_num)]
Returns detections with shape:
nx6 (x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, cls)
"""
# Settings
merge = False # merge for best mAP
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
t = time.time()
nc = prediction[0].shape[1] - 5 # number of classes
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box
output = [None] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # Image index and image information traverse each picture
# Apply constraints
x = x[x[:, 4] > conf_thres] # Confidence excludes background objects according to obj confidence
x = x[((x[:, 2:4] > min_wh) & (x[:, 2:4] < max_wh)).all(1)] # Width height eliminates small targets
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[..., 5:] *= x[..., 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label: # Non maximum suppression is performed for each category
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).t()
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5].unsqueeze(1), j.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)
else: # best class only performs non maximum suppression directly for the category with the highest probability in each category
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1)
x = torch.cat((box, conf.unsqueeze(1), j.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)[conf > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes:
x = x[(j.view(-1, 1) == torch.tensor(classes, device=j.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# If none remain process next image
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n:
continue
# Sort by confidence
# x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)]
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5] * 0 if agnostic else x[:, 5] # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4].clone() + c.view(-1, 1) * max_wh, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres)
i = i[:max_num] # Keep only the first max at most_ Num target information
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
try: # update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
# i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
except: # possible CUDA error https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/1139
print(x, i, x.shape, i.shape)
pass
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
break # time limit exceeded
return output
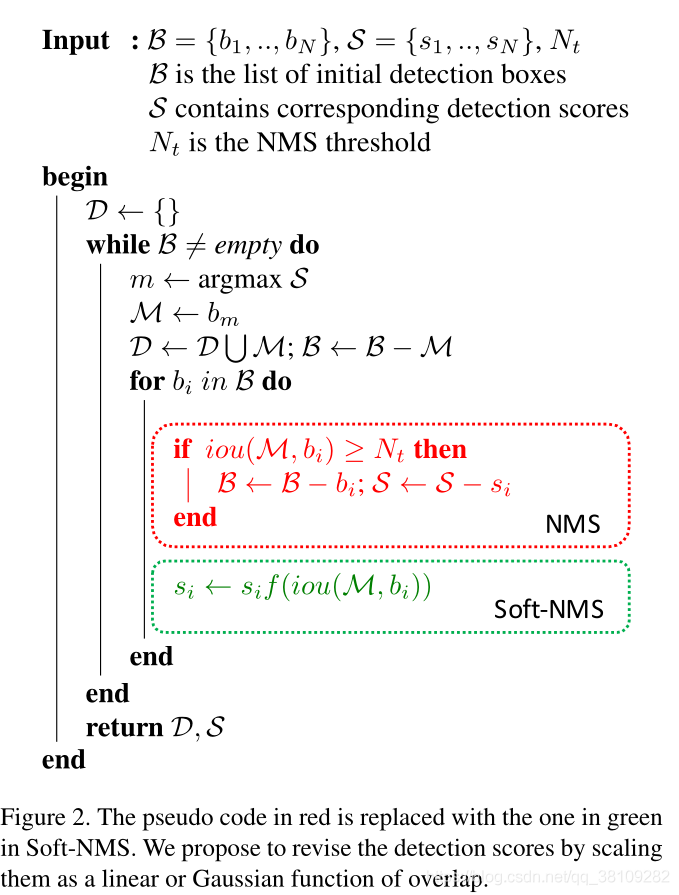
NMS source code analysis
Review NMS
Soft NMS algorithm
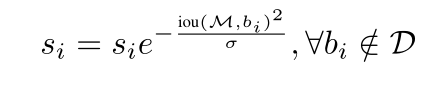
there
i
o
u
(
M
,
b
i
)
iou(M,b_i)
iou(M,bi) uses
G
i
o
u
Giou
Giou
analysis
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.1, iou_thres=0.6,
multi_label=True, classes=None, agnostic=False, max_num=100):
Transmission parameters:
- Predicton: shape is ( b a t c h _ s i z e , a n c h o r × g r i d _ x × g r i d _ y , x y w h + o b j _ c o n f + c l s _ n u m ) (batch\_size,anchor\times grid\_x\times grid\_y,xywh+obj\_conf+cls\_num) (batch_size,anchor×grid_x×grid_y,xywh+obj_conf+cls_num)
- conf_thres: confidence and category threshold
- Iou_thres:iou threshold
- multi_label: multi class NMS flag bit. True means NMS is executed for each category, and false means NMS is executed only for the largest category (Note: this does not refer to multi classification and single classification, but only the processing method of NMS)
- Classes: the default value is None. It is used to control the category of filter output to the specified classes. As a special function extension, the specified class of output can be specified during prediction output. It is not used by default
- agnostic:
- max_num: only the first Max is reserved after NMS_ Num target information
# Settings
merge = False # merge for best mAP
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
Merge is used to balance the weight of the prediction frame after NMS. It is briefly mentioned here and will be discussed later
min_wh and max_wh function:
- Filter out size prediction box
- At nms, max_wh will distinguish forecast boxes of different categories. The specific operations will be described in detail later
time_limit limit the running time of the cycle cannot exceed 10s
t = time.time()
nc = prediction[0].shape[1] - 5 # number of classes
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box
t = time.time(): returns the timestamp of the current time (the number of floating-point seconds elapsed after the 1970 era).
nc = prediction[0].shape[1] - 5
Here, the shape of the prediction is [batch, num_anchors X (gird_x X gird_y), (xywh+obj_conf+cls_num)]
The above prediction [0] Shape [1] is the length of the last dimension of the predicton. Since the first five are (xywh+obj), the remaining CLS can be obtained by subtracting the previous dimension_ The length of num, and nc represents the number of classes.
multi_label &= nc > 1
This is the and operation & the two formulas are: multi_label and NC > 1, the two Boolean values take and &.
output = [None] * prediction.shape[0]
prediction.shape[0] refers to batch_size number, output is list, and list number is the batch of the current incoming predict_ Size. If a picture is passed in the prediction phase, batch_size=1, then the output is 1 list. In short, the number of output lists is batch_size.
for loop code interpretation
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # Image index and image information traverse each picture
For the nms processing of a single picture, this cycle will only be executed once, while for the verification set processing, it is a batch for nms processing, and the number of cycles is batch_size.
Predicton's shape[batch, num_anchors X (gird_x X gird_y), (xywh+obj_conf+cls_num)]
The shape of X is [num_anchors X (gird_x X gird_y), (xywh+obj_conf+cls_num)]
# Apply constraints
x = x[x[:, 4] > conf_thres] # Confidence excludes background objects according to obj confidence
x = x[((x[:, 2:4] > min_wh) & (x[:, 2:4] < max_wh)).all(1)] # Width height filtering small targets
x = x[x[:, 4] > conf_thres]
Filter out obj_ conf > conf_ Prediction box of thres
x = x[((x[:, 2:4] > min_wh) & (x[:, 2:4] < max_wh)).all(1)]
Filter out the prediction frame information with the prediction frame width and height between [min_wh,max_wh]
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
x.shape[0] is the number of prediction boxes filtered out by the current picture. If the current picture passes conf_ If the prediction frame obtained by thres and filtering out small targets is 0, this picture does not need nms. continue to nms the next picture
# Compute conf
x[..., 5:] *= x[..., 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
X [..., 5:] indicates cls_conf dimension, x [..., 4:5] indicates obj_conf
Here is a review of the YOLO-V1 paper

Each grid cell predicts CLS_ Conditional probability of num classes
P
r
(
C
l
a
s
s
i
∣
O
b
j
e
c
t
)
Pr(Class_i\mid Object)
Pr(Classi ∣ Object), we need to get the actual category probability
P
r
(
C
l
a
s
s
i
)
=
P
r
(
C
l
a
s
s
i
∣
O
b
j
e
c
t
)
∗
P
r
(
O
b
j
e
c
t
)
Pr(Class_i)=Pr(Class_i\mid Object)\ast Pr(Object)
Pr(Classi)=Pr(Classi∣Object)∗Pr(Object)
Actually equivalent to
P
r
(
C
l
a
s
s
i
)
=
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
∗
o
b
j
_
c
o
n
f
Pr(Class_i)=cls\_conf\ast obj\_conf
Pr(Classi)=cls_conf∗obj_conf
After the above code, x is in CLS_ The content of the location of conf is from P r ( C l a s s i ∣ O b j e c t ) Pr(Class_i\mid Object) Pr(Classi ∣ Object) becomes P r ( C l a s s i ) Pr(Class_i) Pr(Classi)
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
The xywh2xyxy method is as follows
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = torch.zeros_like(x) if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.zeros_like(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
Convert xywh in yolo format into xyxy and assign it to box, but do not change the content of x corresponding to position
Multi class NMS pre-processing and single class NMS pre-processing
Multi class NMS
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label: # Non maximum suppression is performed for each category
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).t()
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5].unsqueeze(1), j.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)
else: # best class only performs non maximum suppression directly for the category with the highest probability in each category
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1)
x = torch.cat((box, conf.unsqueeze(1), j.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)[conf > conf_thres]
multi_label: multi class NMS is true and single class NMS is false.
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).t()
x[:, 5:] > conf_thres represents the CLS of all prediction frames_ Conf and conf_thres. If it is greater than this threshold, the cls_conf is set to true, otherwise it is set to false. The details of debug are as follows:

Here, Tensor:(1779,2) indicates that there are 1779 prediction frames in my current prediction picture, which need to be classified into 2
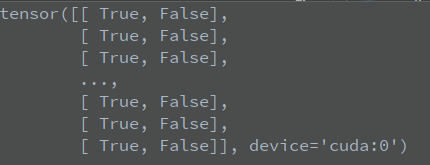
The above is x [:, 5:] > conf_ Status of thres
nonzero(as_tuple=False).t() saves the non-zero value of the above variable, that is, the matrix position content (prediction box id, category) of the True value, and assigns it to the i, J variables (the (i,j) coordinates can be greater than conf by addressing the x[:, 5:] variables_ Category confidence CLS of thres_ Conf, figuratively speaking, the addressed tensor is (number of prediction frame IDS, category), where i represents the prediction frame id and j represents the category)
Note: among the number of prediction frame IDS represented by i, the prediction frame may come from the same id, but the categories are different, indicating that the confidence of the two categories of the prediction frame is > conf_thres
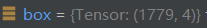
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5].unsqueeze(1), j.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)
box[i] indicates prediction box I, and the status is as follows:
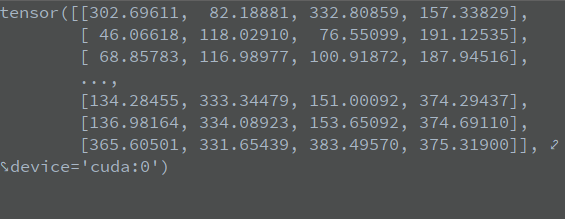
x[i, j + 5].unsqueeze(1) means to expand X in the second dimension. The original shape is [number of prediction boxes, xywh+obj+cls_num]
The status of x[i, j + 5] is as follows:

After unsqueeze(1), the status is as follows:

j.float().unsqueeze(1) converts the category to a floating-point type and promotes the dimension of the position. The status is as follows:

Splice the above three variables on the second dimension to obtain the status of x as follows:
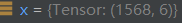
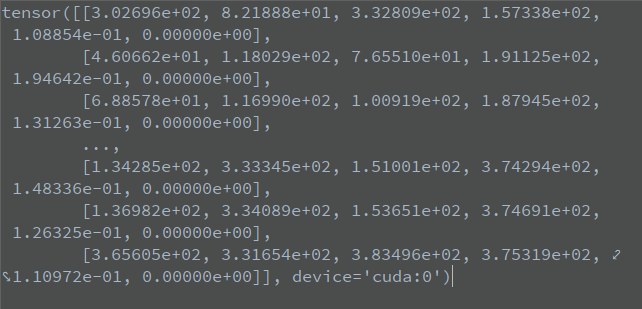
Where x[0]=[3.02696e+02, 8.21888e+01, 3.32809e+02, 1.57338e+02, 1.08854e-01, 0.00000e+00]
There are 6 values, represented by the first four parameters
(
x
l
e
f
t
−
t
o
p
,
y
l
e
f
t
−
t
o
p
,
x
r
i
g
h
t
−
t
o
p
,
y
r
i
g
h
t
−
t
o
p
)
(x_{left-top},y_{left-top},x_{right-top},y_{right-top})
(xleft − top, yleft − top, xright − top, yright − top). The latter two parameters represent
(
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
,
j
.
f
l
o
a
t
(
)
)
(cls\_conf,j.float())
(cls_conf,j.float())
Single class NMS
else: # best class only performs non maximum suppression directly for the category with the highest probability in each category
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1)
x = torch.cat((box, conf.unsqueeze(1), j.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)[conf > conf_thres]
max(1) means to take the maximum value of the category dimension of x[:, 5:] and return the largest cls_conf and its category j
torch.cat is the same as multi class NMS processing
Differences between multi class NMS and single class NMS
The above two parts are screening operations before NMS. For illustration, the experiments I do are divided into two categories. Then I will define the variables before screening as
(
b
o
x
_
i
d
,
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
1
,
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
2
)
(box\_id,cls\_conf1,cls\_conf2)
(box_id,cls_conf1,cls_conf2)
Multi category NMS: as long as the prediction category predicted by this prediction box
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
1
cls\_conf1
cls_ Conf 1 and
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
2
cls\_conf2
cls_ The confidence of conf 2 is greater than conf_thres, then the forecast category will be saved and finally filtered
(
b
o
x
_
i
d
,
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
1
)
(box\_id,cls\_conf1)
(box_id, cls_conf 1) and
(
b
o
x
_
i
d
,
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
2
)
(box\_id,cls\_conf2)
(box_id,cls_conf2)
Note here that the filtered prediction box contains different
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
1
cls\_conf1
cls_ Conf 1 and
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
2
cls\_conf2
cls_ The prediction box of conf 2 may be the same
b
o
x
_
i
d
box\_id
box_id, they may be sent to NMS for processing Because this prediction box is the same prediction box, it is only predicted
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
1
cls\_conf1
cls_ Conf 1 and
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
2
cls\_conf2
cls_ Conf 2. During NMS, it indicates that the same prediction box predicts that the ious of two targets of different classes completely overlap. From the two targets of the same box, we can analyze which box will be retained. For the NMS principle, assuming the soft NMS principle, at least one box will be retained. The most extreme case is when the two targets of the same prediction box have the same value
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
cls\_conf
cls_conf, then both boxes may be retained.
Single category NMS: the prediction box only filters the target of one category. The filtering criteria are m a x ( c l s _ c o n f 1 , c l s _ c o n f 2 ) max(cls\_conf1,cls\_conf2) Max (cls_conf 1, cls_conf 2). Note that single type NMS does not need to go through conf_ For thres filtering, only the prediction box with the maximum category confidence is selected, then all prediction boxes will be filtered, and one prediction box corresponds to a target.
Role of the classes parameter
# Filter by class
if classes:
x = x[(j.view(-1, 1) == torch.tensor(classes, device=j.device)).any(1)]
My experimental classes are set to None, which means that the above code is not executed, which means:
The classes parameter description is very clear
The status of j is:

j. The status of view (- 1,1) is:

classes is a list or nparray, defined as the specified category list. Controlling NMS means NMS for the specified category, discarding other categories, and outputting the prediction or verification of the specified category. It is used more when estimating the prediction. As a function extension, it is not used by default
# If none remain process next image
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n:
continue
After the class threshold filtering of the above code, judge whether x can continue NMS
Function of agnostic parameter
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5] * 0 if agnostic else x[:, 5] # classes
agnostic uses false by default, and the parameter of c is tensor (prediction box id,)
The shape of x is
(
x
l
e
f
t
−
t
o
p
,
y
l
e
f
t
−
t
o
p
,
x
r
i
g
h
t
−
t
o
p
,
y
r
i
g
h
t
−
t
o
p
,
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
,
j
.
f
l
o
a
t
(
)
)
(x_{left-top},y_{left-top},x_{right-top},y_{right-top},cls\_conf,j.float())
(xleft−top,yleft−top,xright−top,yright−top,cls_conf,j.float())
x[:, 5] represents the information of the sixth parameter, j.float(), that is, the category
The status of c is:

If agnostic is True, all the obtained category variables c are the first category. If false, c obtains the classes corresponding to all prediction frame IDs
The specific role of this variable is unknown. Since it is not used, the specific role is not clear.
boxes, scores = x[:, :4].clone() + c.view(-1, 1) * max_wh, x[:, 4]
X [:,: 4] indicates
(
x
l
e
f
t
−
t
o
p
,
y
l
e
f
t
−
t
o
p
,
x
r
i
g
h
t
−
t
o
p
,
y
r
i
g
h
t
−
t
o
p
)
(x_{left-top},y_{left-top},x_{right-top},y_{right-top})
(xleft − top, yleft − top, xright − top, yright − top) information
c. The status of view (- 1, 1) is:

max_wh is 4096
When agnostic is fasle, max_wh can transfer the coordinate information of non-0 class in c
(
x
l
e
f
t
−
t
o
p
,
y
l
e
f
t
−
t
o
p
,
x
r
i
g
h
t
−
t
o
p
,
y
r
i
g
h
t
−
t
o
p
)
(x_{left-top},y_{left-top},x_{right-top},y_{right-top})
(xleft − top, yleft − top, xright − top, yright − top) times max_wh.
During nms, the boxes coordinates will be distinguished
When agnostic is True, the values of c will all be 0, and the boxes information will not distinguish different coordinate information. NMS operation will be performed on all classes
The concrete realization of the above agnostic parameters lies in the processing of different types of nms in boxes
boxes are different, coordinate information is distinguished, and NMS operation is carried out by classification
boxes = x[:, :4].clone() + c.view(-1, 1) * max_wh, where the coordinates of different categories are expressed as max_wh multiples are distinguished. See the following debug for specific functions. The boxes information of my 0 class is debugged as follows:
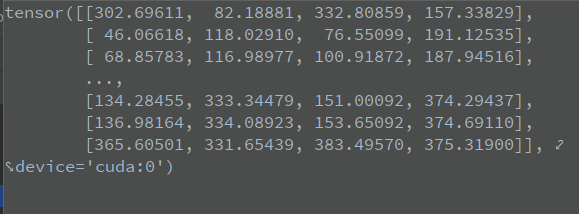

After distinguishing, the iou of different types of boxes information is 0, so nms will only operate on similar prediction frames.
scores is the fifth parameter of x, namely cls_conf, class confidence
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) i = i[:max_num] # Keep only the first max at most_ Num target information
Call the NMS library function of torchvision and use giou to perform NMS
Function of merge parameter
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
try: # update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
# i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
except: # possible CUDA error https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/1139
print(x, i, x.shape, i.shape)
pass
The merge parameter defaults to false:
If true, the filtered boundingbox will be assigned width and height with a certain weight. The weight allocation will be calculated based on the currently filtered box information and the total box information, and iou > iou_ Save the box of thres and update the width and height of the current best box with the following formula:
b
o
x
i
=
0
[
x
1
,
y
1
,
x
2
,
y
2
]
=
∑
i
=
1
t
a
r
g
e
t
c
l
s
i
[
x
1
_
i
,
y
1
_
i
,
x
2
_
i
,
y
2
_
i
]
∑
i
=
1
t
a
r
g
e
t
c
l
s
i
box_{i=0}[x_1,y_1,x_2,y_2]=\frac{\sum_{i=1}^{target}cls_i[x_{1\_i},y_{1\_i},x_{2\_i},y_{2\_i}]}{\sum_{i=1}^{target}cls_i}
boxi=0[x1,y1,x2,y2]=∑i=1targetclsi∑i=1targetclsi[x1_i,y1_i,x2_i,y2_i]
Among them,
i
=
0
i=0
i=0 indicates
c
l
s
_
c
o
n
f
cls\_conf
cls_ The box with the highest conf,
i
=
1
i=1
i=1 to
t
a
r
g
e
t
target
target boxes are all related to
b
o
x
m
a
x
_
c
o
n
f
box_{max\_conf}
box max_ iou of conf > iou_ Boxes filtered by thres
If you don't understand the code here, you can read the code of this version:
Original text: Interpretation of nms source code
elif method == 'merge': # weighted mixture box
while len(dc): # dc is the box information in order of confidence
if len(dc) == 1:
det_max.append(dc)
break
i = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc) > nms_thres # I = set of true / false
weights = dc[i, 4:5] # According to i, keep all True
dc[0, :4] = (weights * dc[i, :4]).sum(0) / weights.sum() # Solving the average value of overlapping box position information
det_max.append(dc[:1])
dc = dc[i == 0]
The specific operation in NMS is relatively simple, and the main complex is some processing before NMS The NMS of the above code is used for packet transfer. I'm not sure about the specific source code implementation. Here are several versions of NMS implementation, hard NMS, hard NMS and, soft NMS, Diou NMS, original text: Interpretation of nms source code
# Reasoning time: 0.0030s
elif method == 'soft_nms': # soft-NMS https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04503
sigma = 0.5 # soft-nms sigma parameter
while len(dc):
# if len(dc) == 1: This is the source code of version U. I made a small change
# det_max.append(dc)
# break
# det_max.append(dc[:1])
det_max.append(dc[:1]) # The first line of append dc is target
if len(dc) == 1:
break
iou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:]) # Calculate the iou of target and other boxes
# Different from the direct setting of 0 above, setting 0 does not need to control the dimension
dc = dc[1:] # DC = all prediction boxes after target
# dc must not include target and its previous prediction box, because it must be multiplied by the value, and the dimension must be the same
dc[:, 4] *= torch.exp(-iou ** 2 / sigma) # Score attenuation
dc = dc[dc[:, 4] > conf_thres]
# Reasoning time: 0.00299
elif method == 'diou_nms': # DIoU NMS https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.08287.pdf
while dc.shape[0]: # dc.shape[0]: number of prediction boxes in the current class
det_max.append(dc[:1]) # Let the prediction box with the largest score (the first one after sorting) be target
if len(dc) == 1: # When there is only one box left in the exit dc, break
break
# dc[0]: target DC [1:]: other prediction boxes
diou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:], DIoU=True) # Calculate diou
dc = dc[1:][diou < nms_thres] # Remove dious > threshold leave True delete False